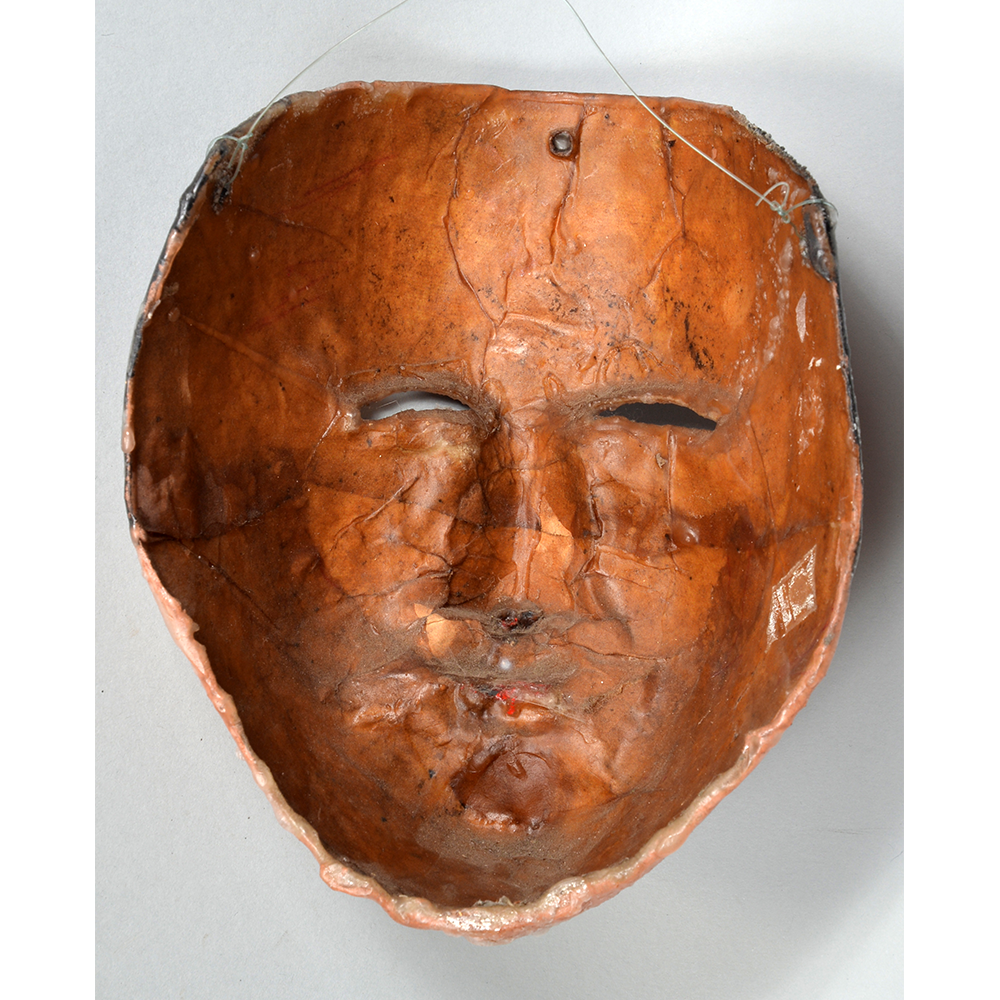
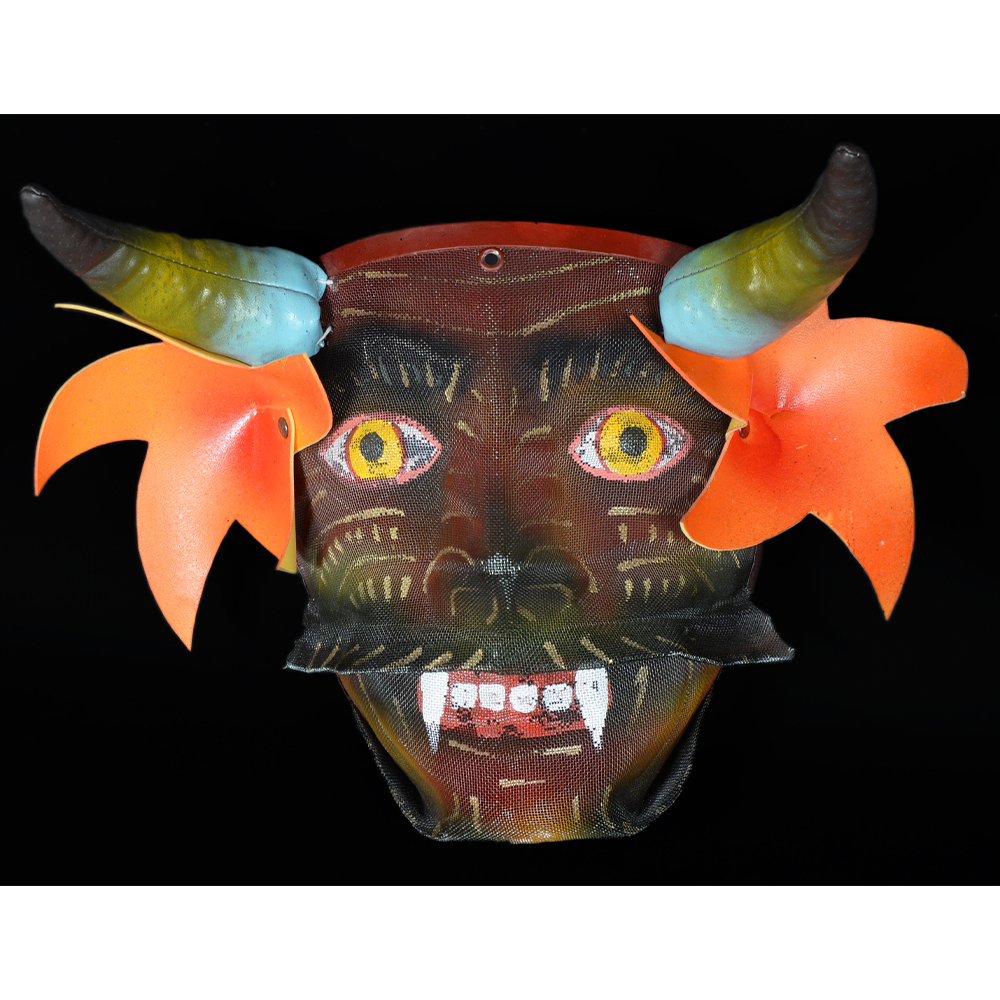
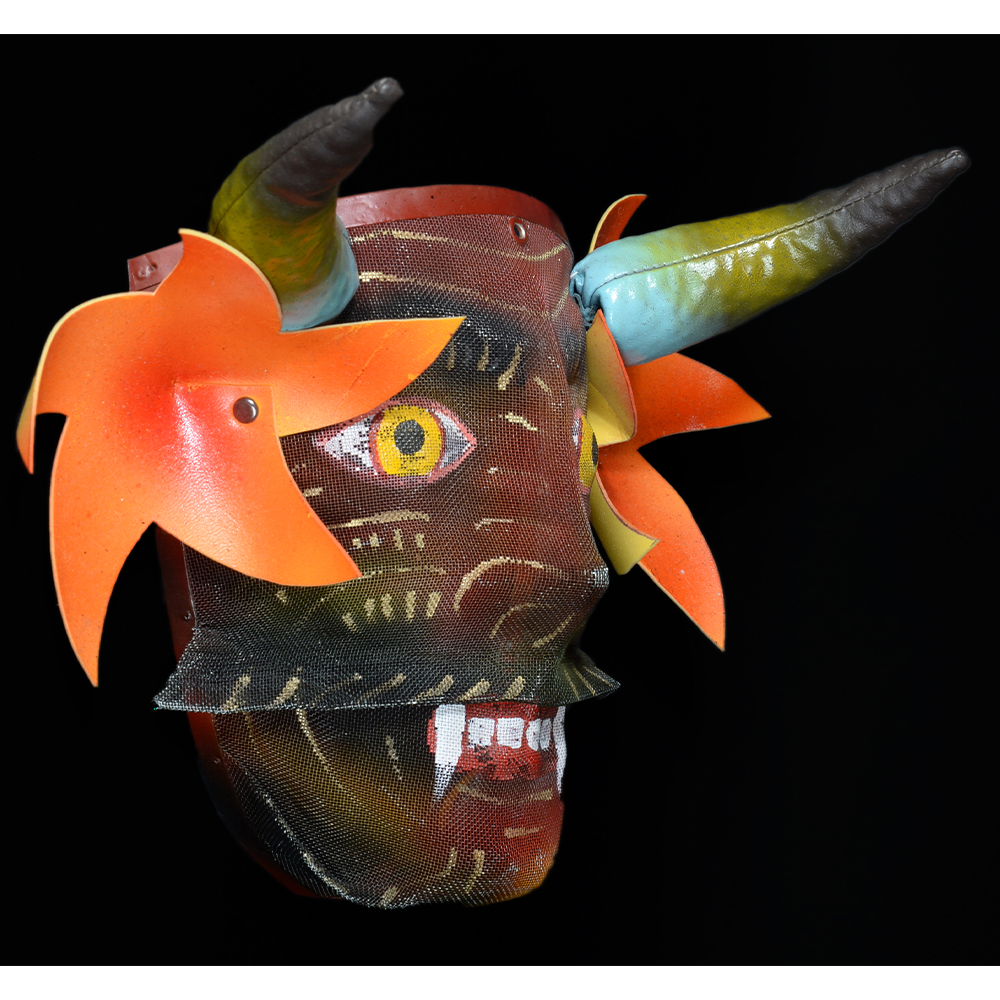
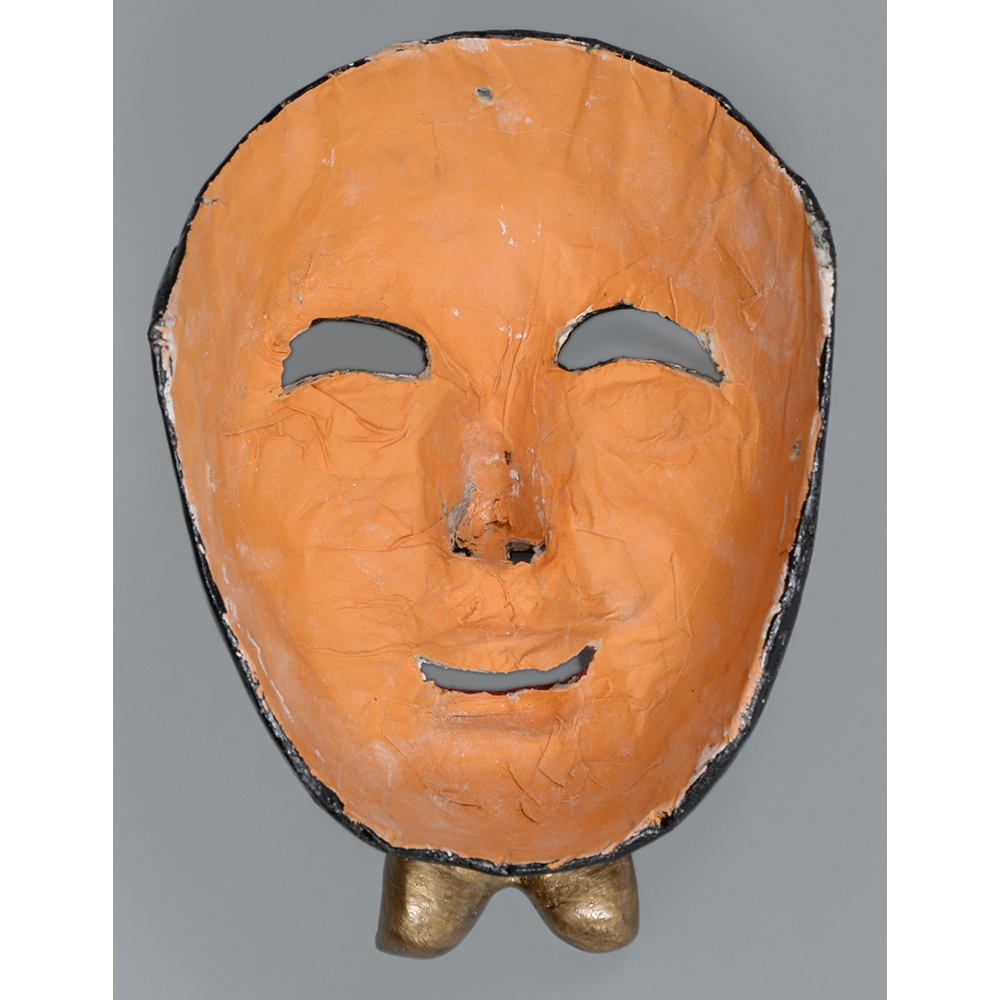
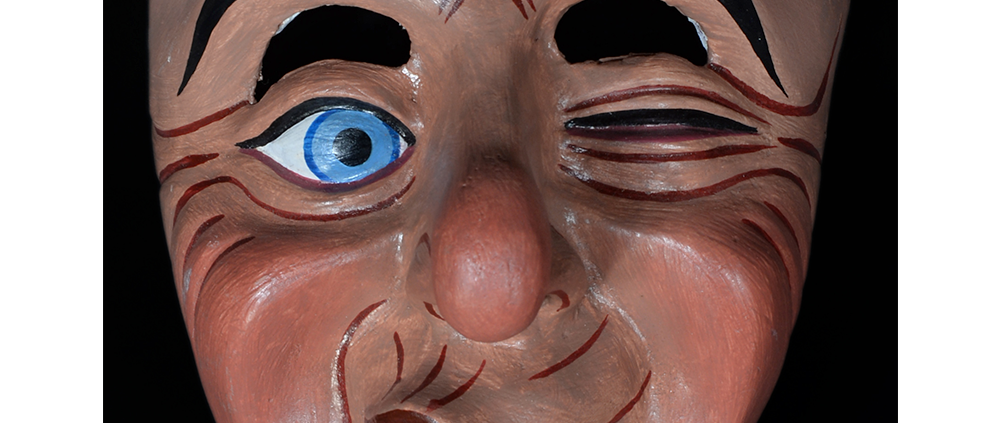
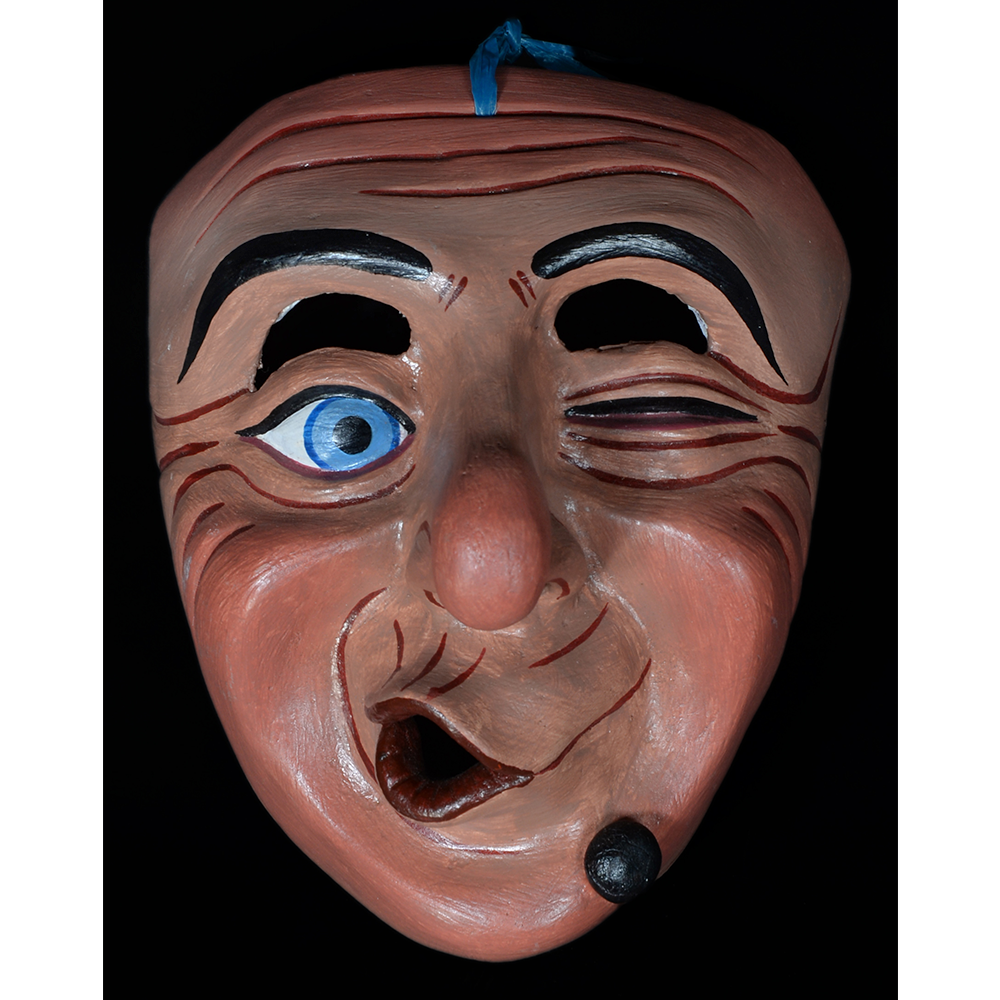
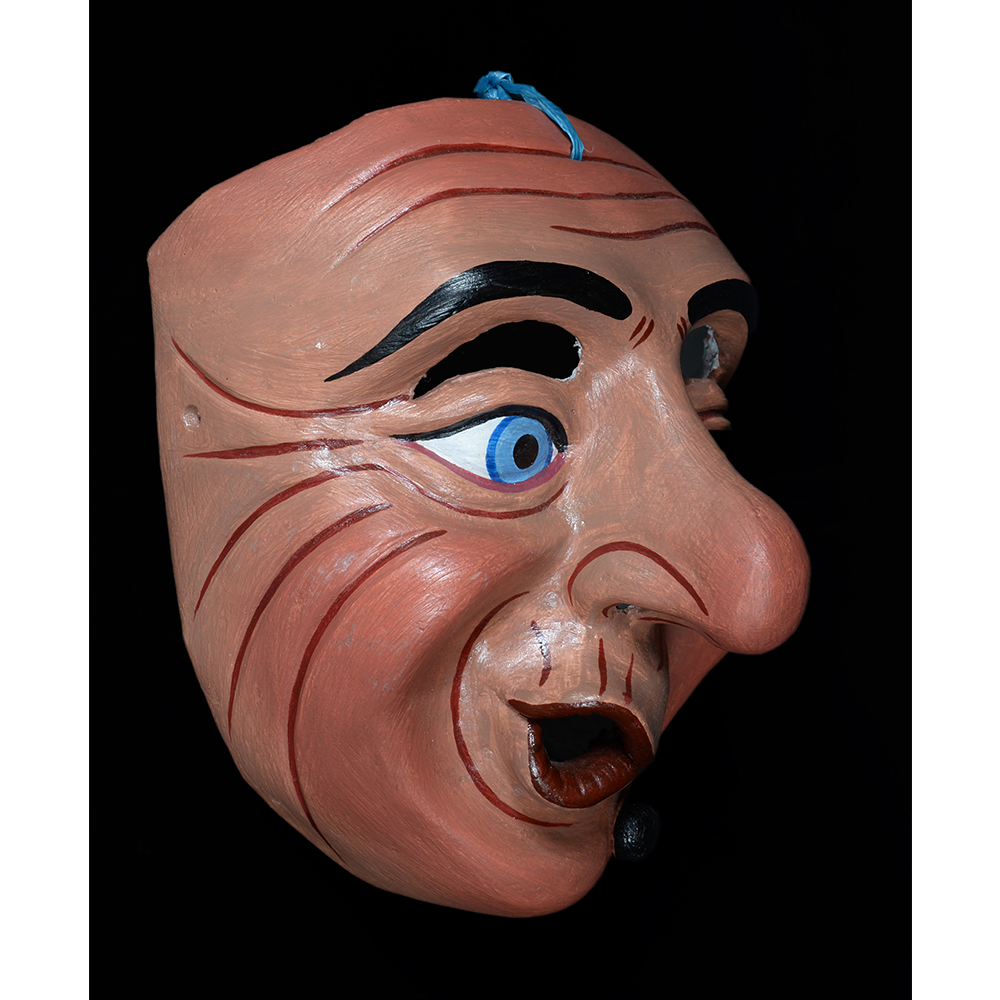
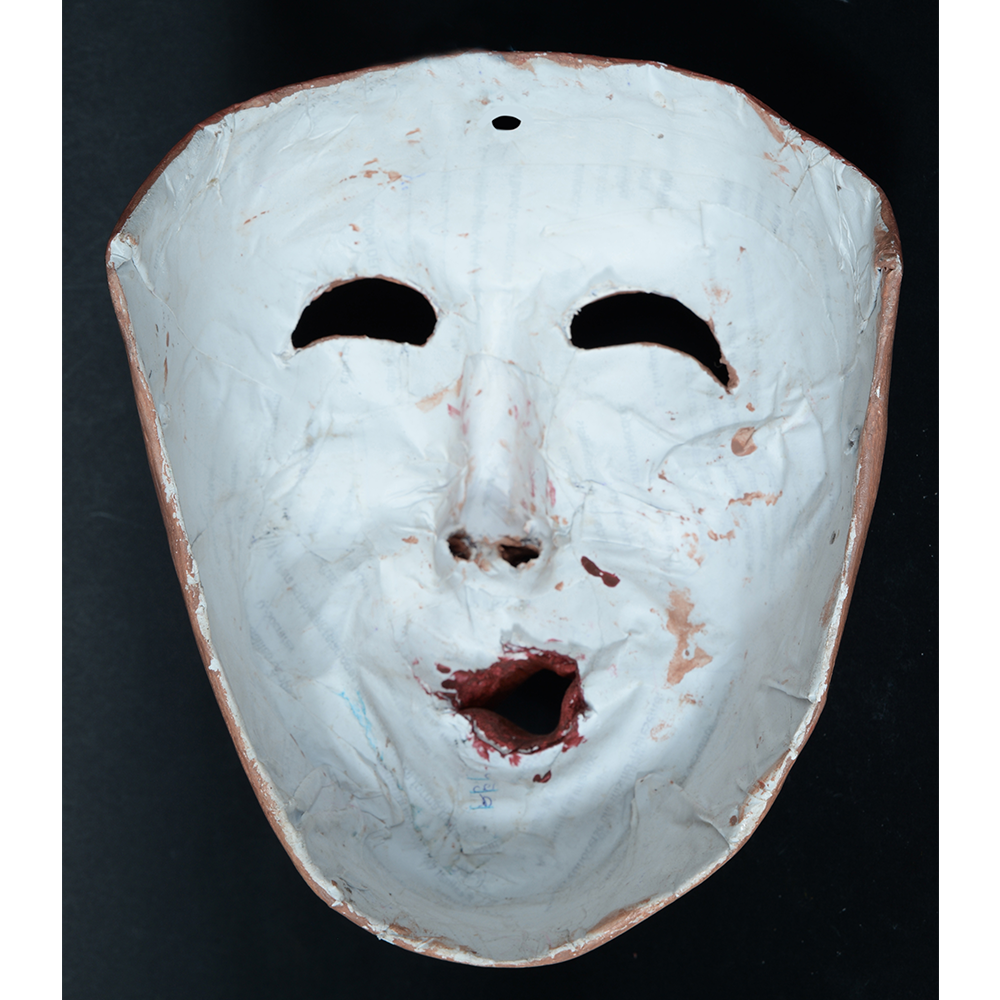
