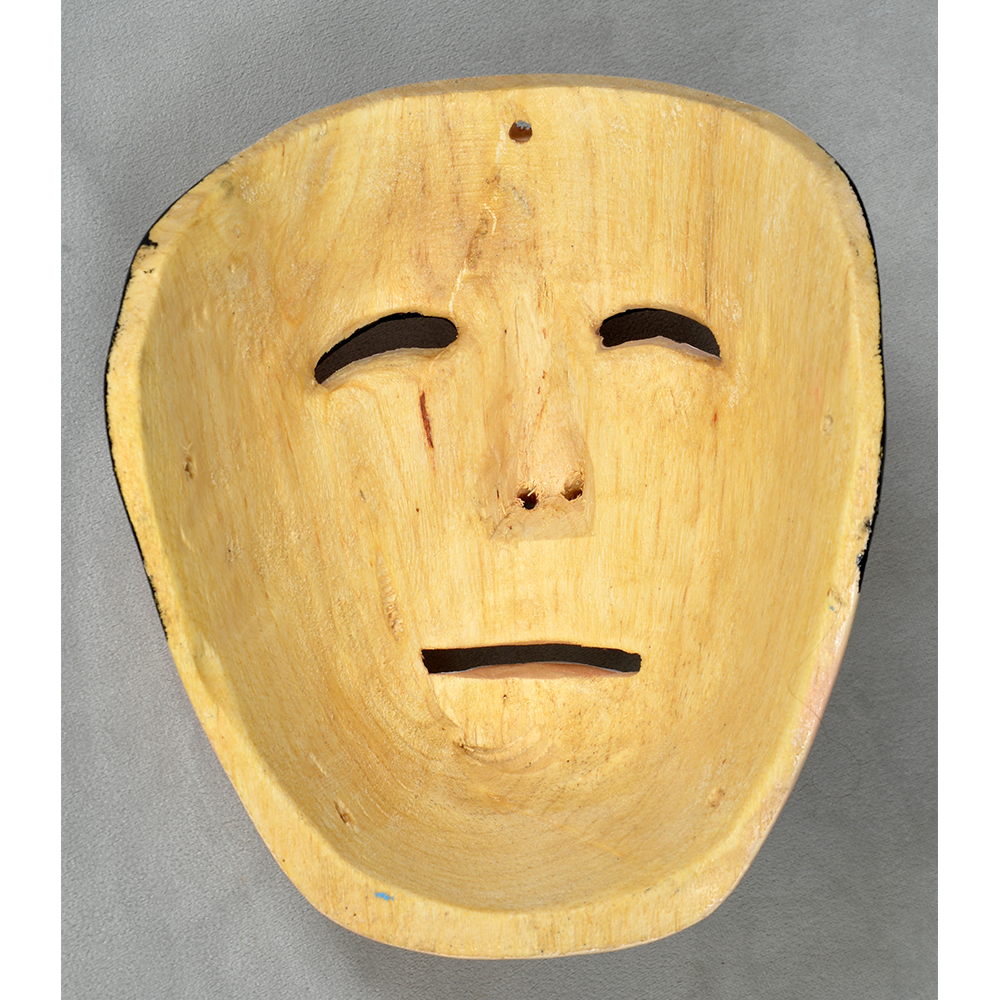
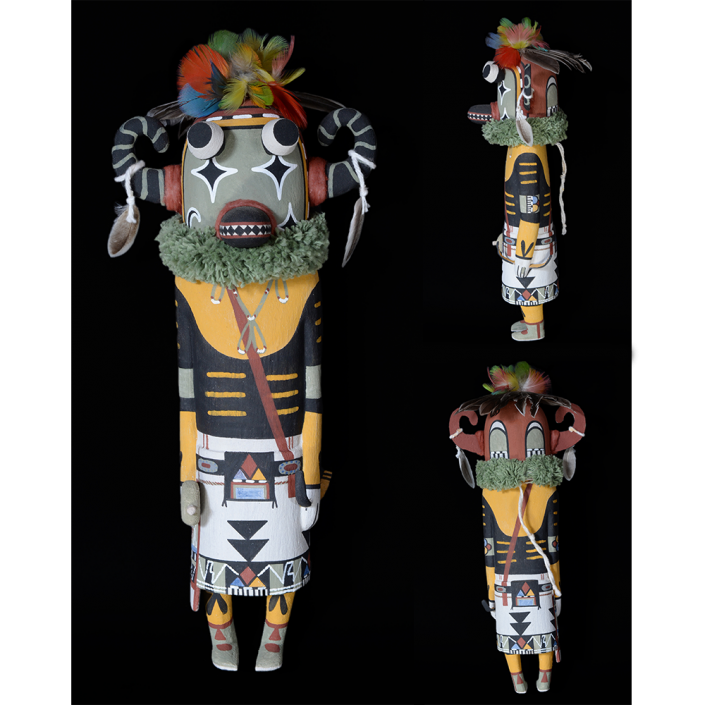
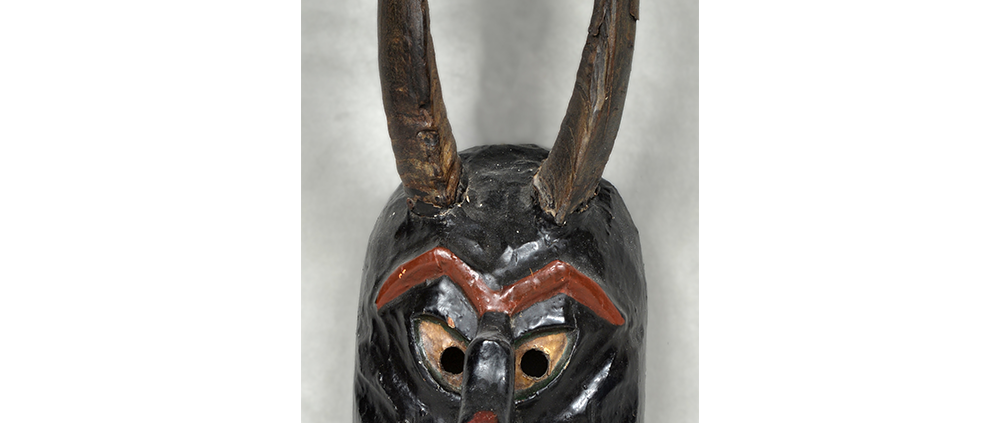
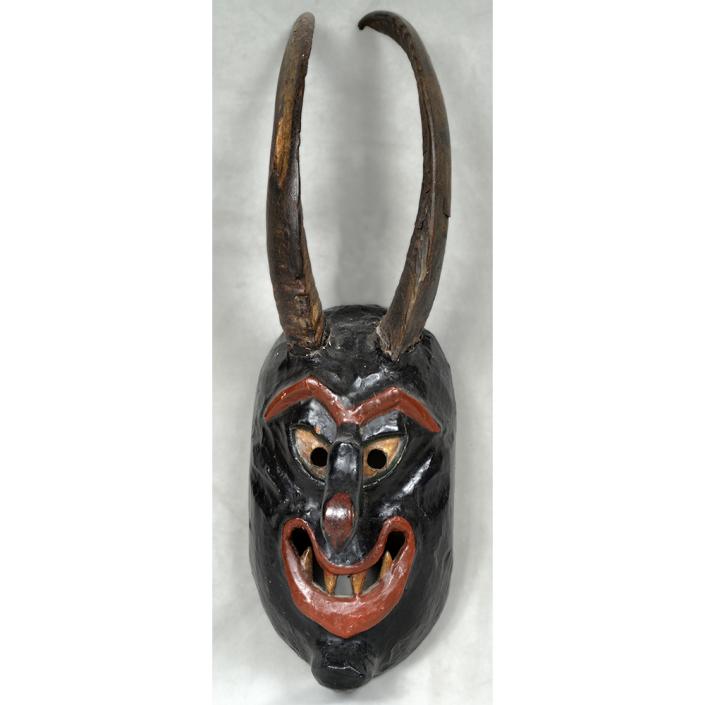
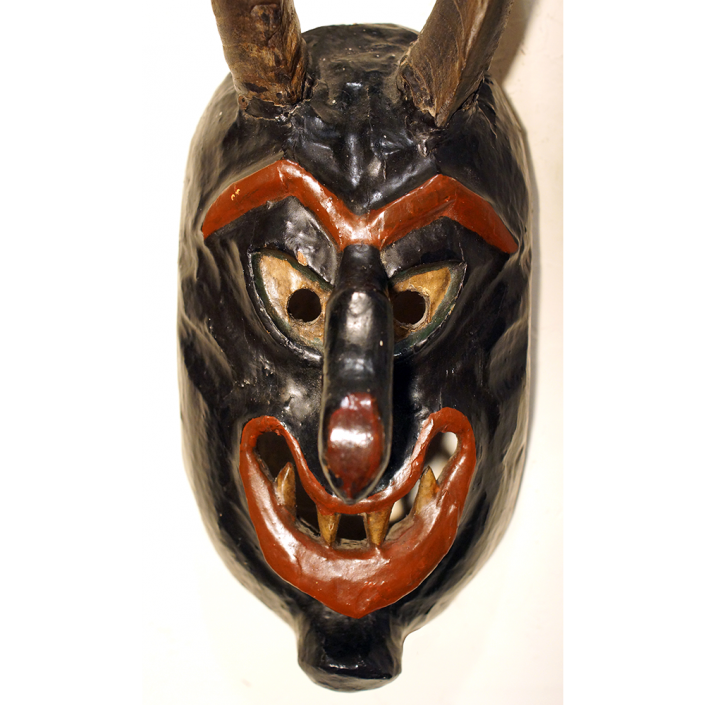
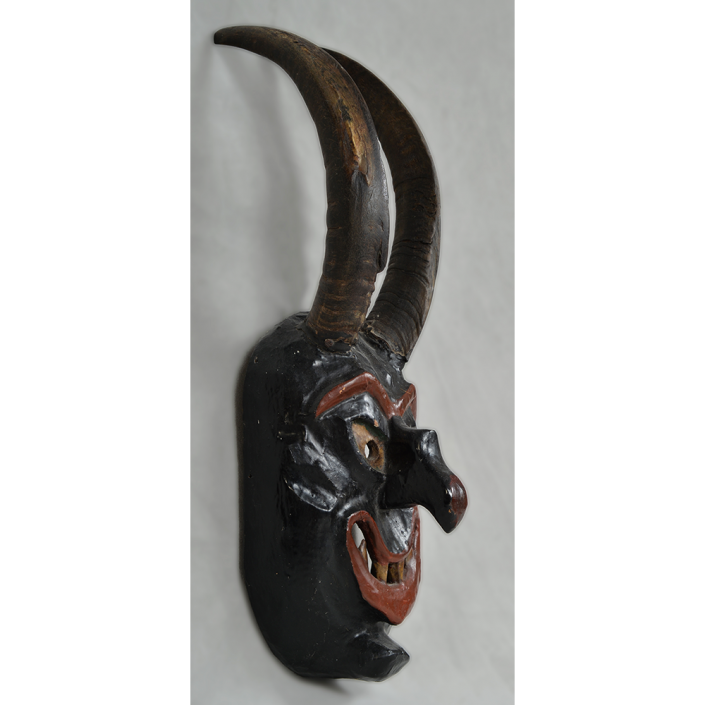
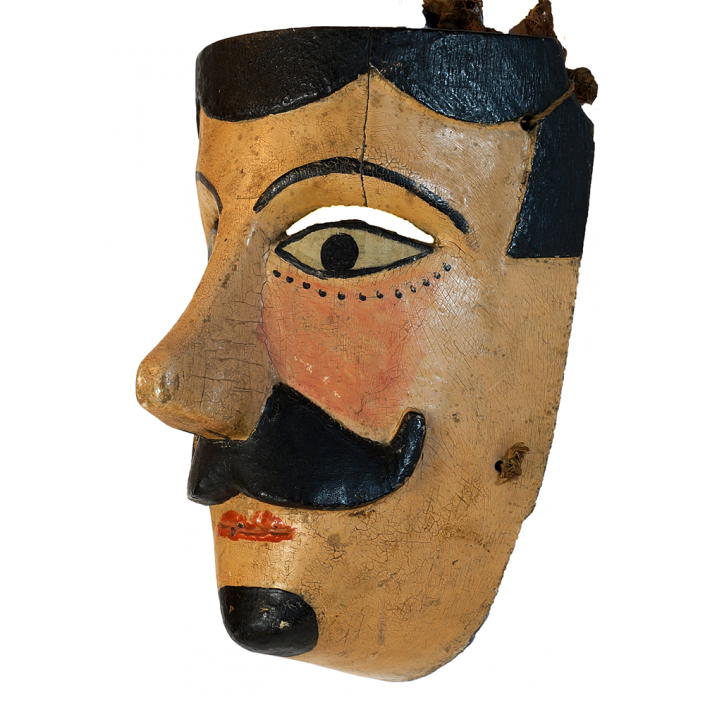
