TITLE: Tigre Mask
TYPE: face mask
GENERAL REGION: Latin America
COUNTRY: Mexico
SUBREGION: Guerrero
ETHNICITY: Nahua
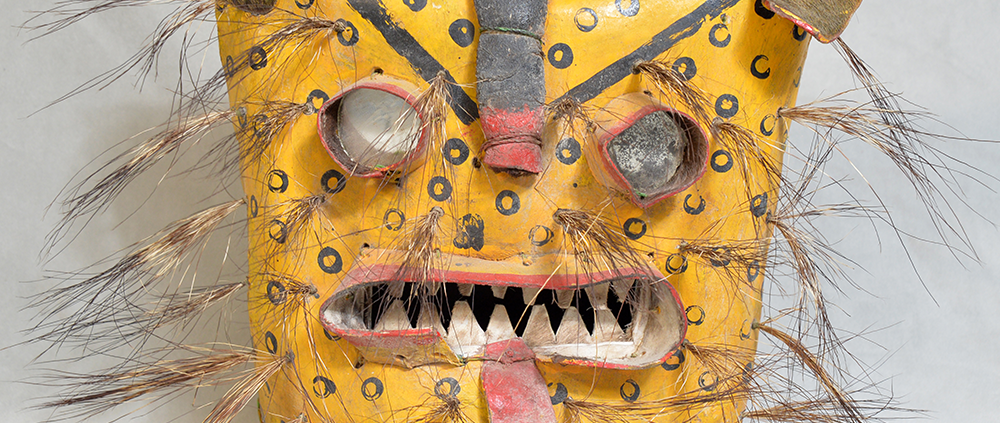
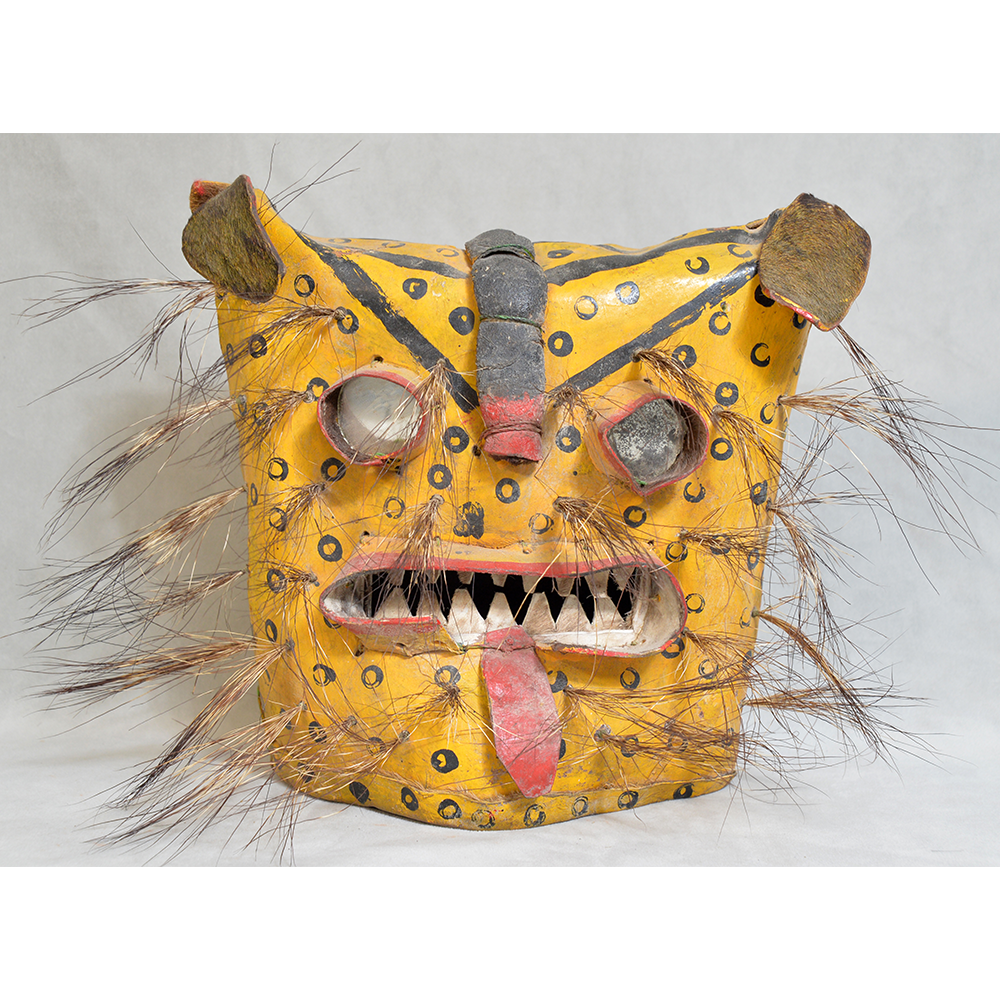
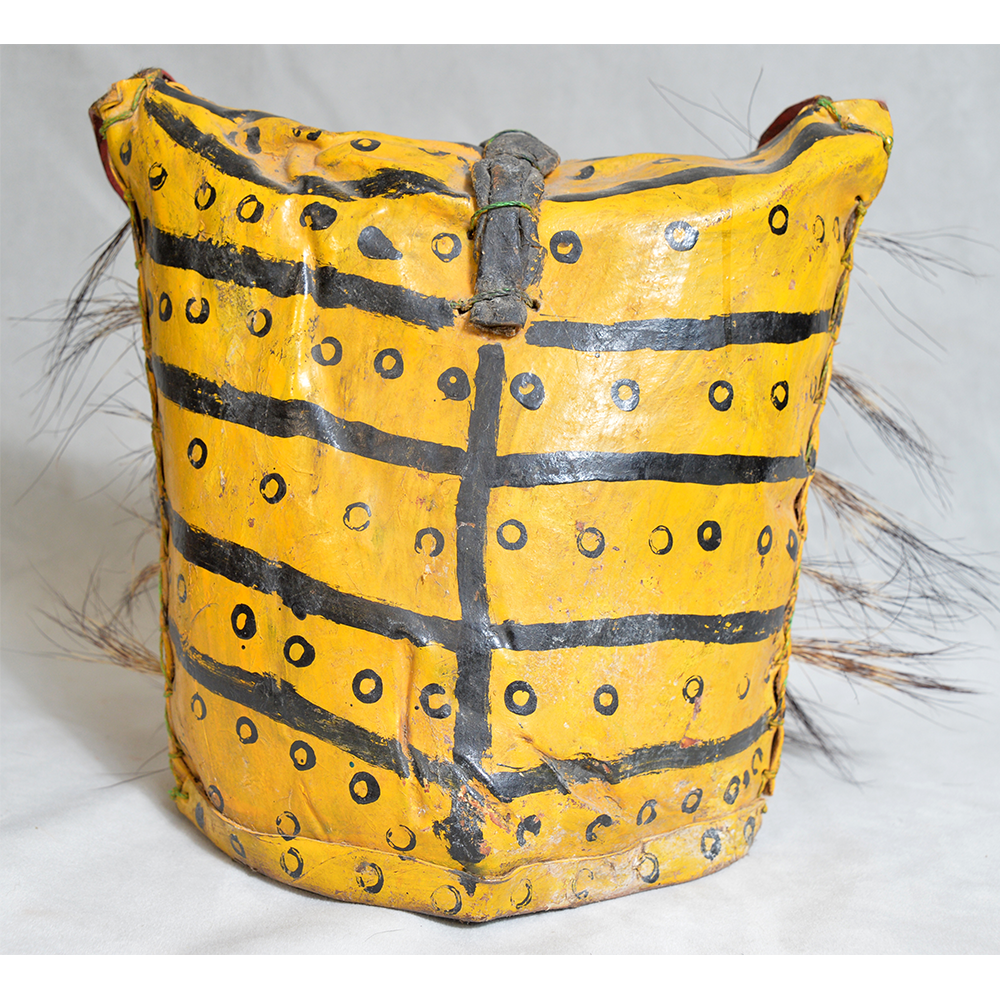
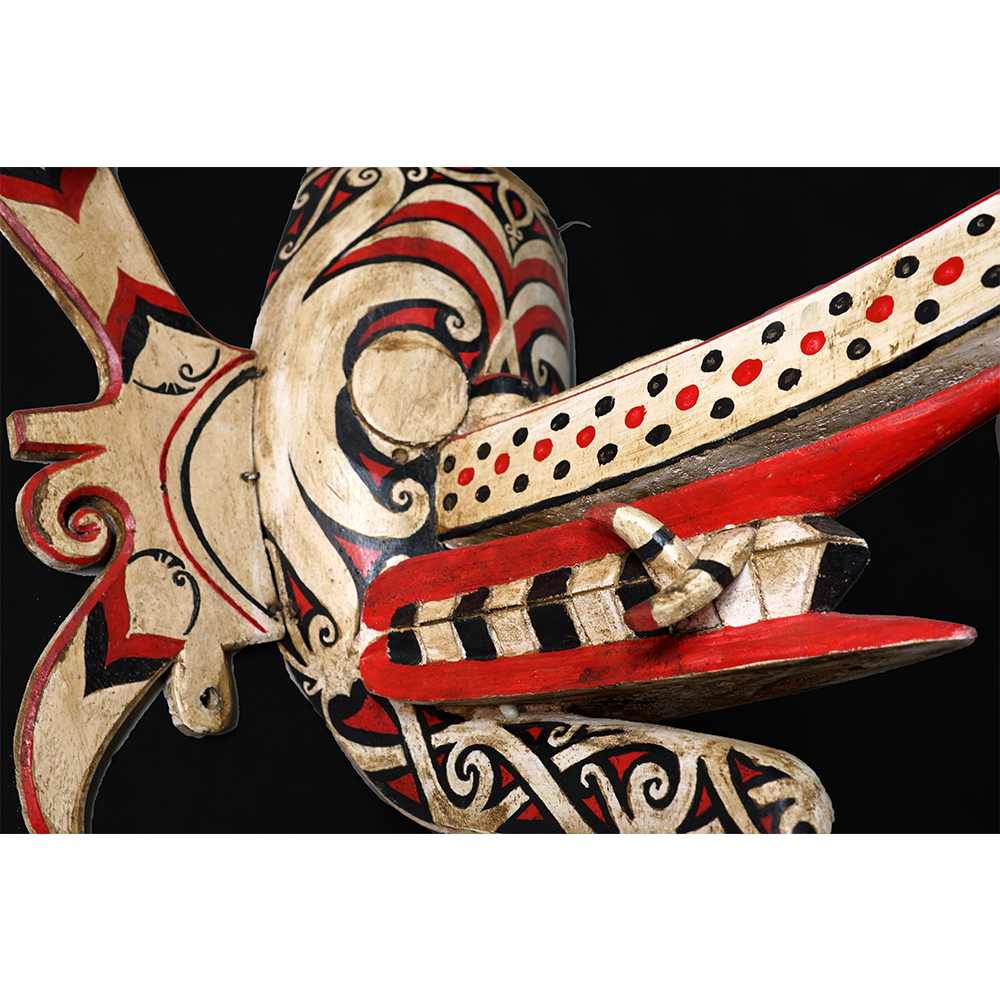