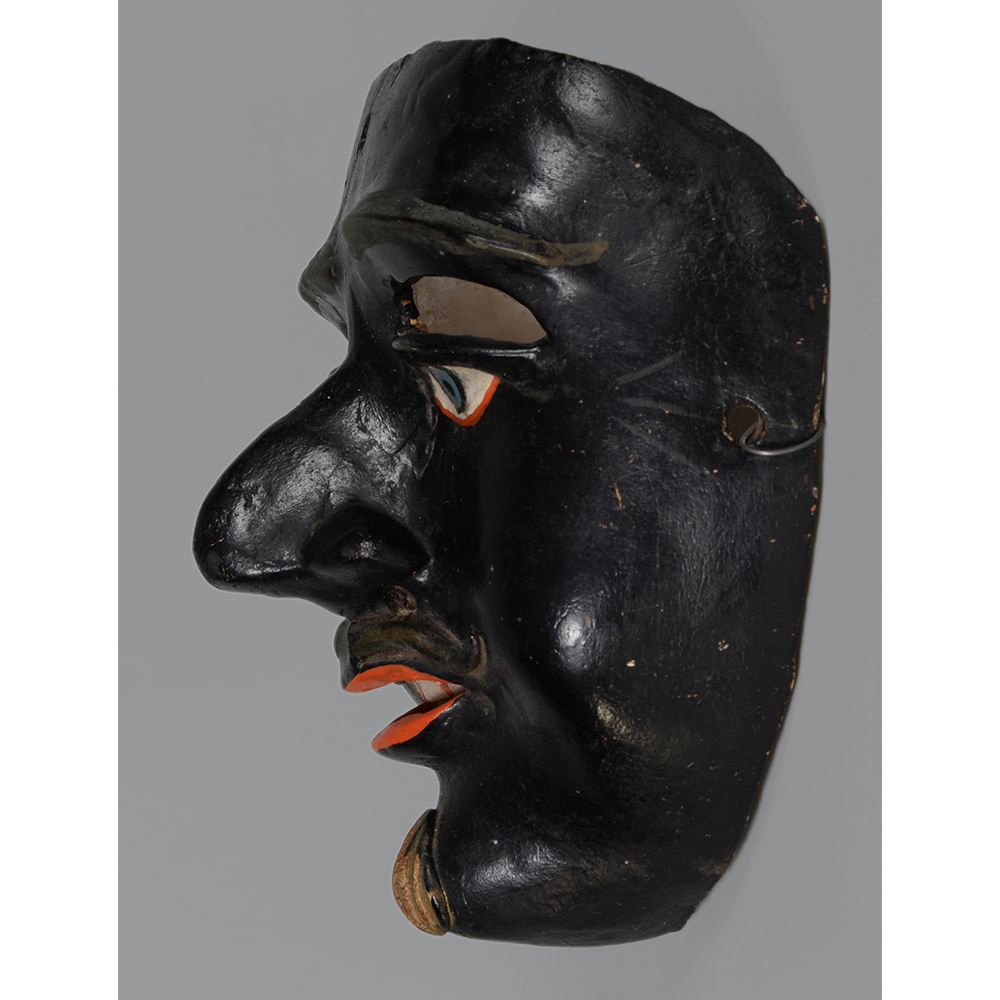
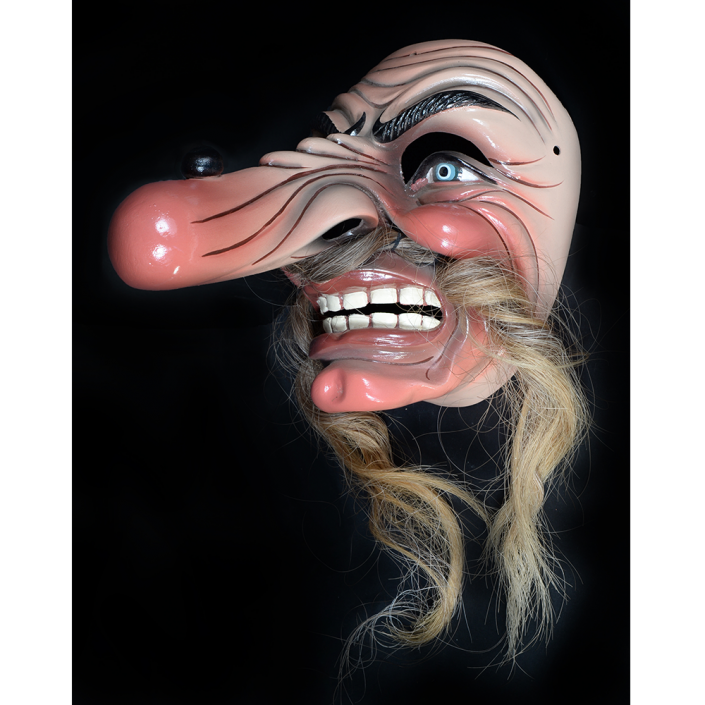
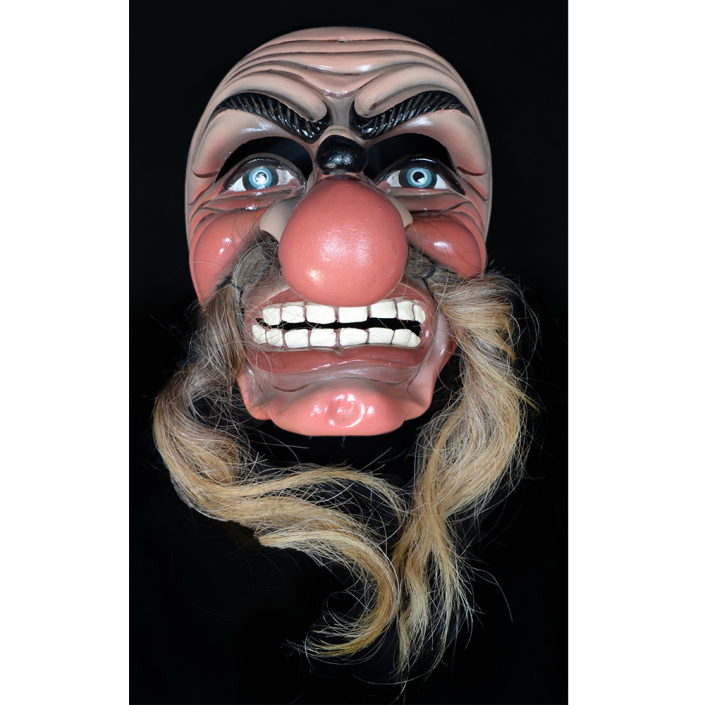
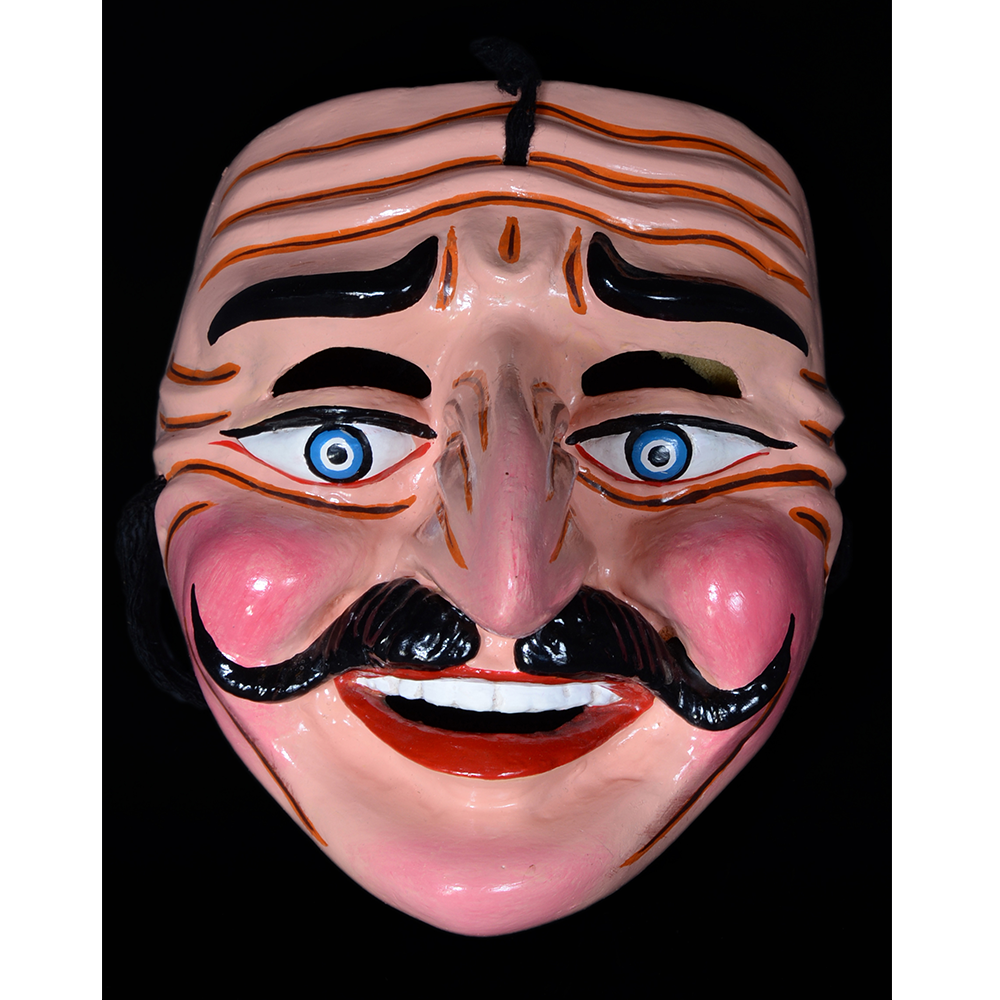
TITLE: Reina de Jardineros
TYPE: face mask
GENERAL REGION: Latin America
COUNTRY: Mexico
SUBREGION: Oaxaca
ETHNICITY: Zapotec