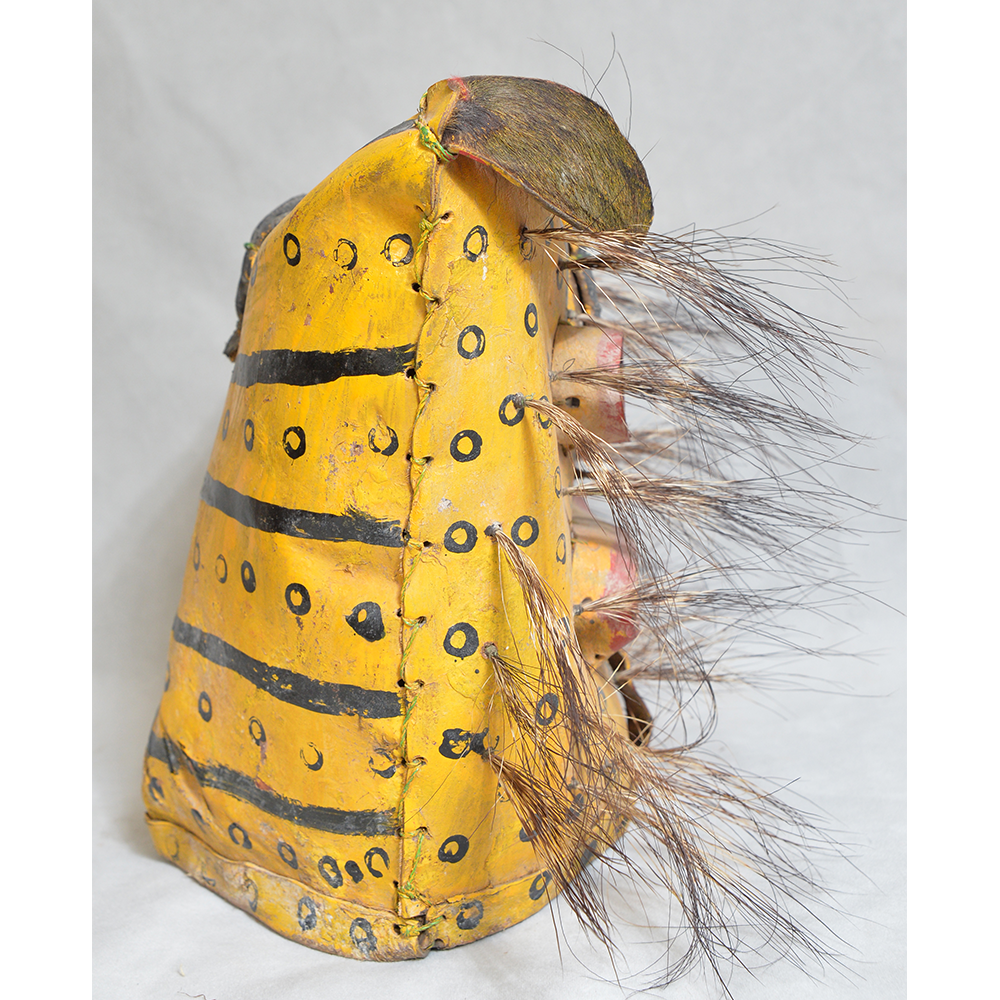
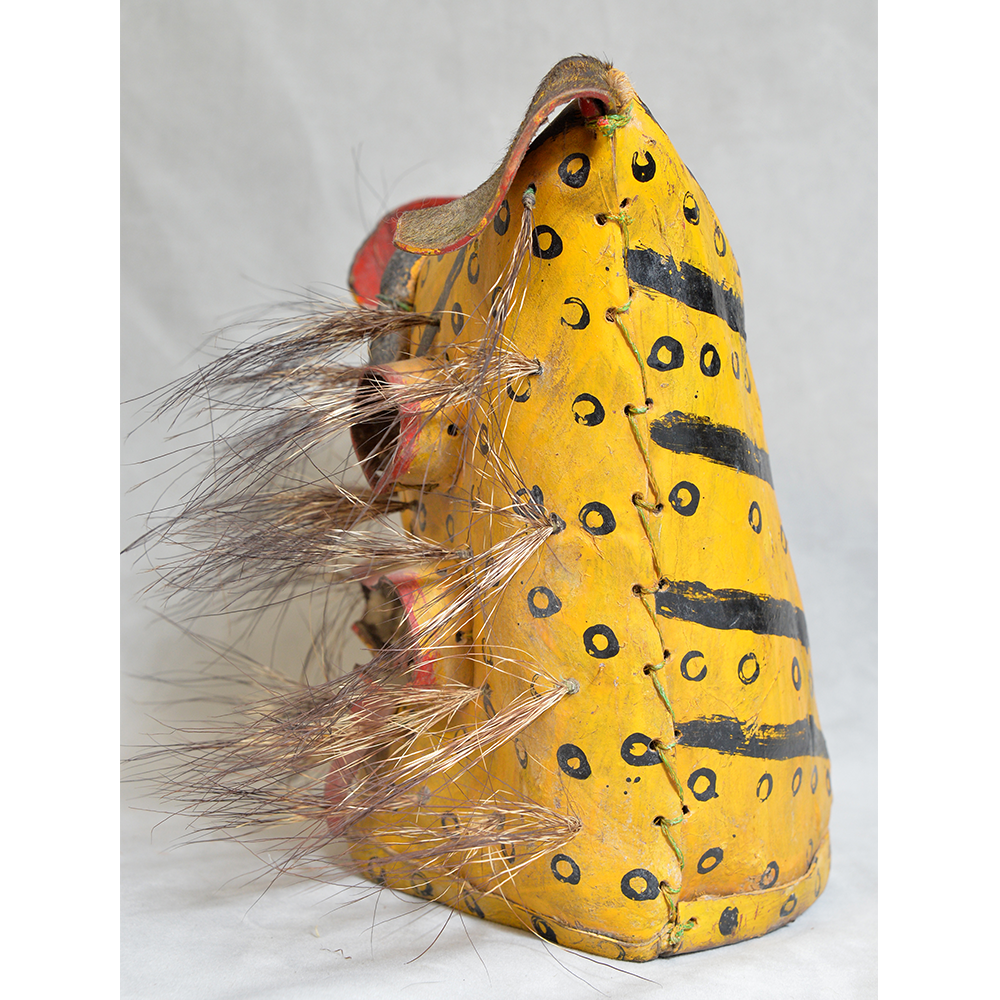
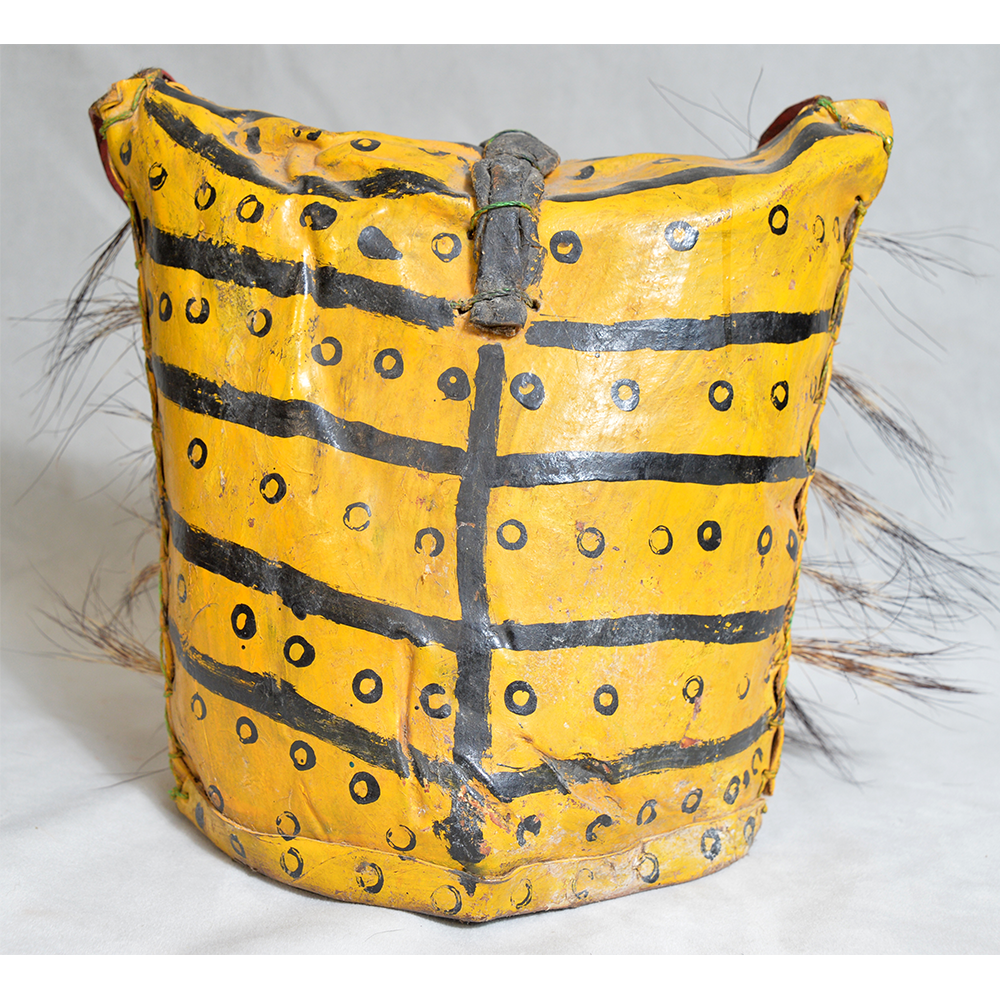
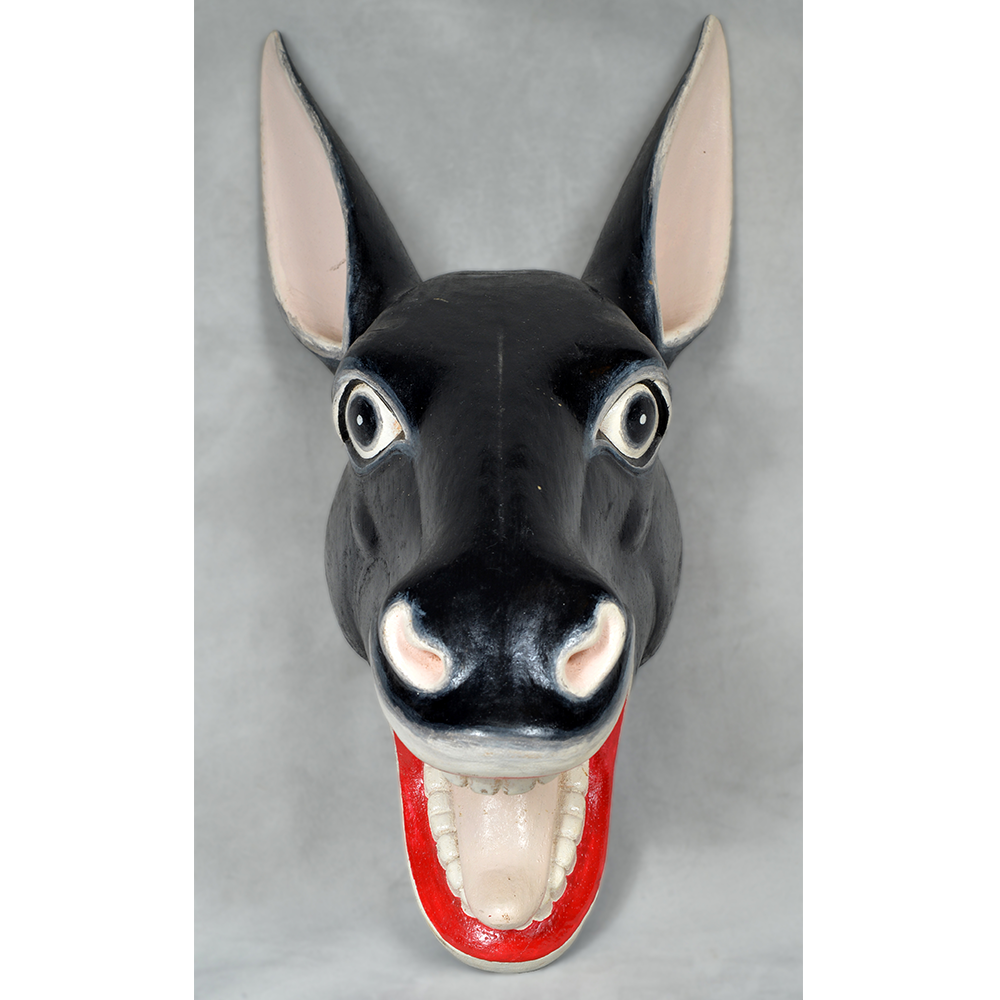
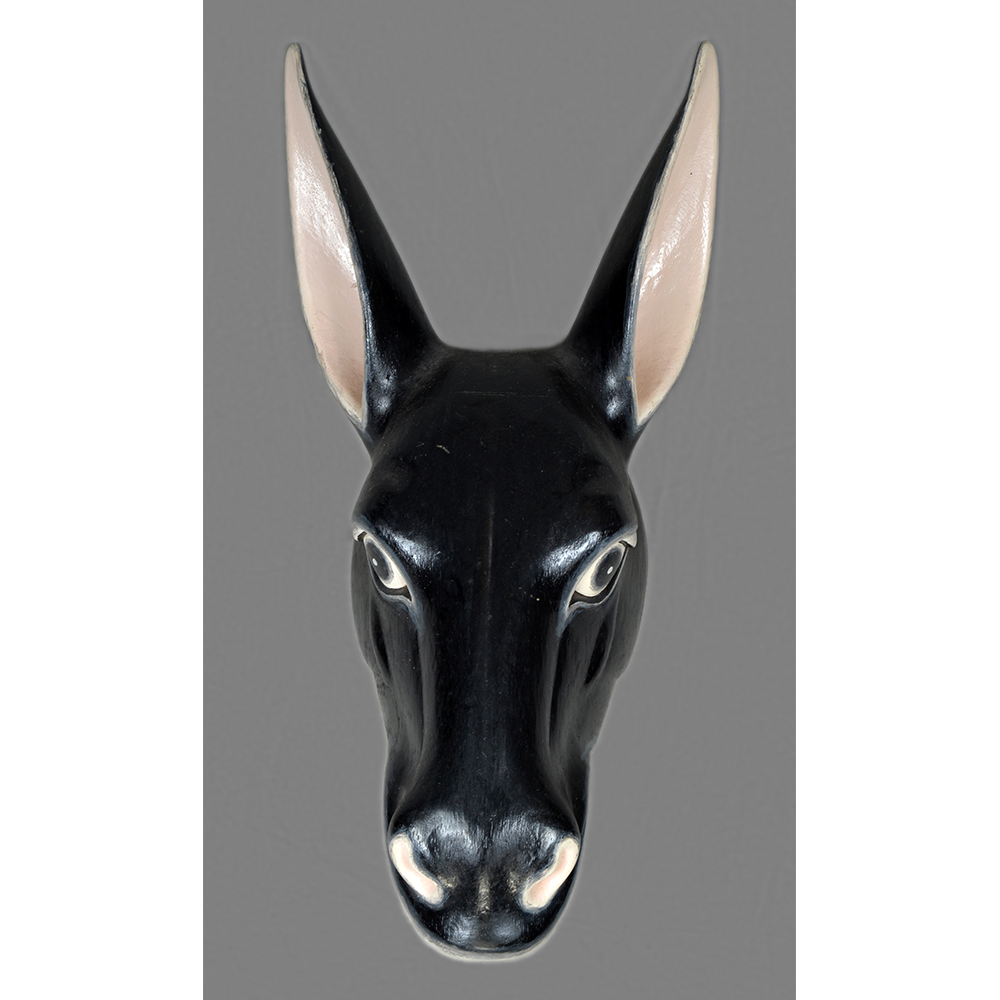
TITLE: Payaso Mask
TYPE: face mask; accessory
GENERAL REGION: Latin America
COUNTRY: Mexico
SUBREGION: Veracruz
ETHNICITY: Nahua