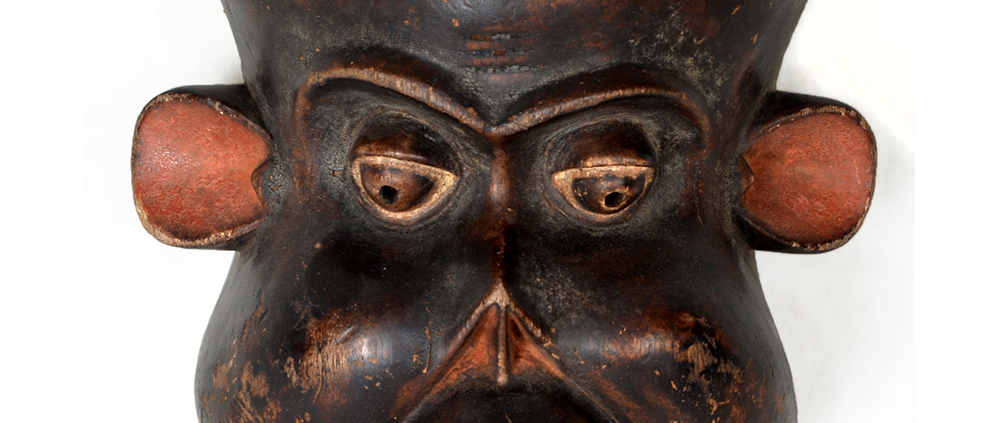
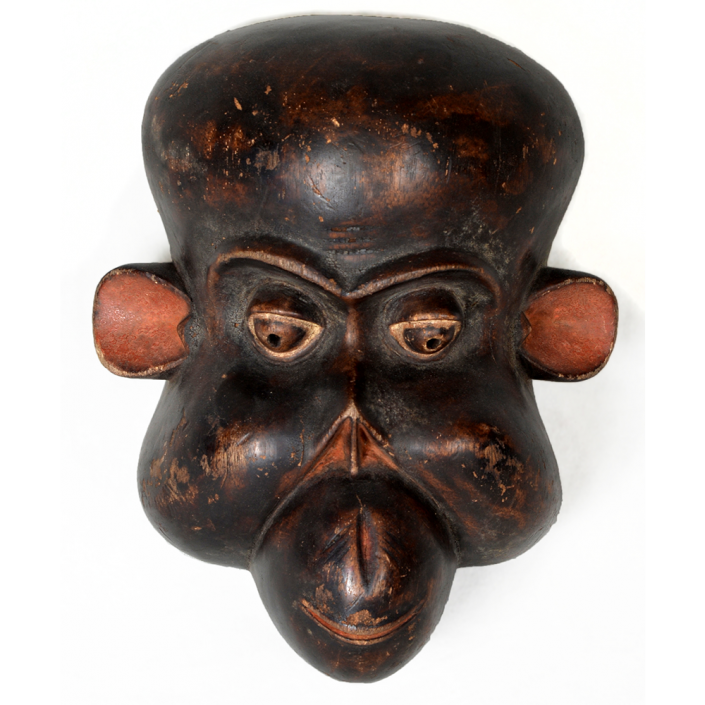
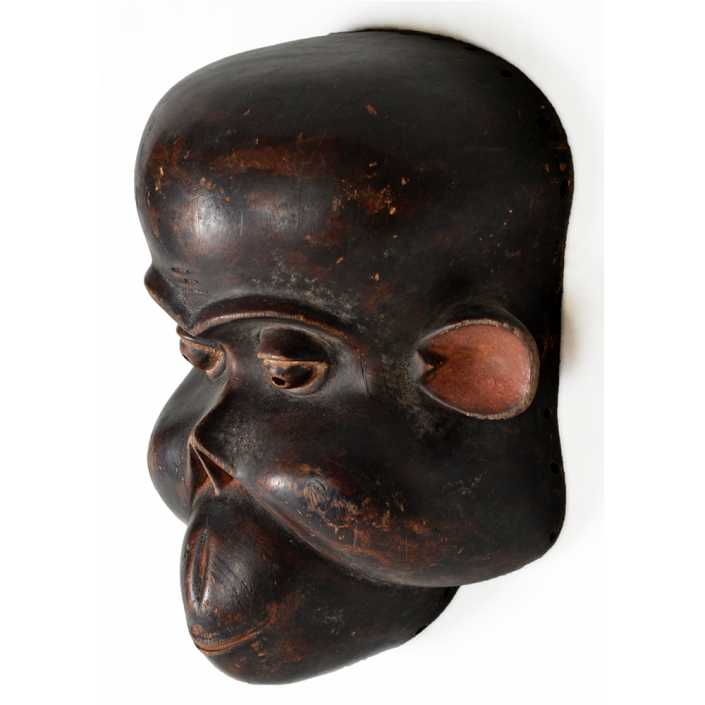