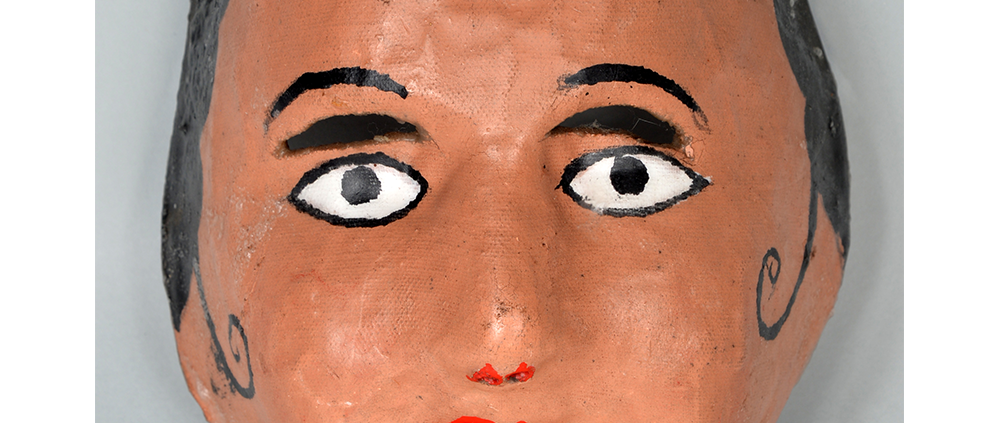
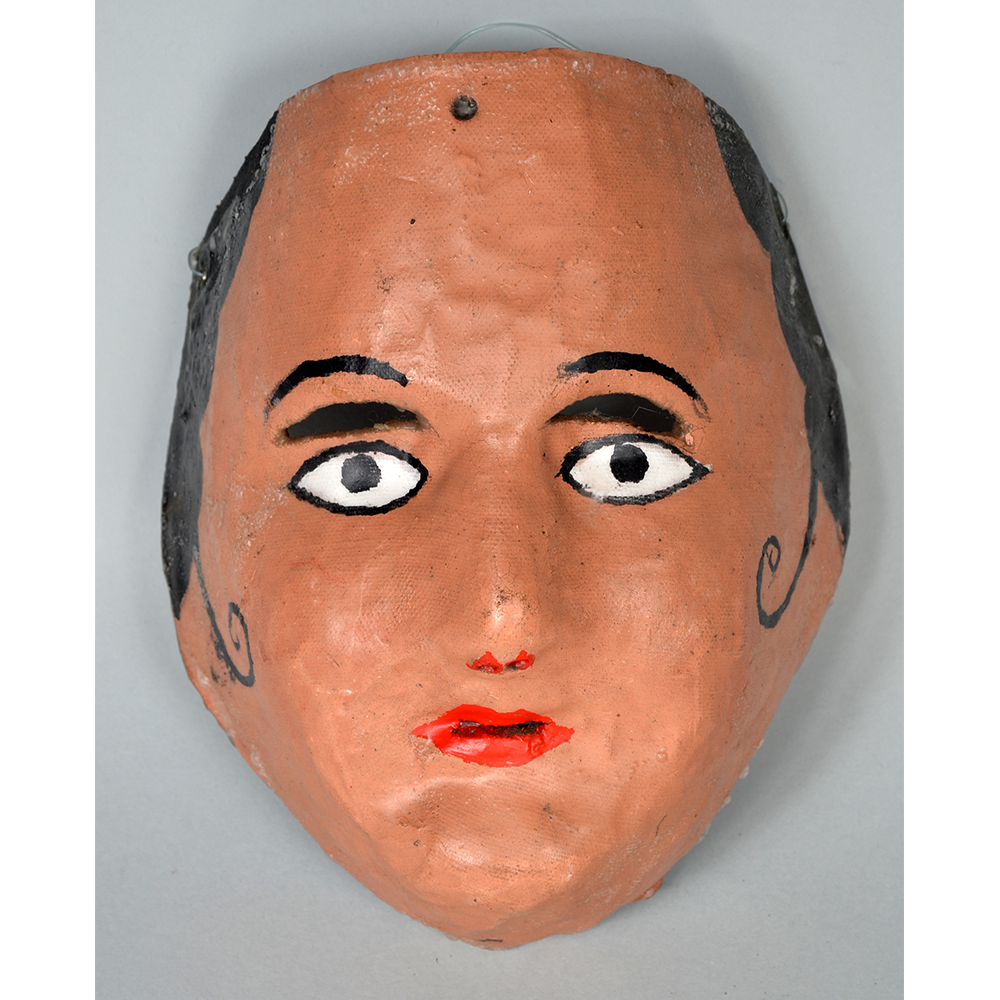
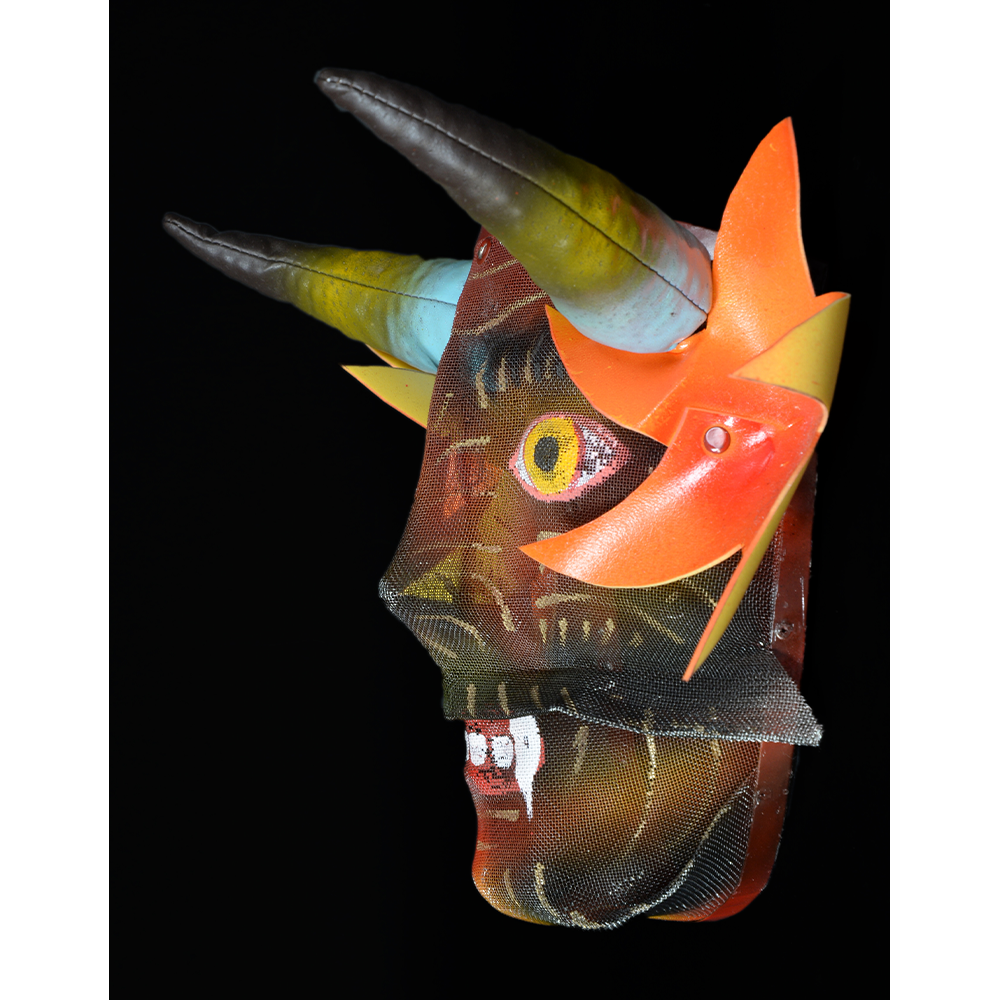
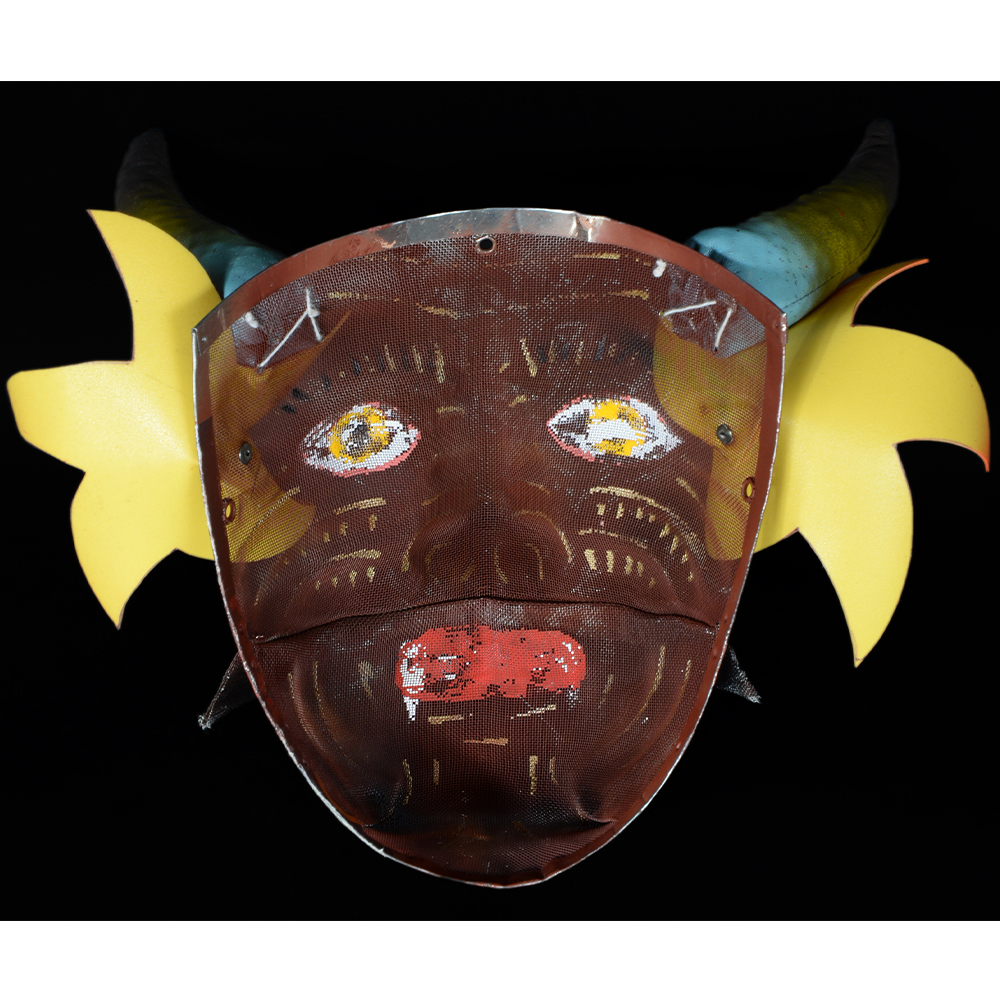
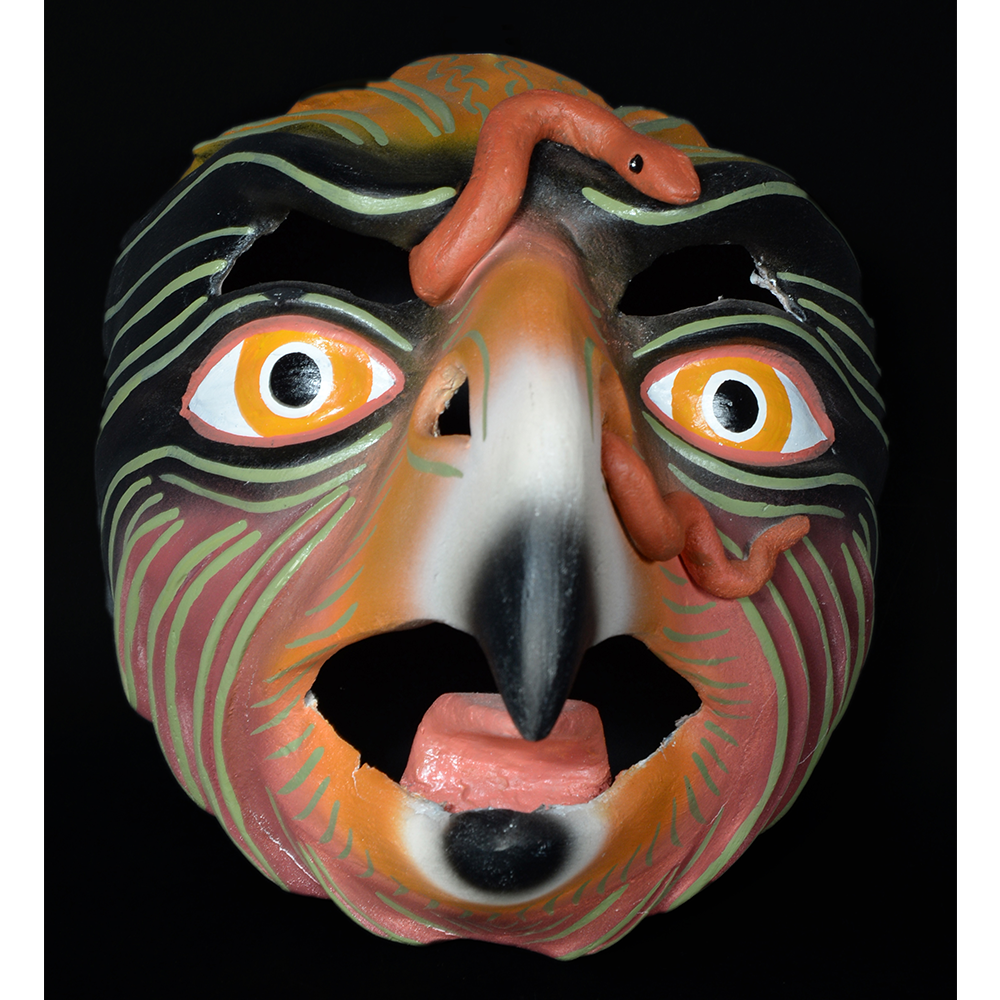
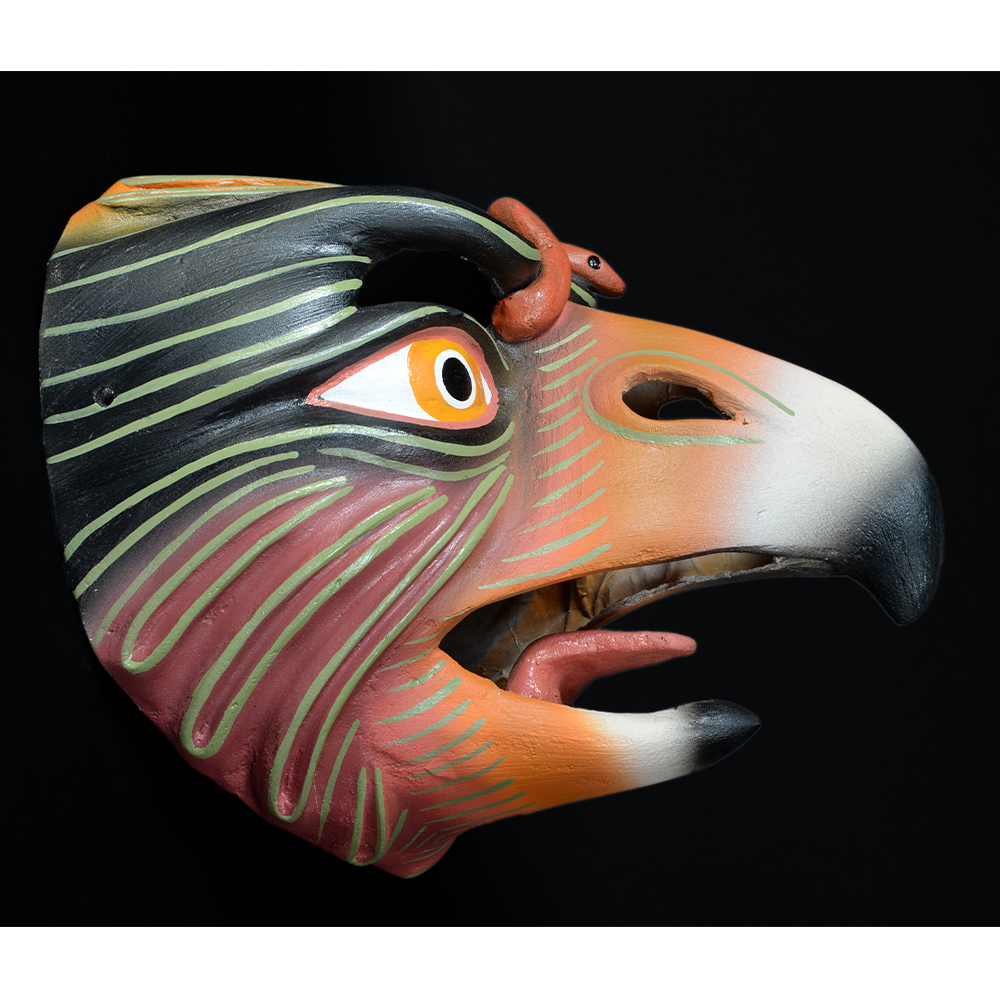
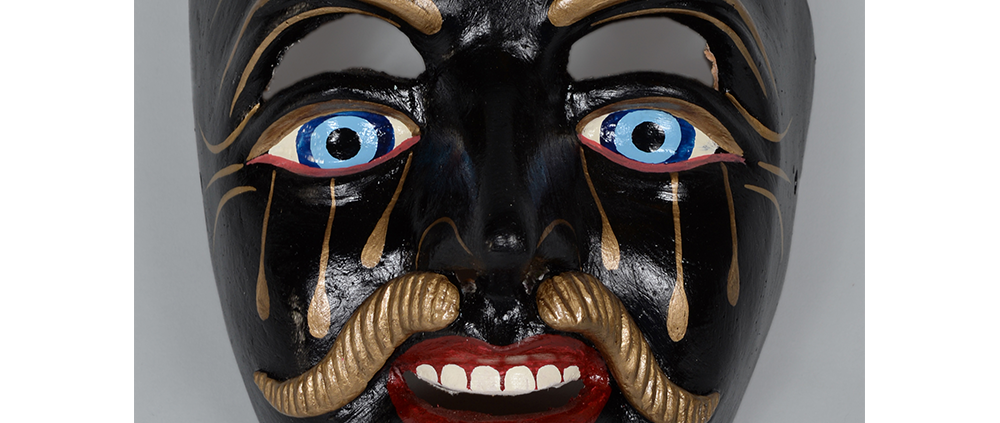
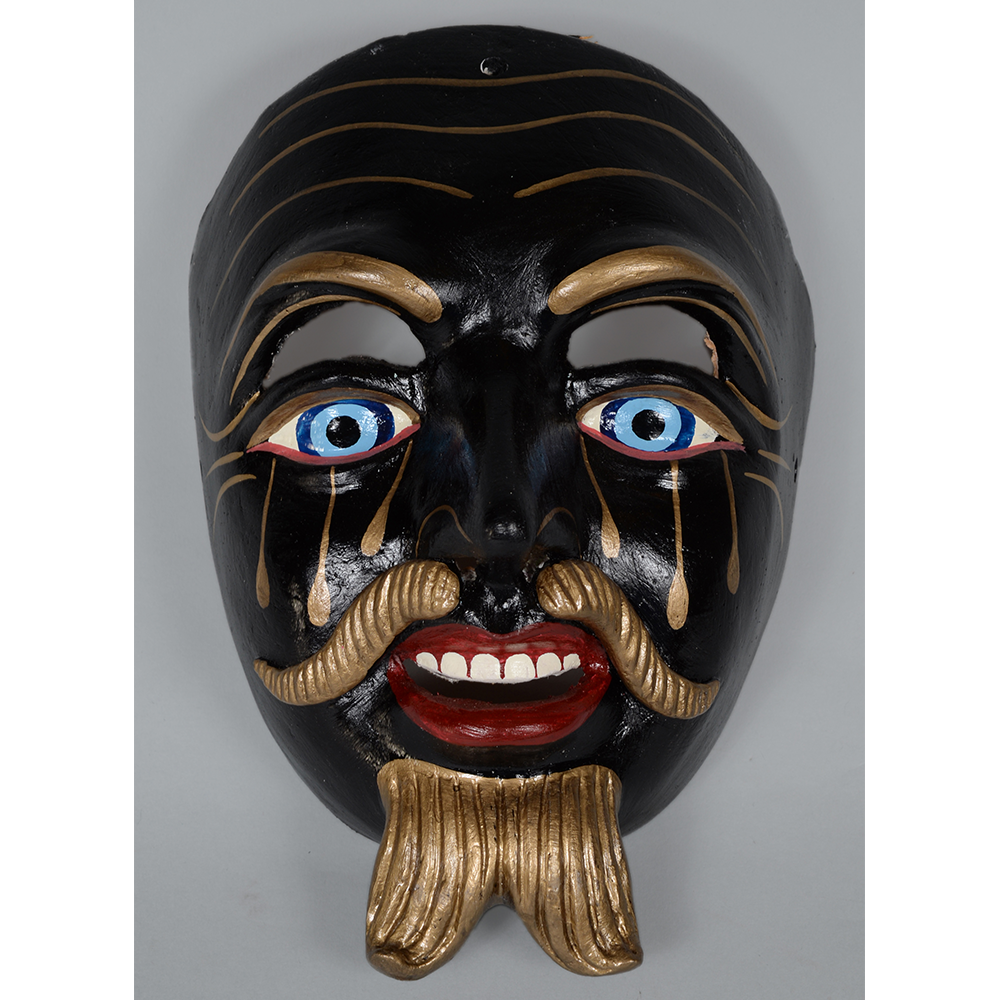