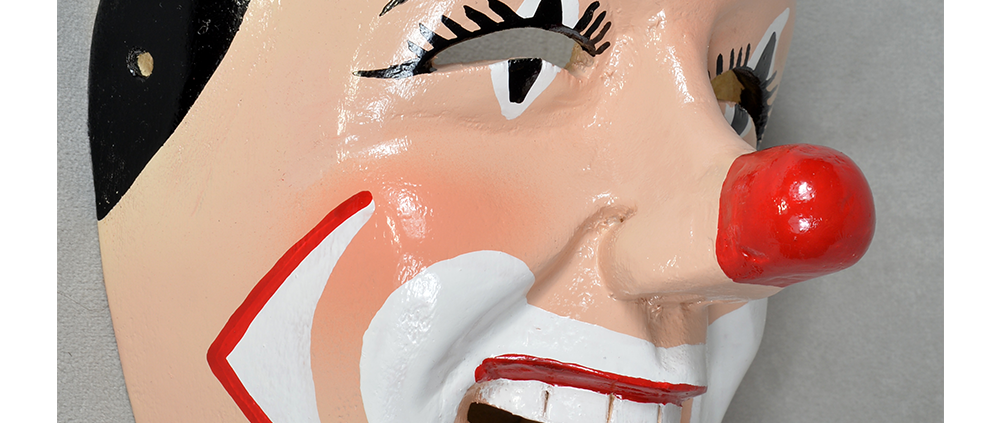
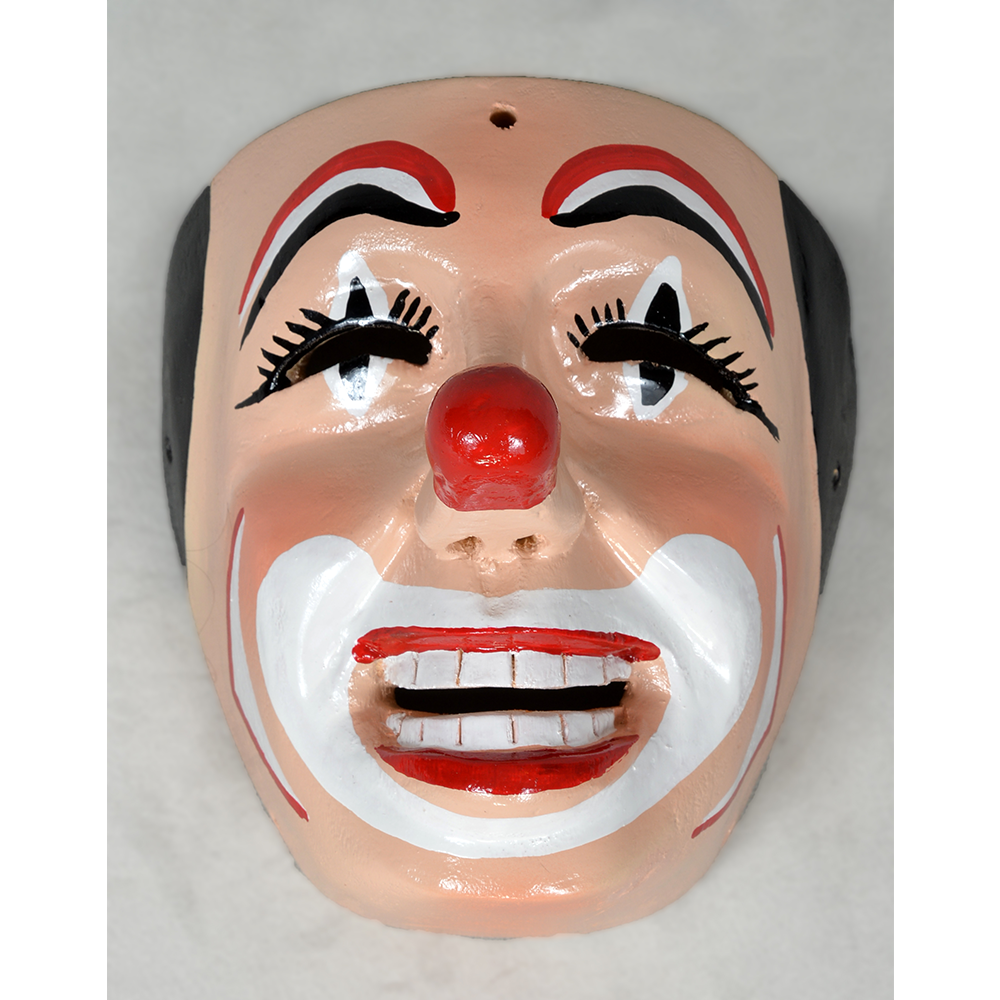
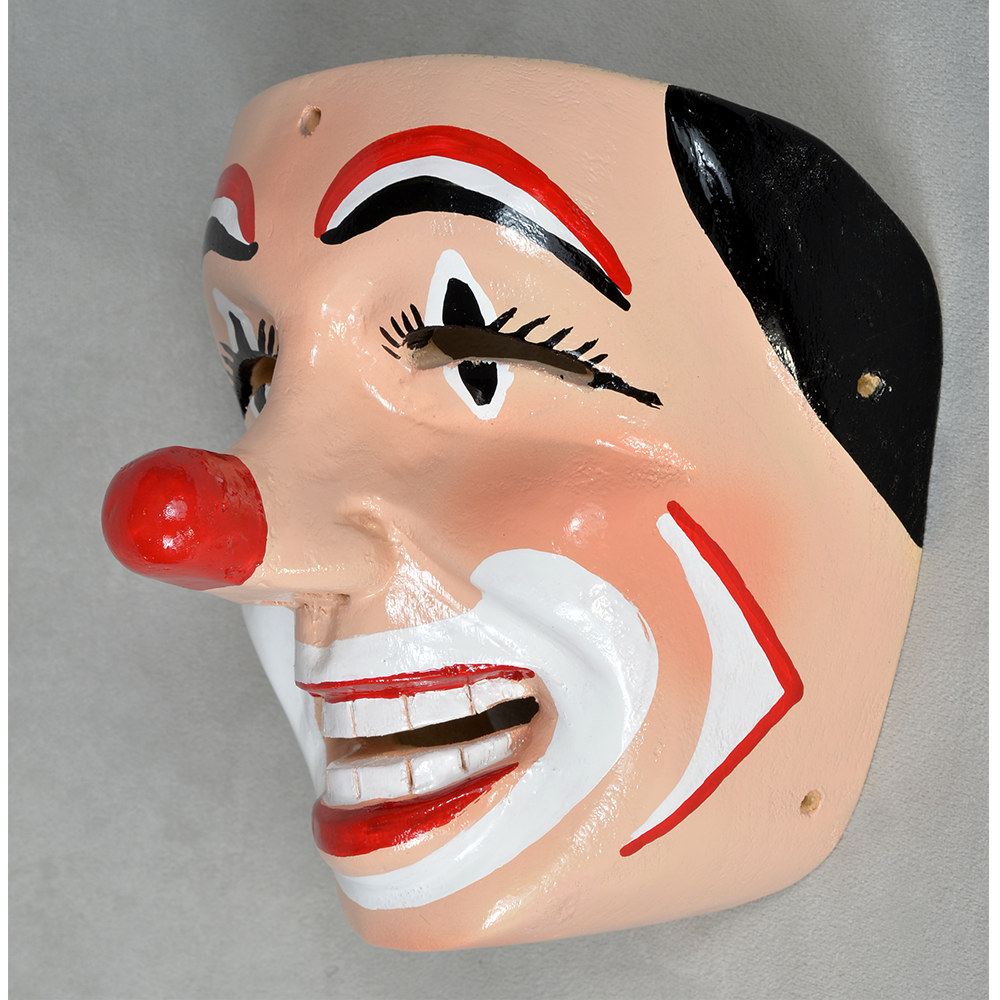
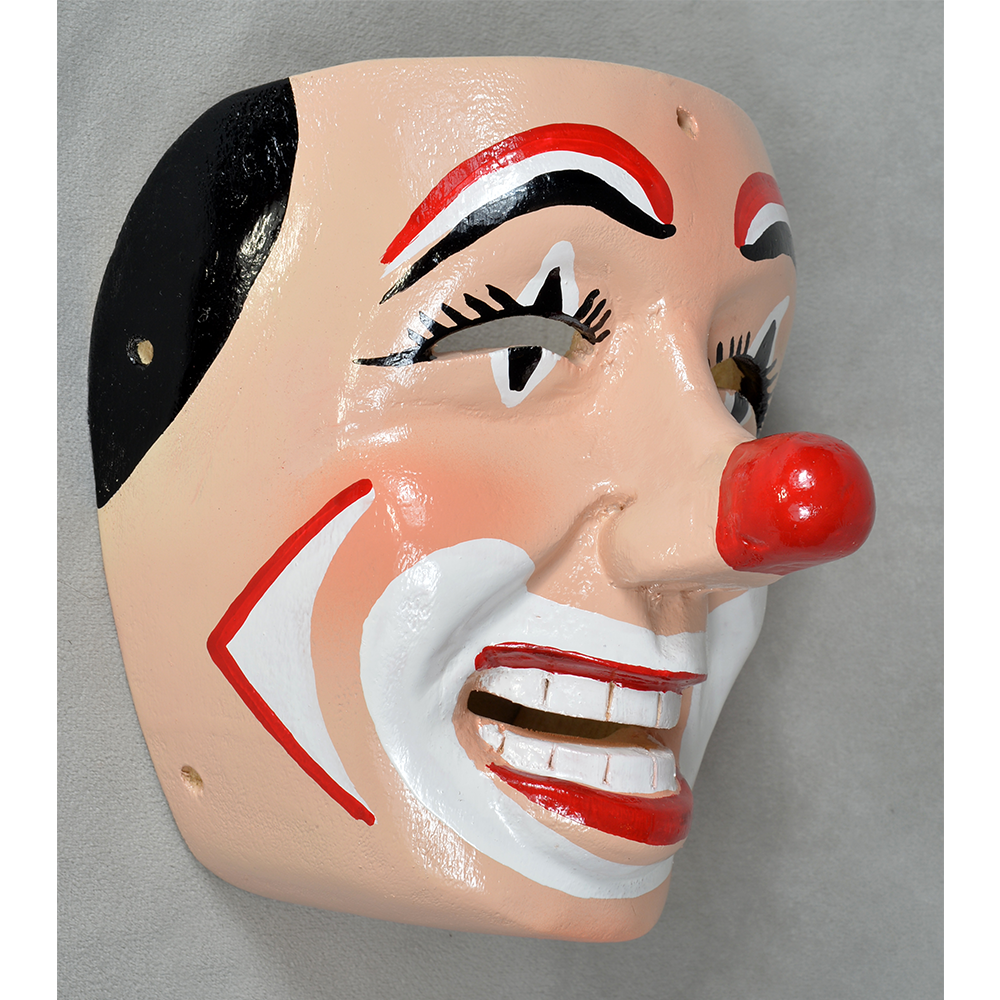
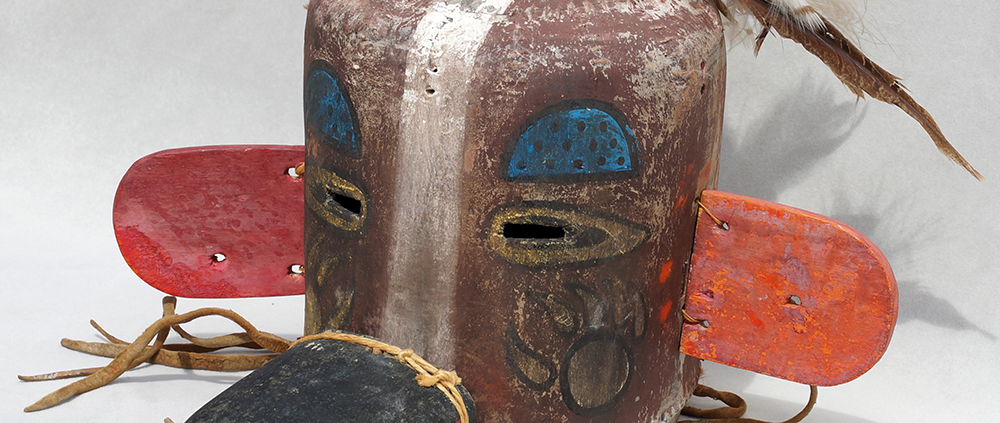
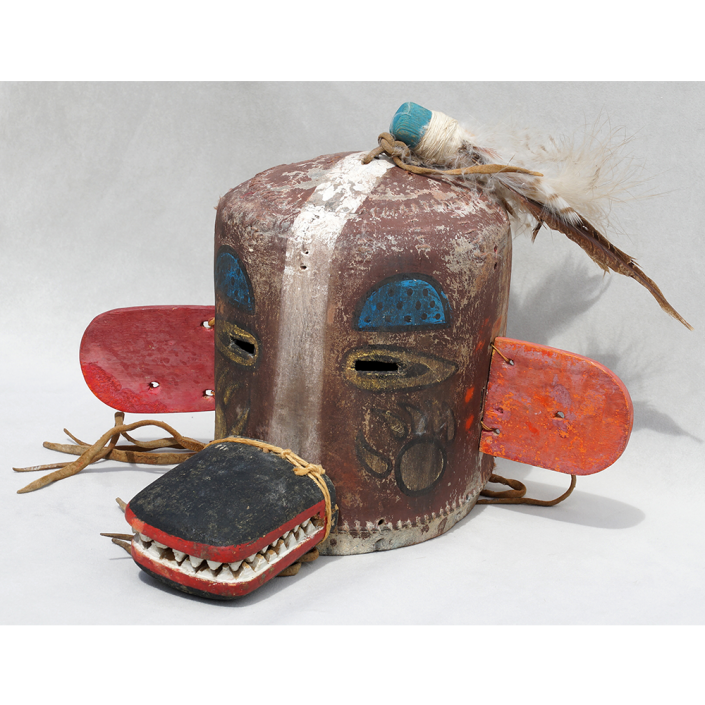
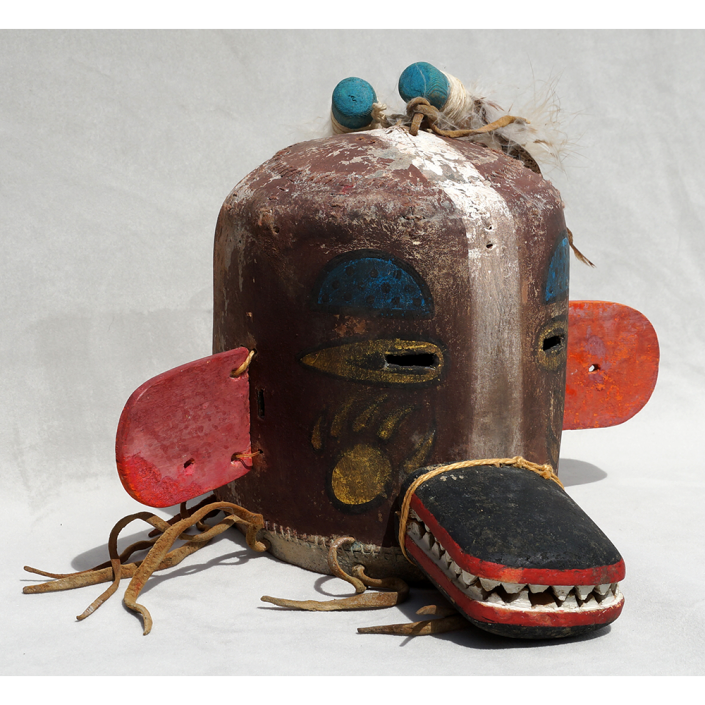