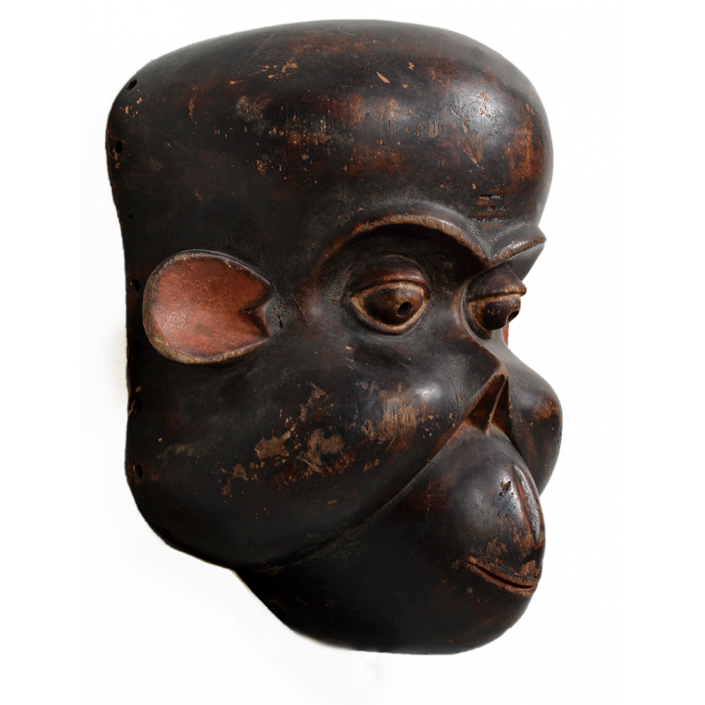
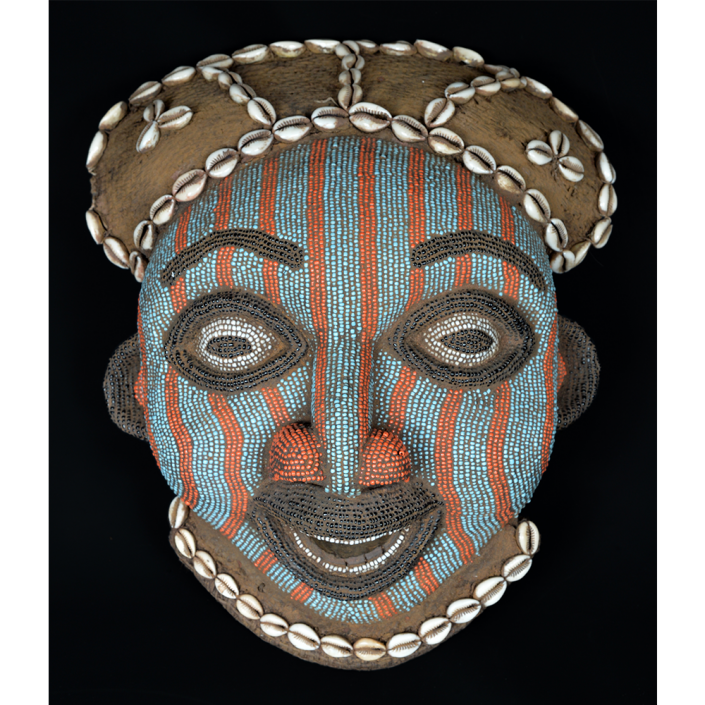
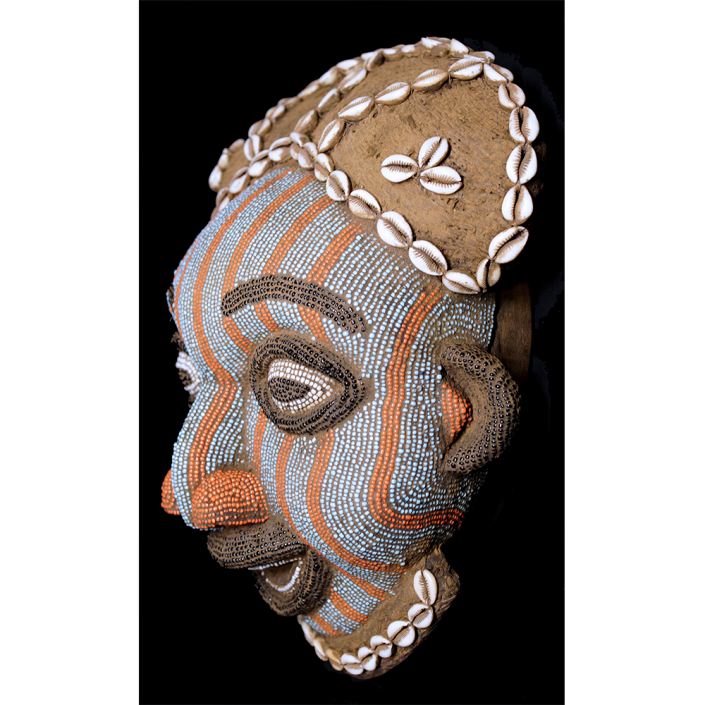