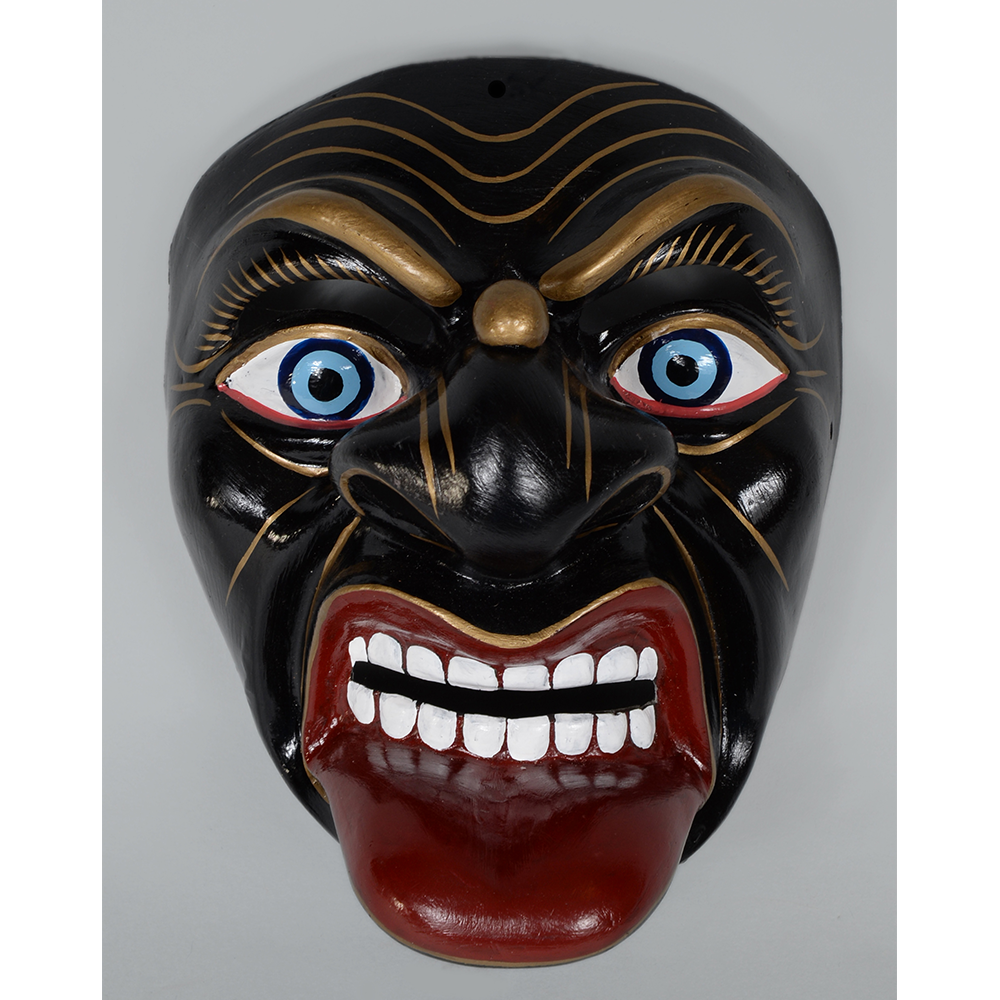
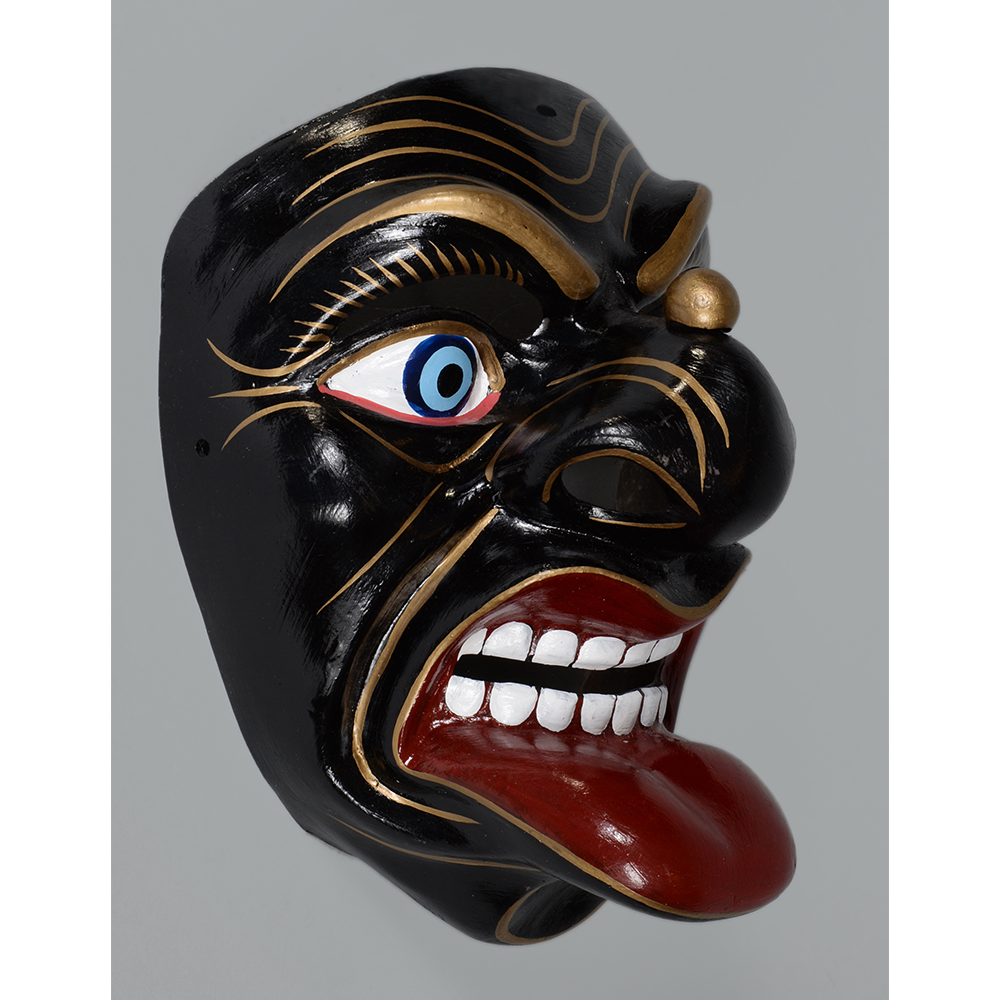
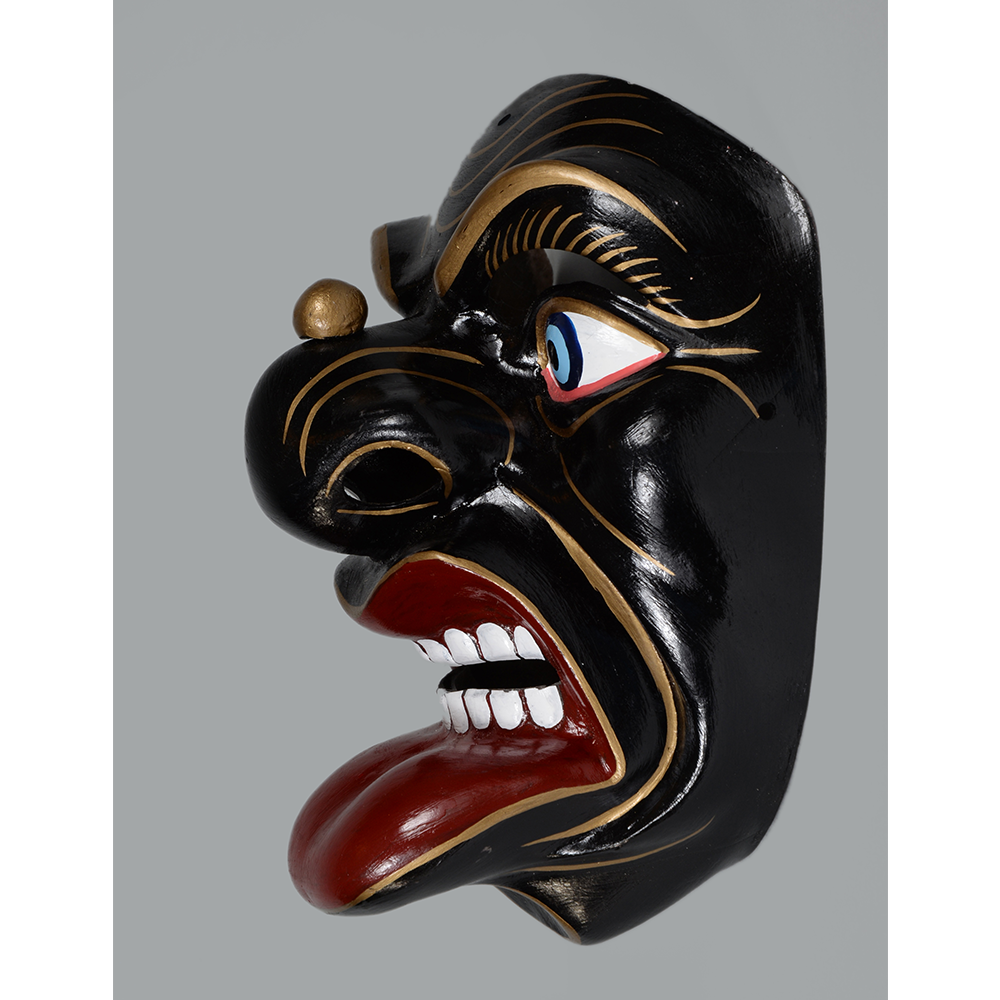
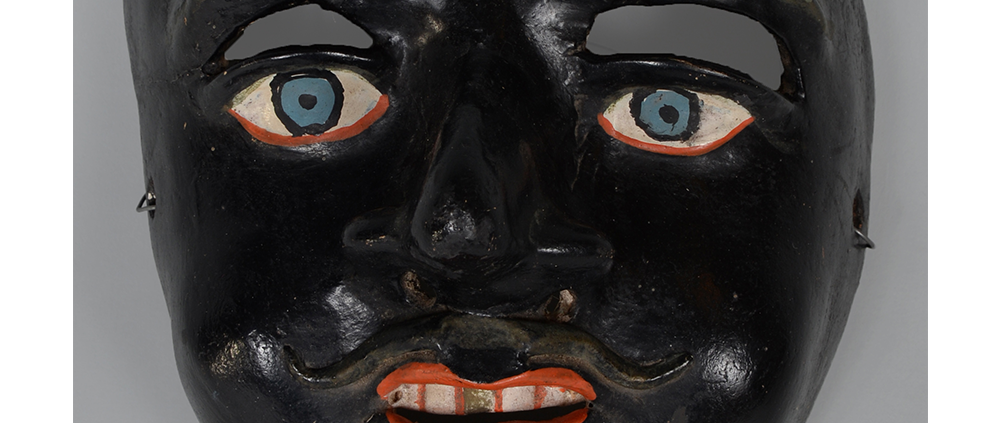
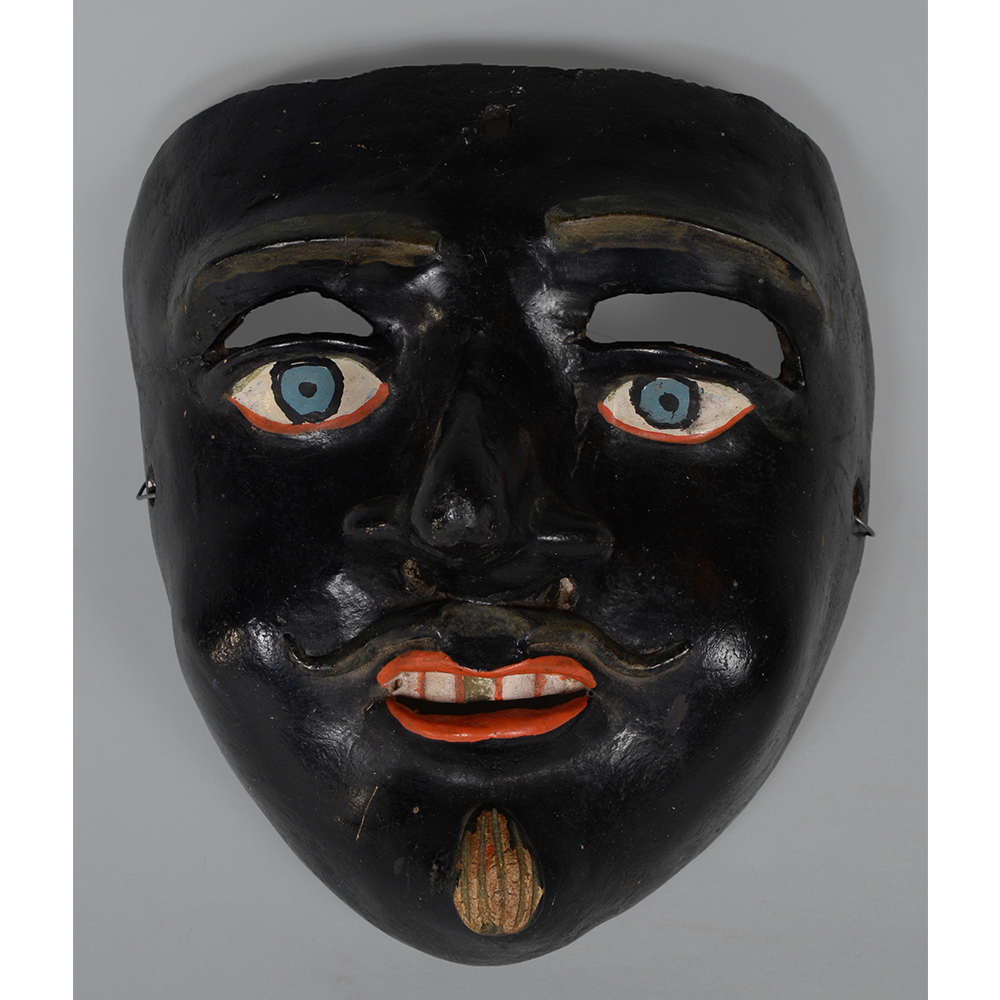
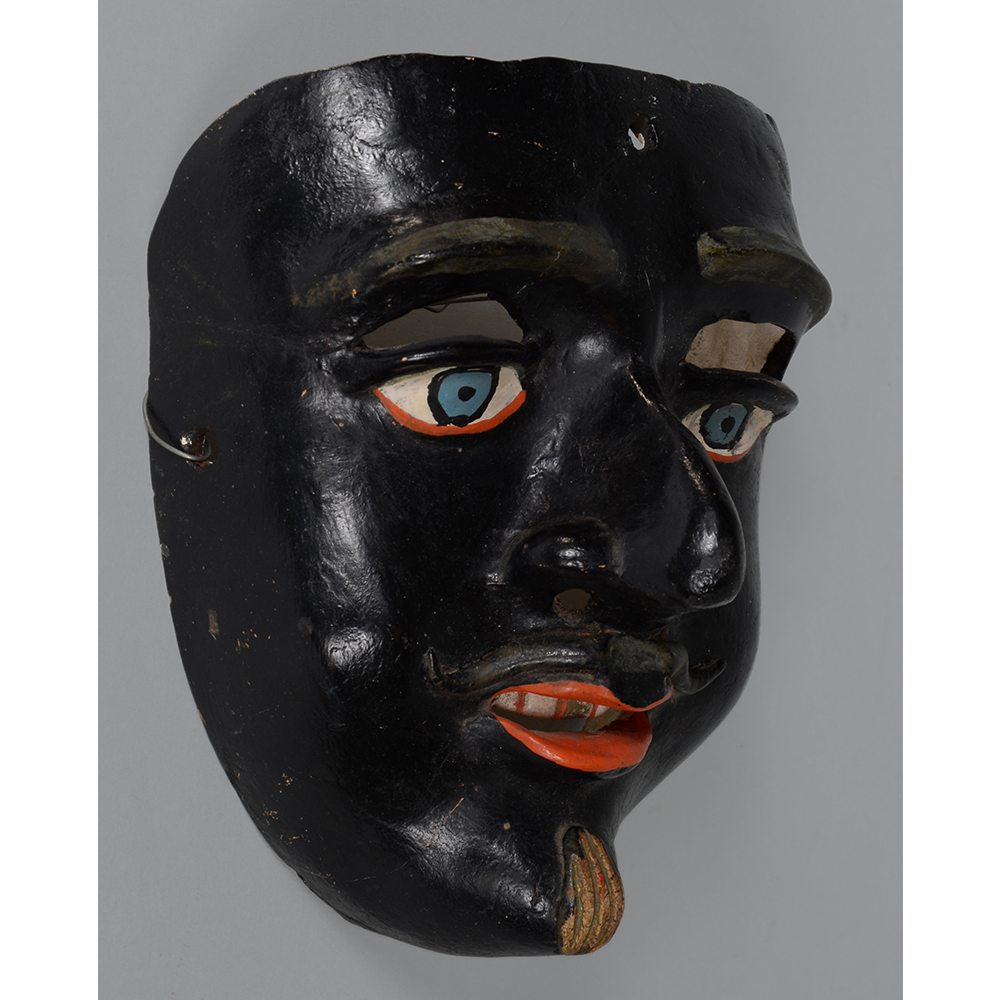
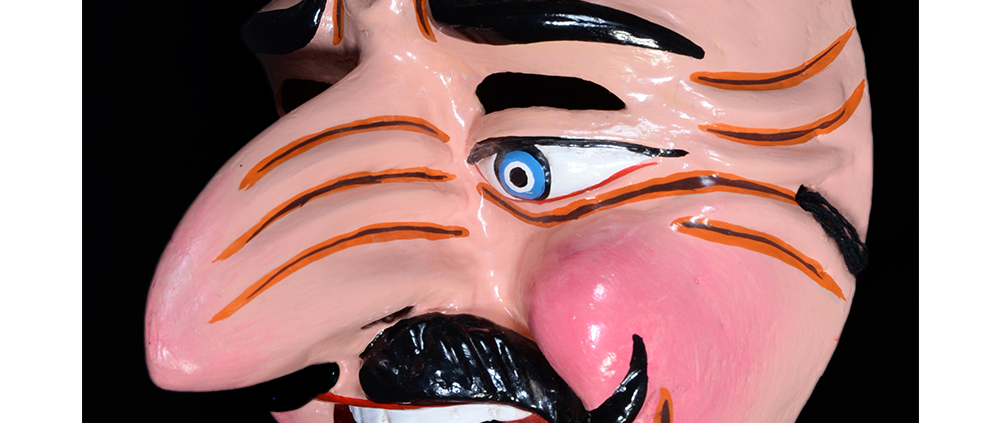
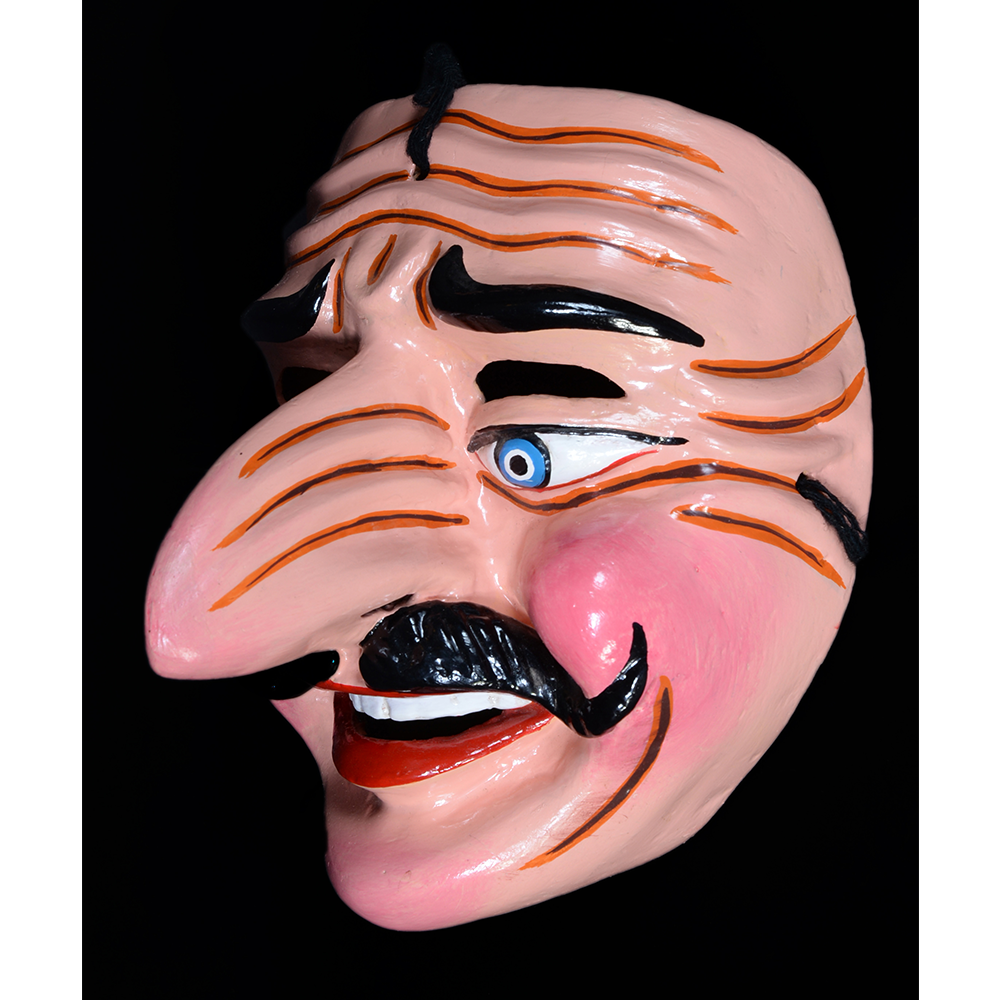