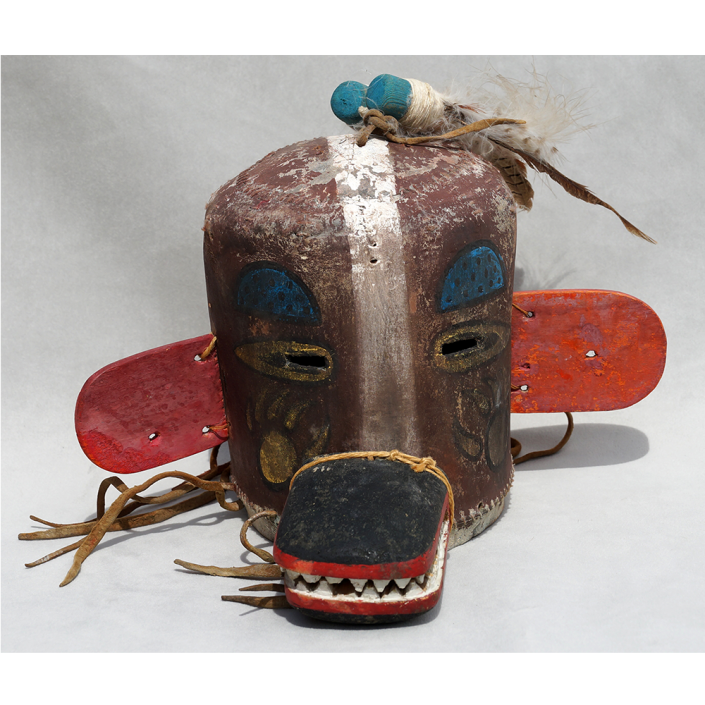
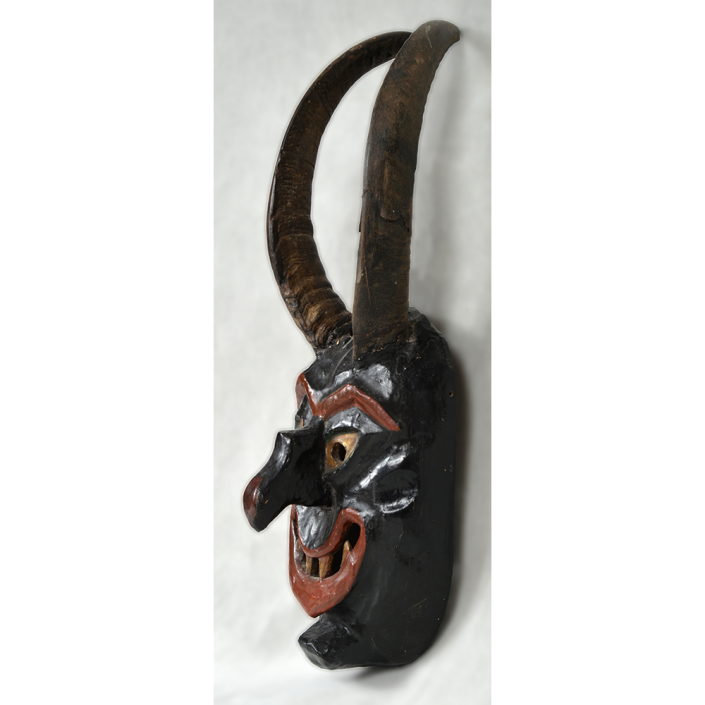
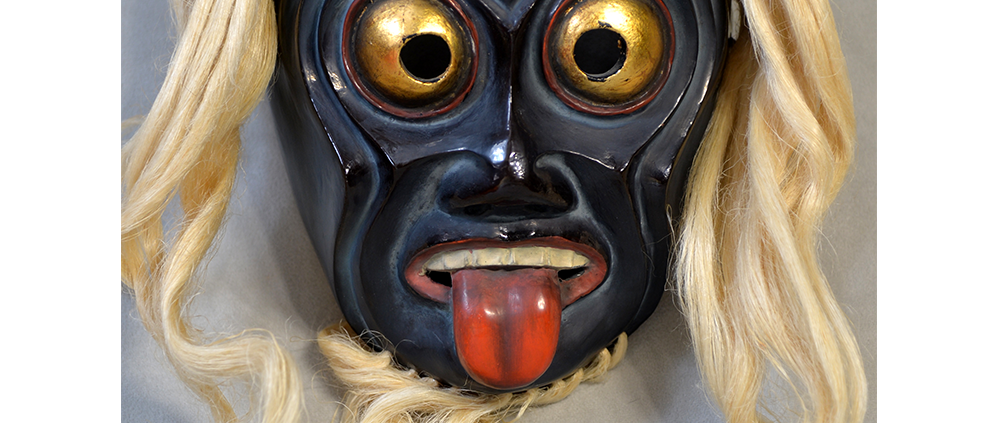
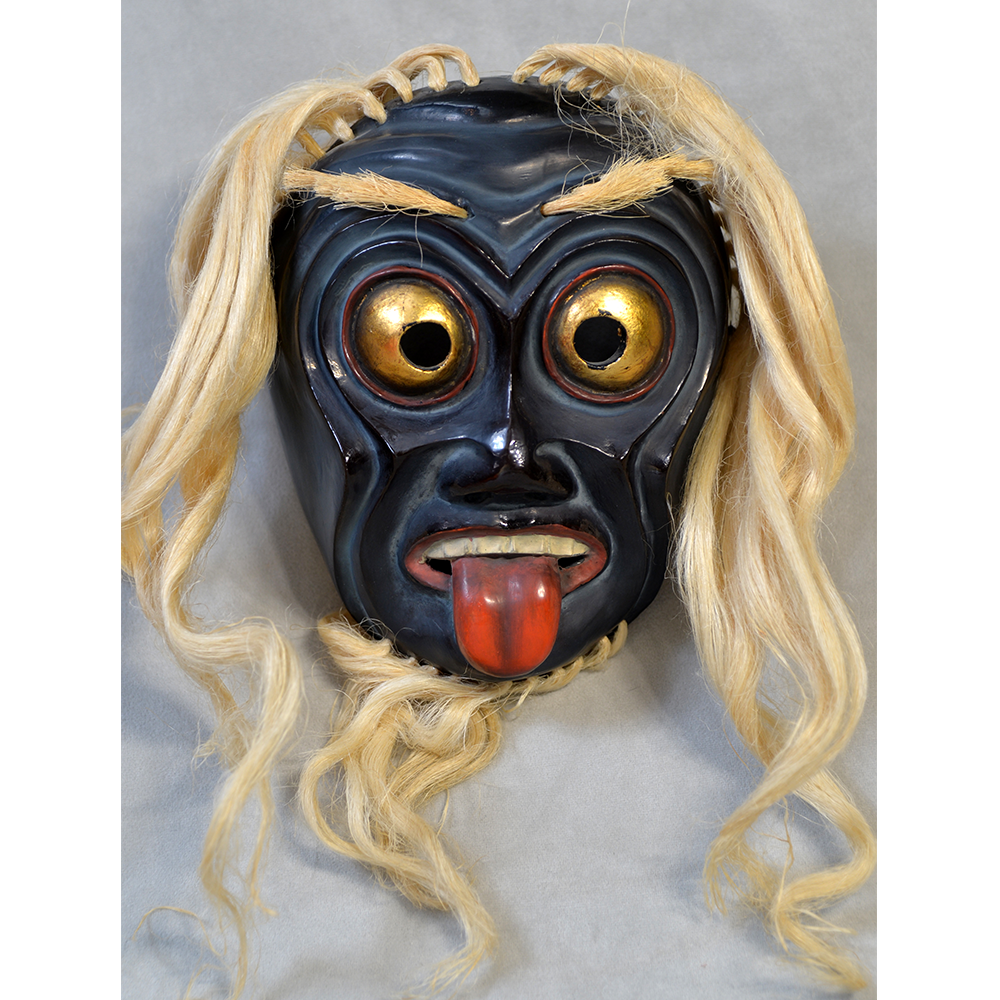
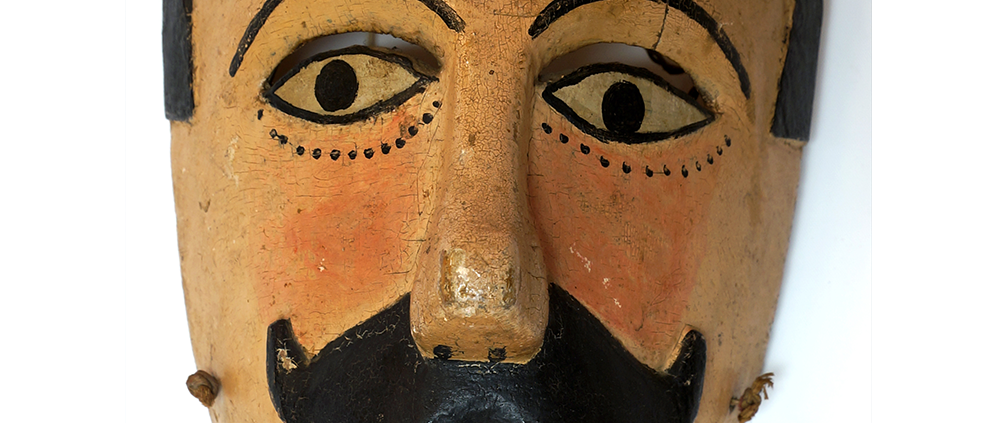
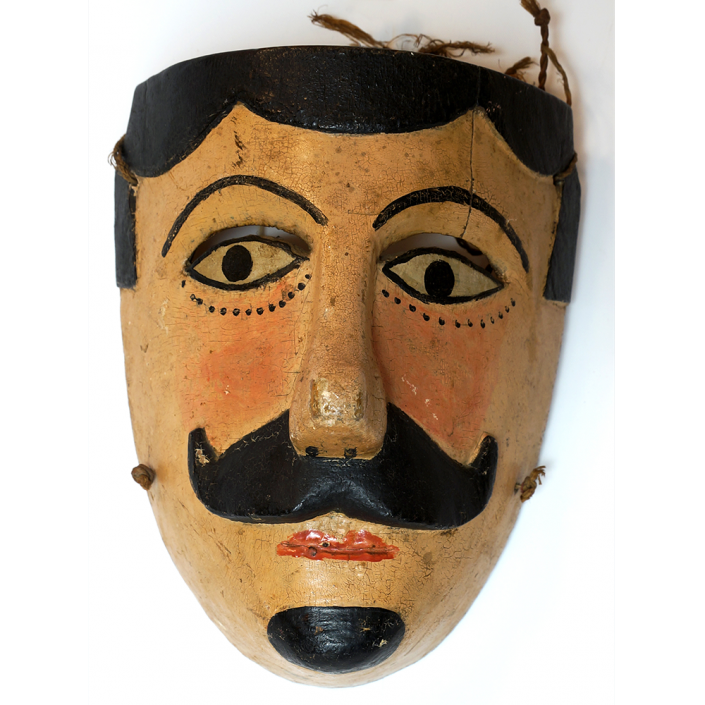
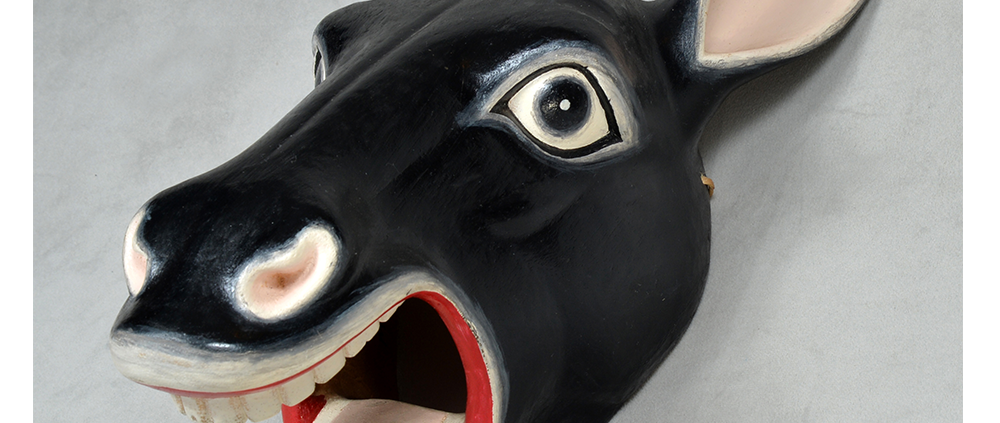
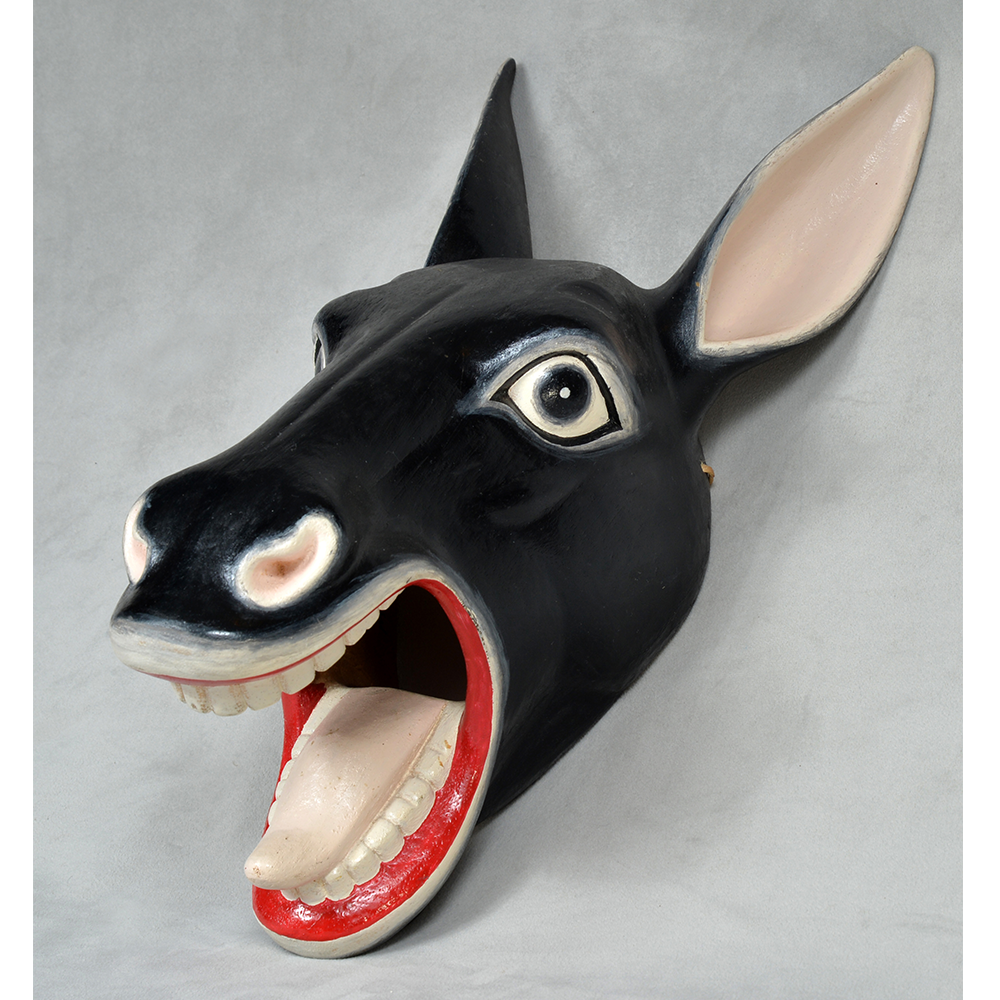