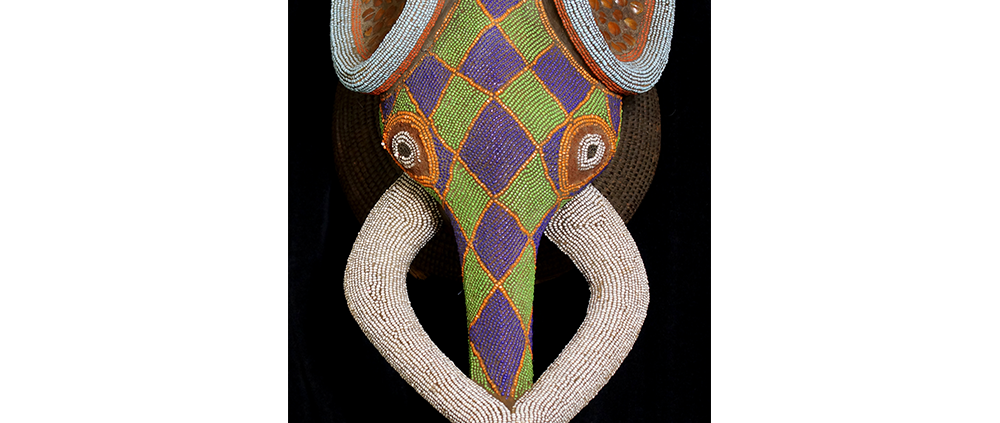
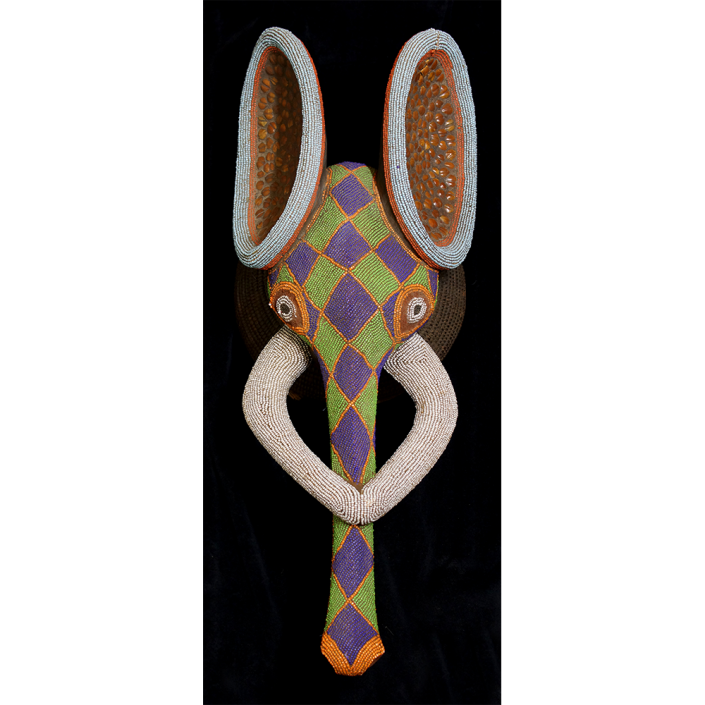
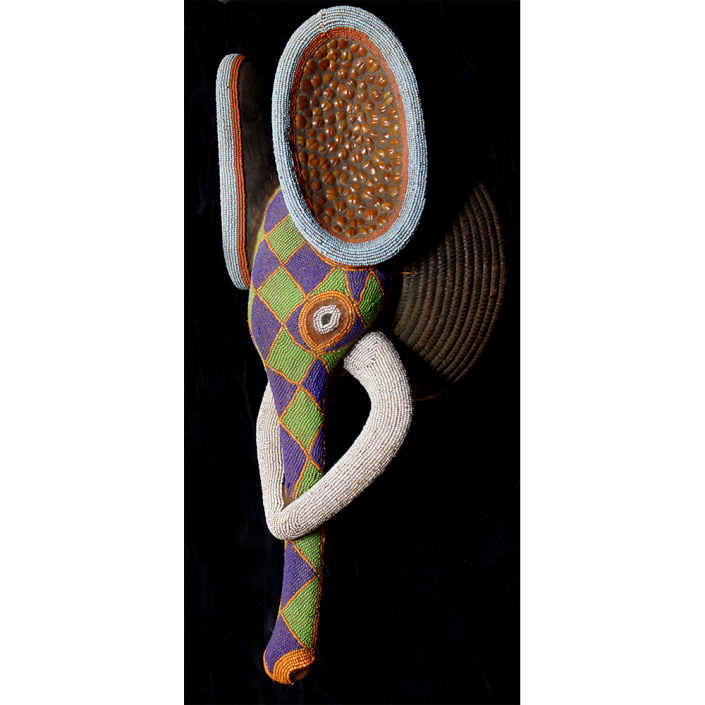