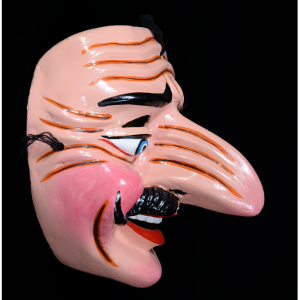
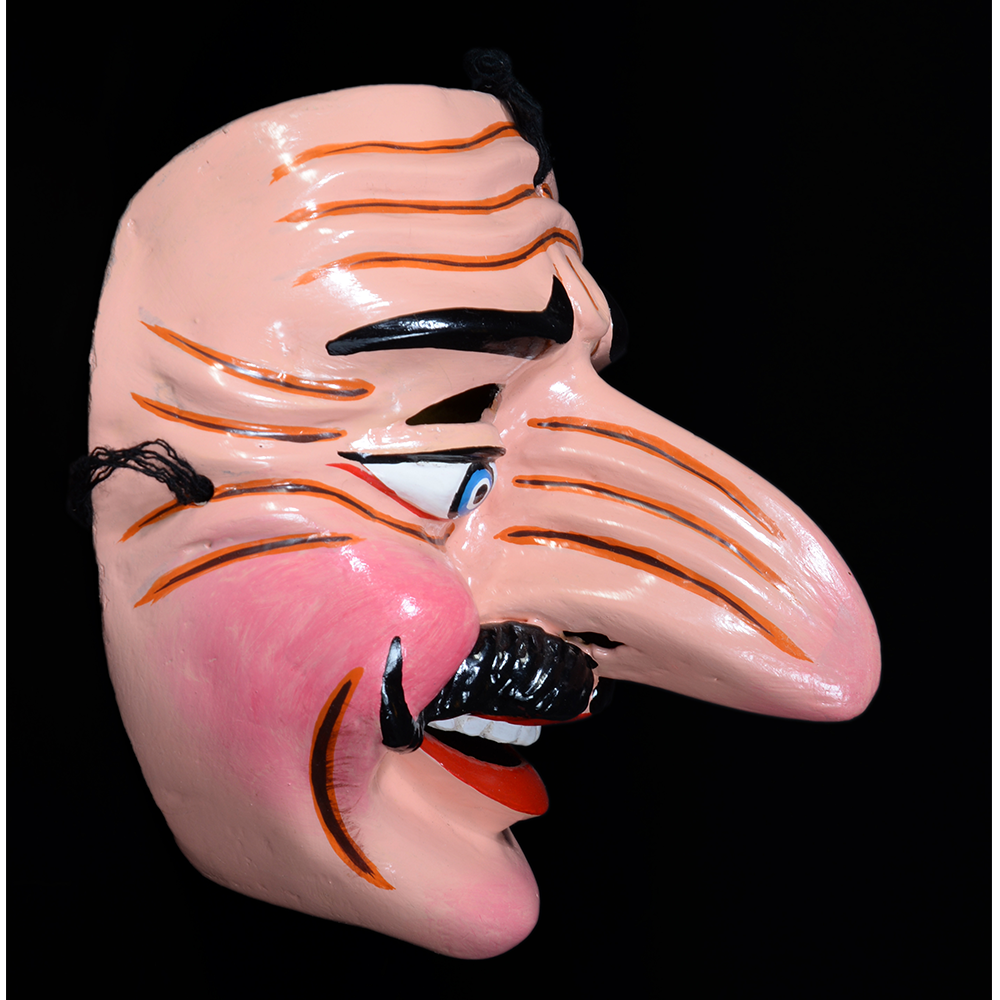
DESCRIPTION: Reina (Queen) de Jardineros
CATALOG ID: LAMX092
MAKER: Unknown
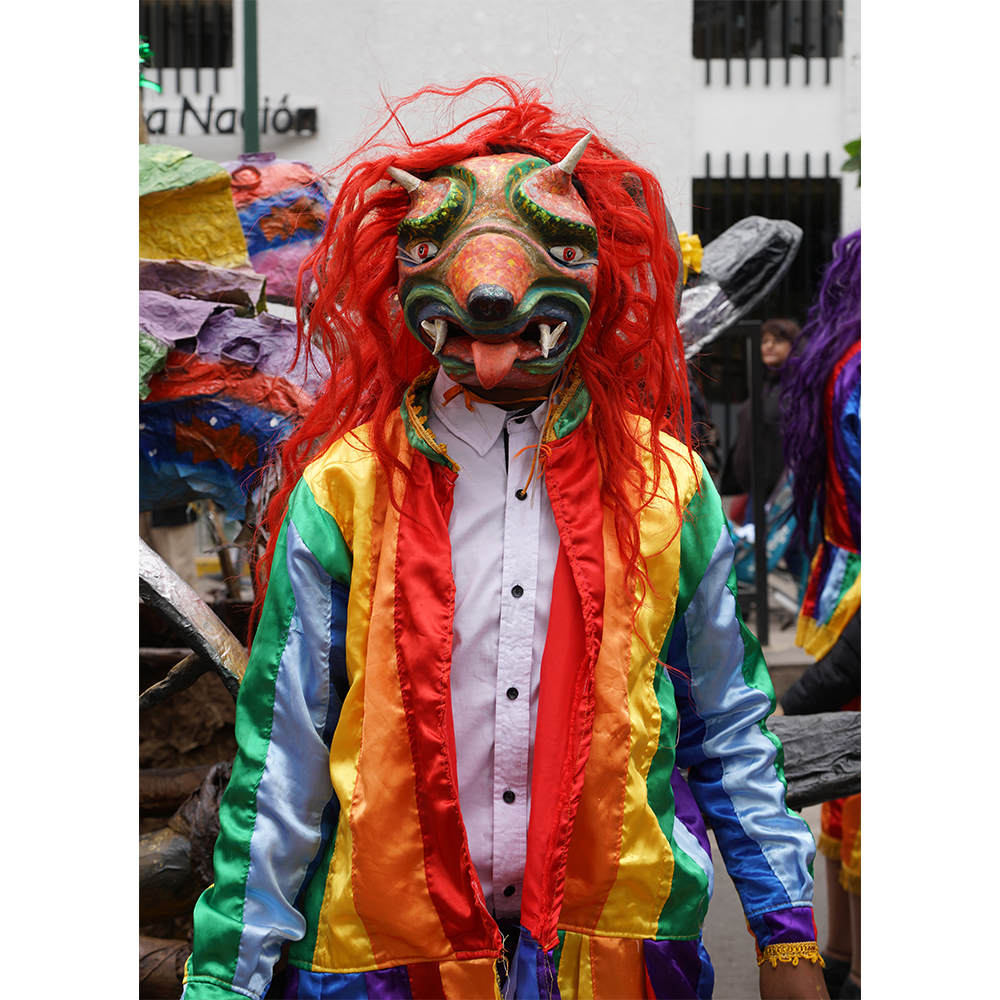
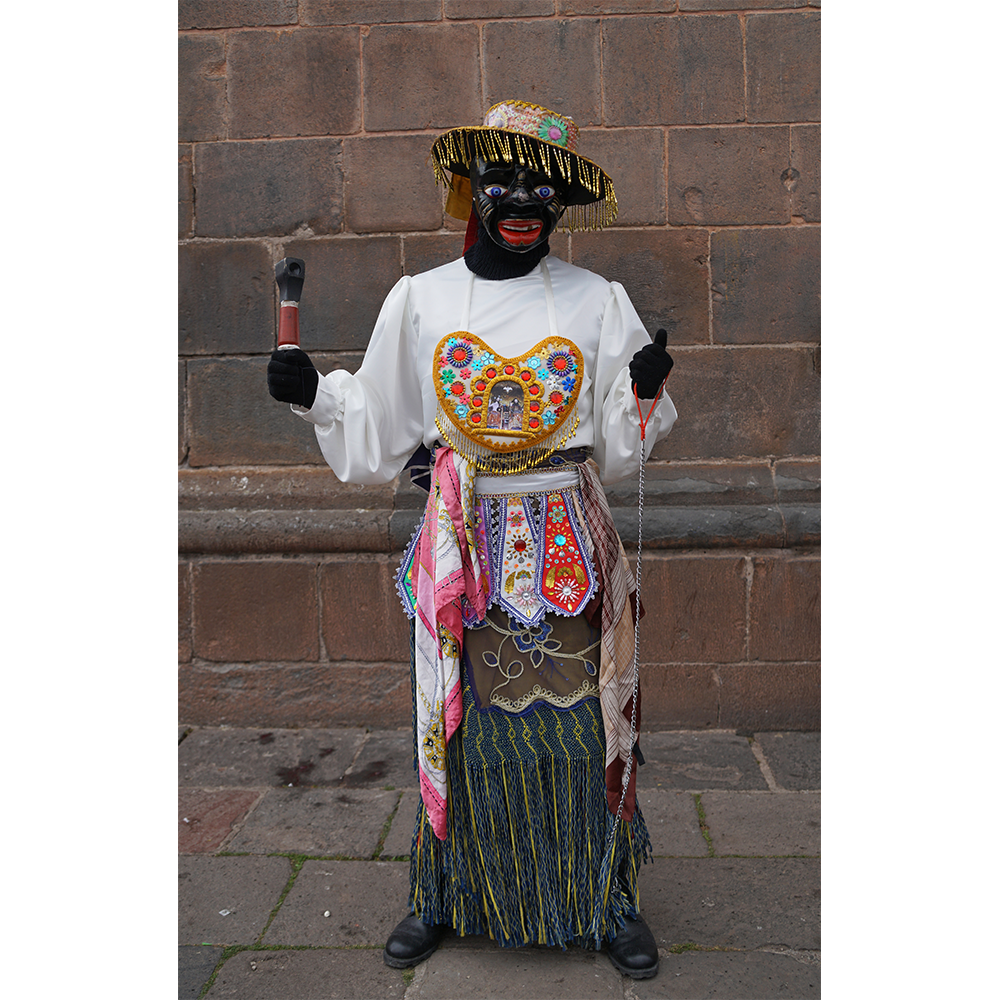
CEREMONY: Danza de Jardineros
AGE: late 1970s
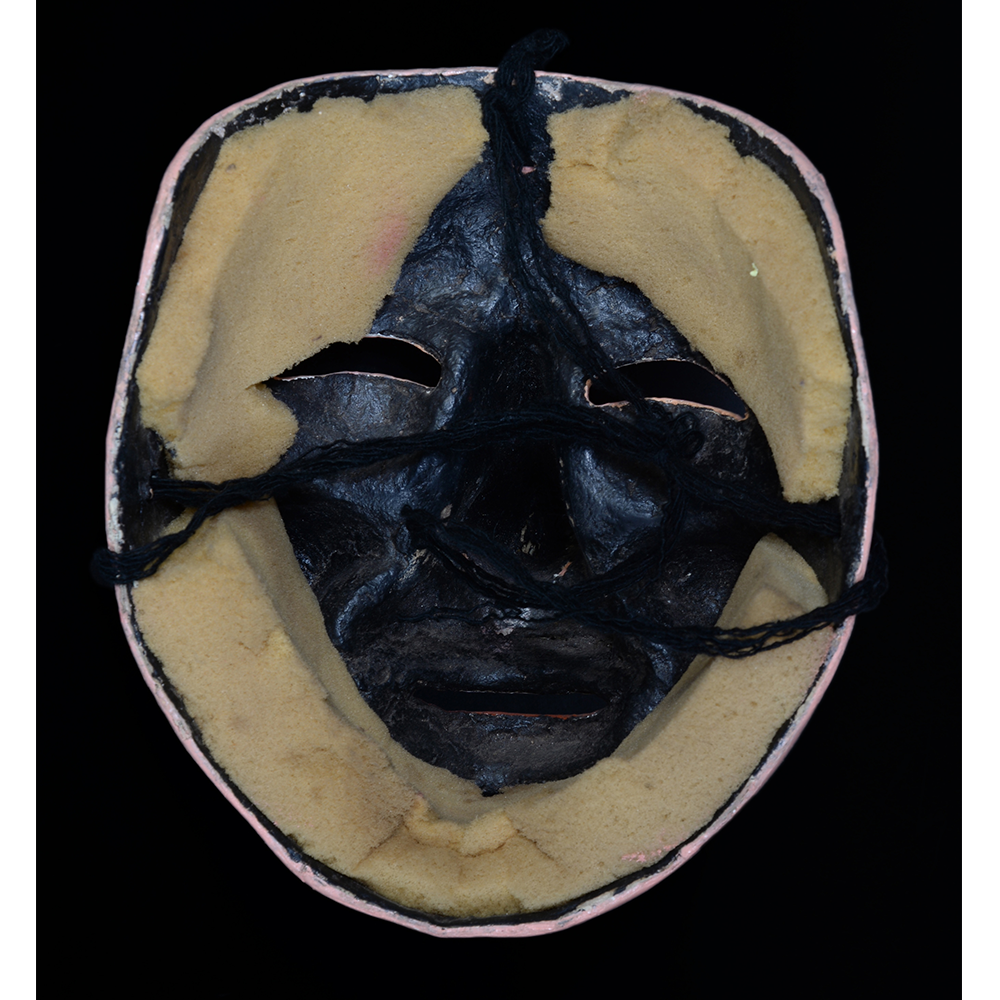
MAIN MATERIAL: cloth covered in beeswax
OTHER MATERIALS: paint; metal o-rings; cotton string
In many parts of Mexico, indigenous populations reenact the Spanish Reconquista, known as the Danza de los Cristianos y los Moros, usually on holidays in honor of the patron saint of the village. In the Zapotec region of Oaxaca, especially San Bartolo Coyotepec, Zaachila, and Santo Tomás Jalieza, this tradition has a unique style and is known as the Dance of the Gardeners. A group formed of a Christian king and queen, a Moorish king and queen, and various princes, princesses, knights and vassals involving an elaborate plot that ends in a machete fight in which the Christians are victorious and force the Muslims to convert to Catholicism. The ceremony is usually performed at the Fiesta de la Virgén de Rosario on the last Sunday of the year, as well as the 2nd and 8th of January. This specific mask represents the Spanish queen.