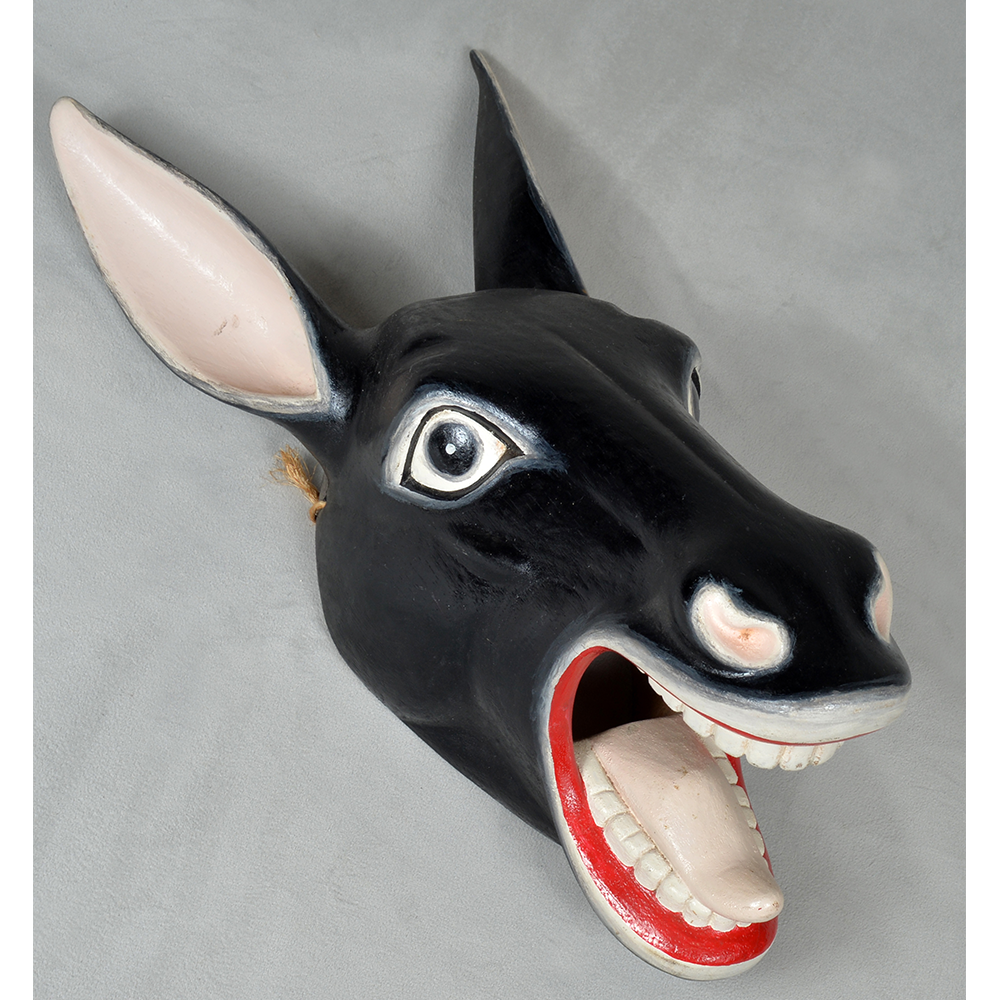
DESCRIPTION: Payaso (clown) with red and white face paint
CATALOG ID: LAMX152
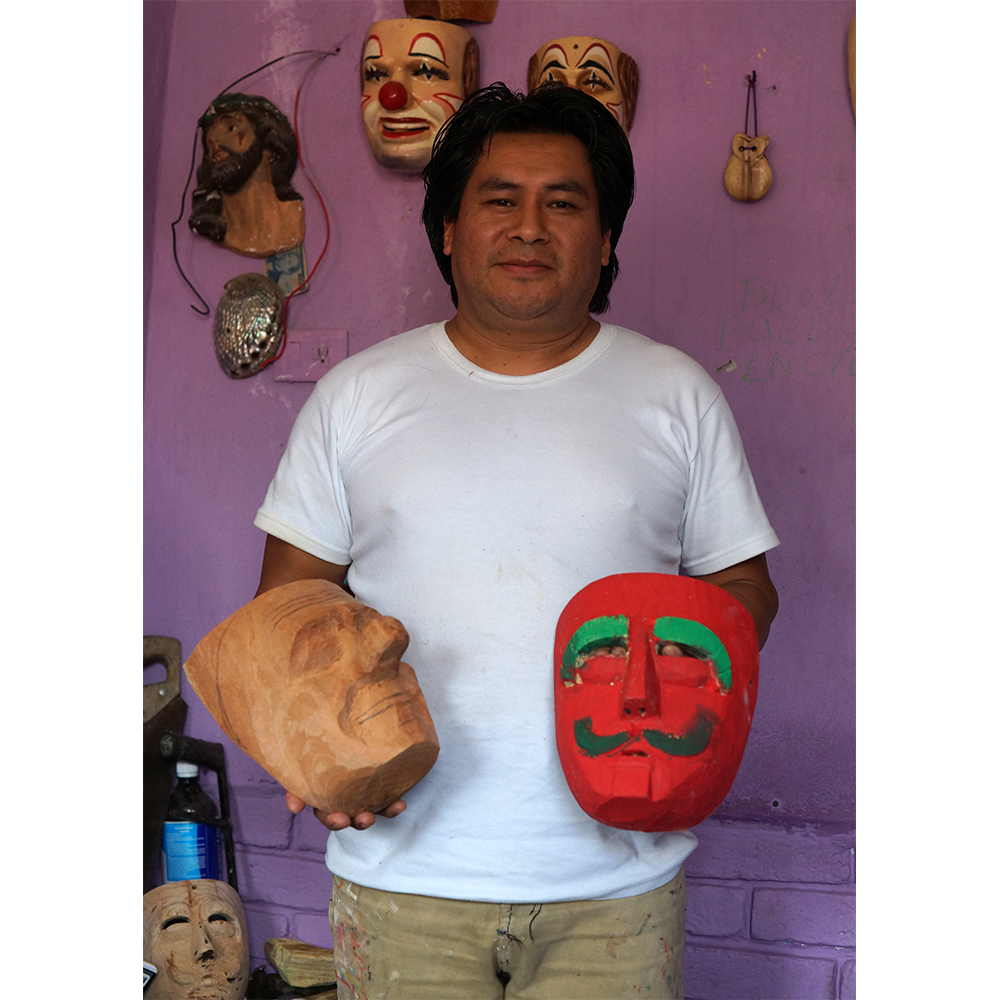
MAKER: Rey Tepo (Xico, 1972- )
CEREMONY: Santo Entierro de Cristo; Fiesta de la Asunción; Carnival
AGE: 2016
MAIN MATERIAL: wood