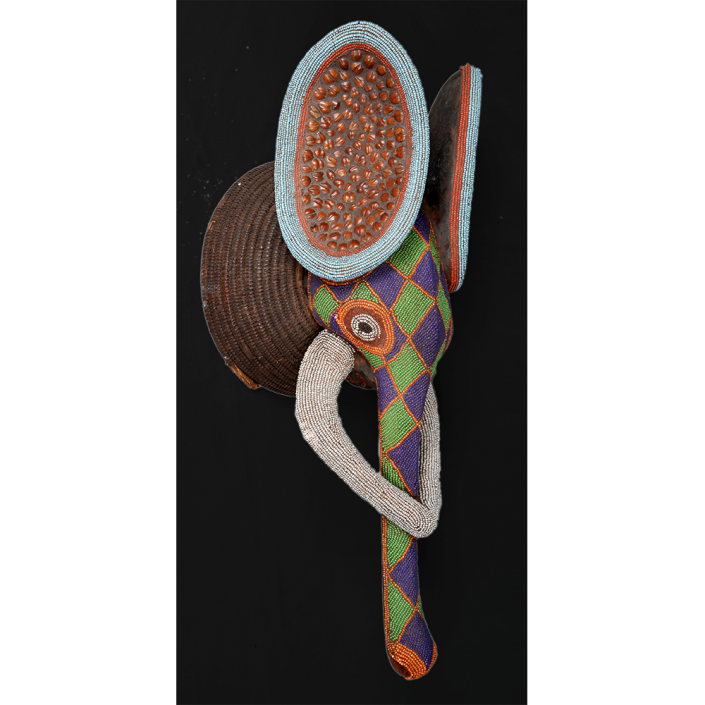
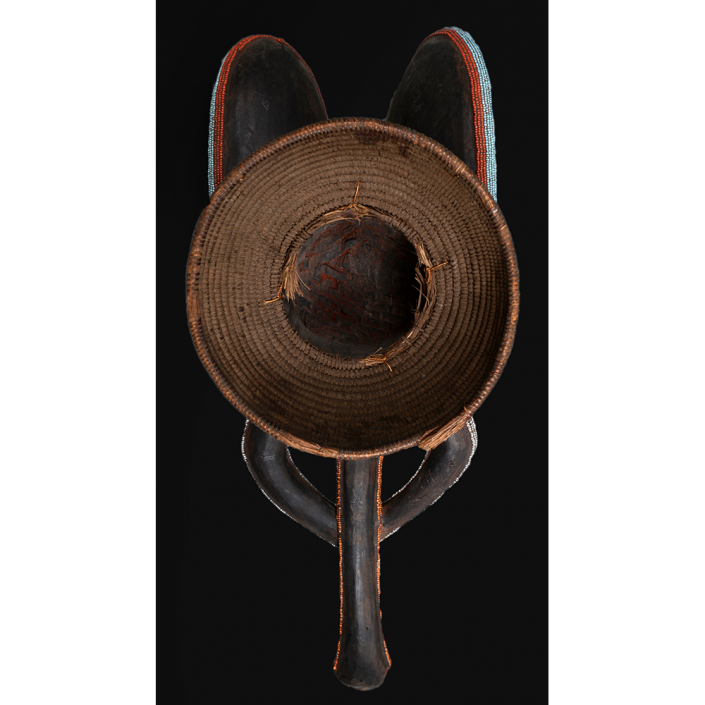
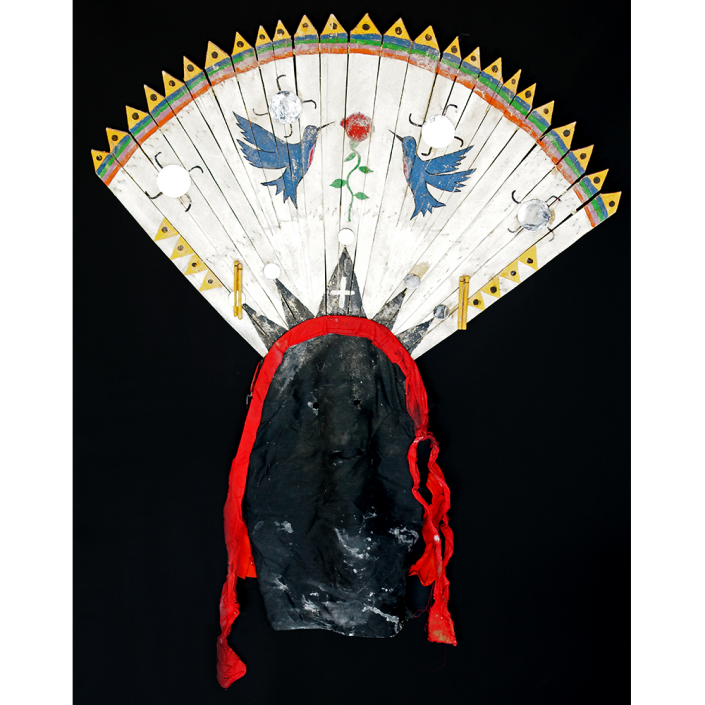
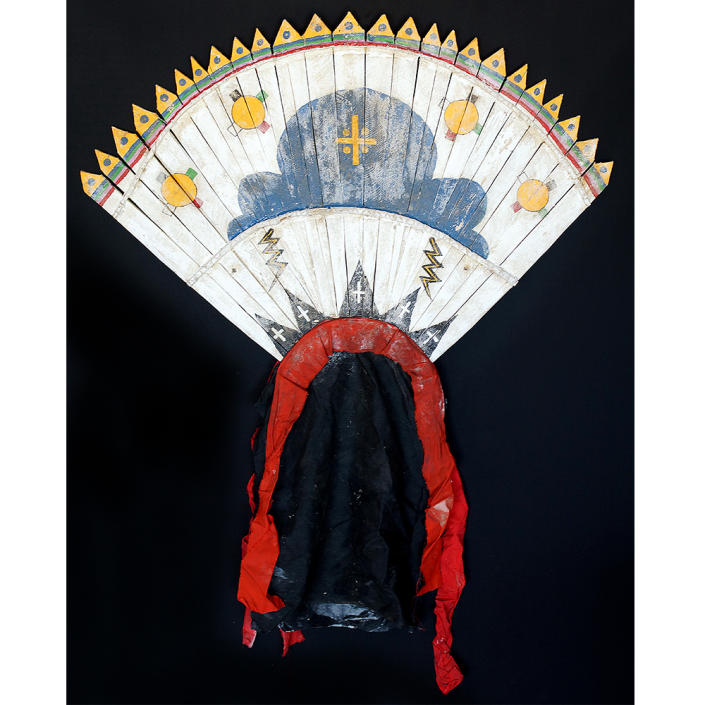
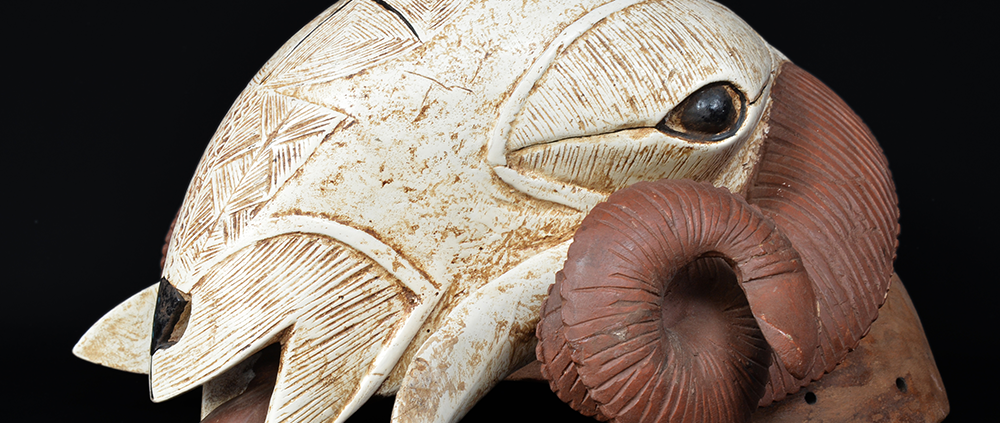
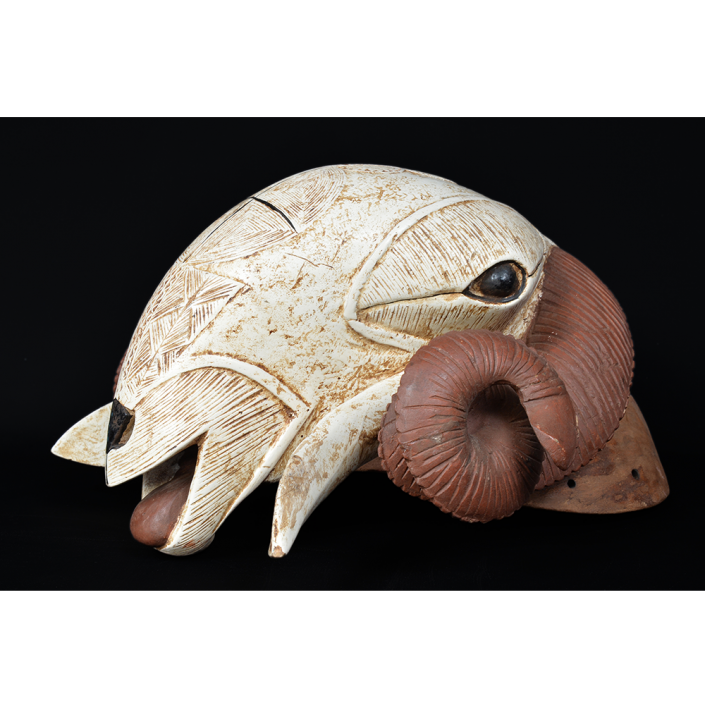
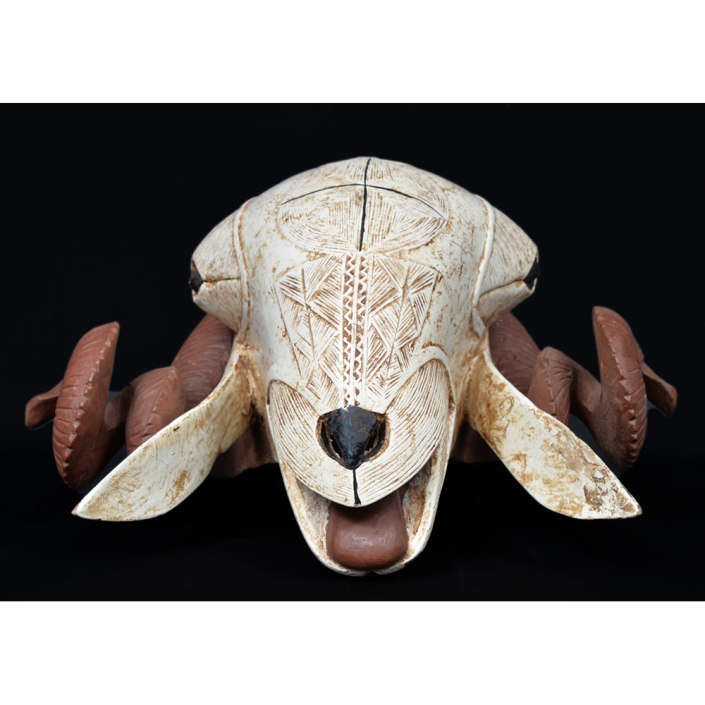