OTHER MATERIALS: oil-based paint
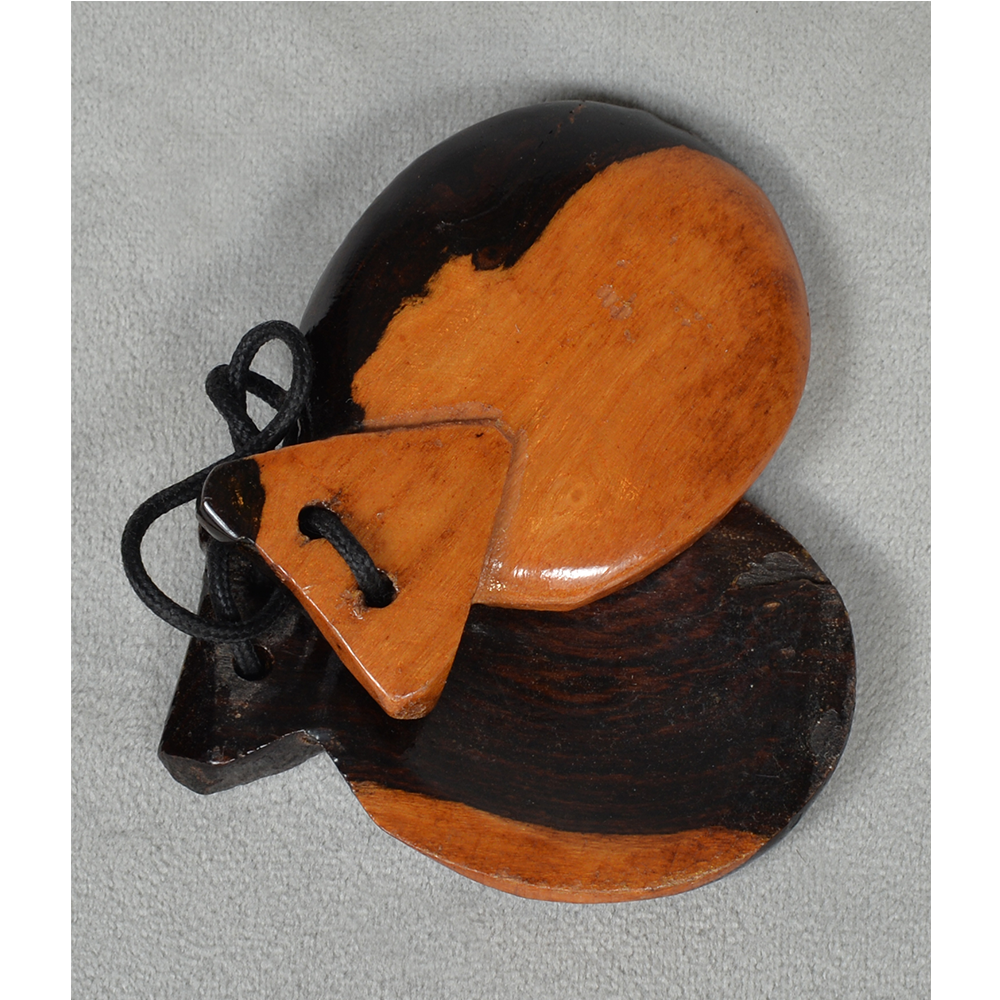
Santo Entierro de Cristo (“Sacred Burial of Christ”) is an important festival in parts of Veracruz, particularly in the region of Teocelo, and is celebrated on the last Sunday in January. During the festival, clowns wearing red-nosed masks, animals, devils, and other characters dance to drum and trumpet music along a parade route, clicking castanets, and accompanying an image of the burial of Jesus of Nazareth. The route proceeds from the local church to a large floral arch dubbed El Calvario, where mass is held. The procession is accompanied by drums and trumpets. Sometimes other masked characters, such as animals, tourists, and cartoon characters accompany the parade. Such masks are also worn at other celebrations, most prominently Carnival and the Asunción (“Assumption,” referring to Jesus’ mother Mary passing into Heaven), held on August 15th.