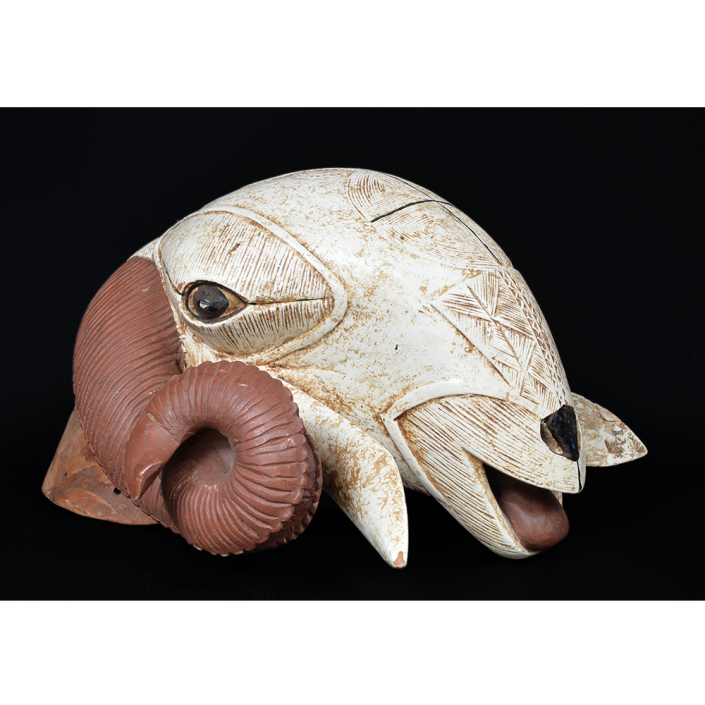
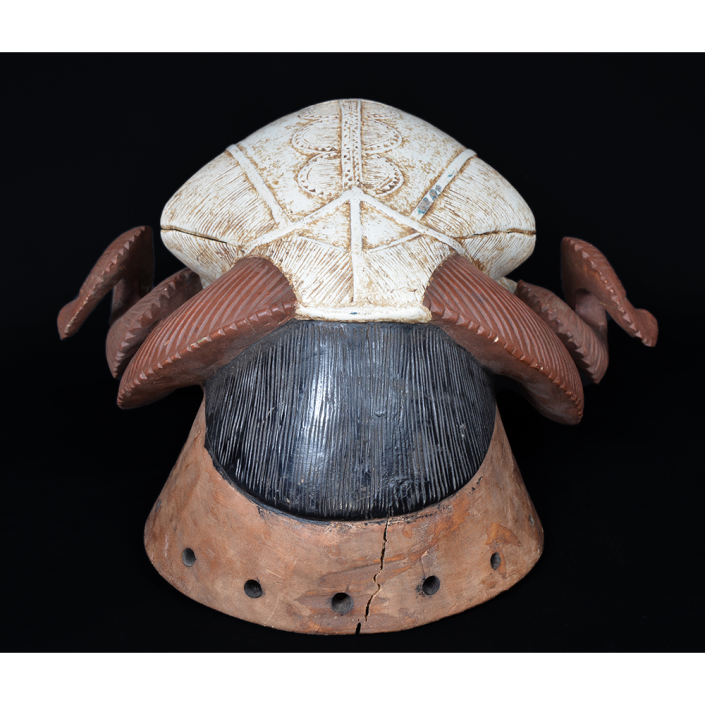
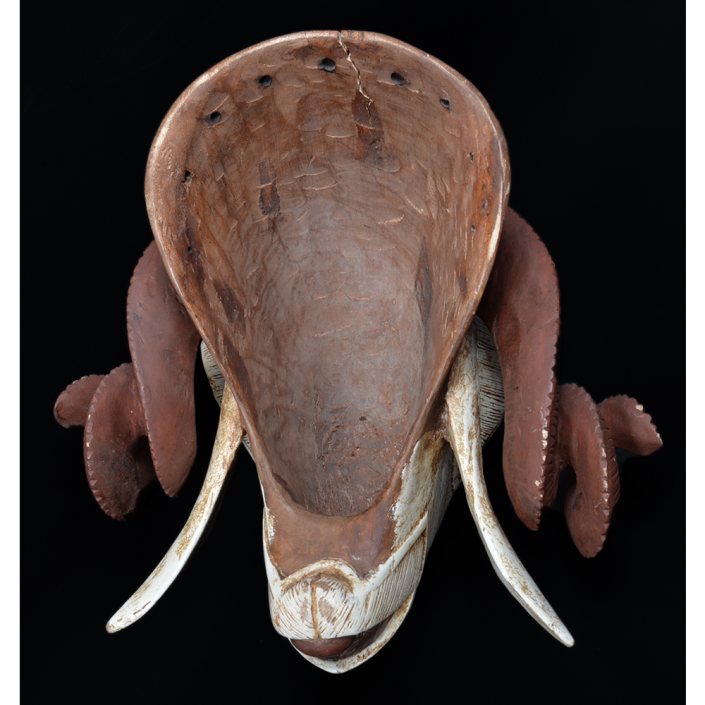
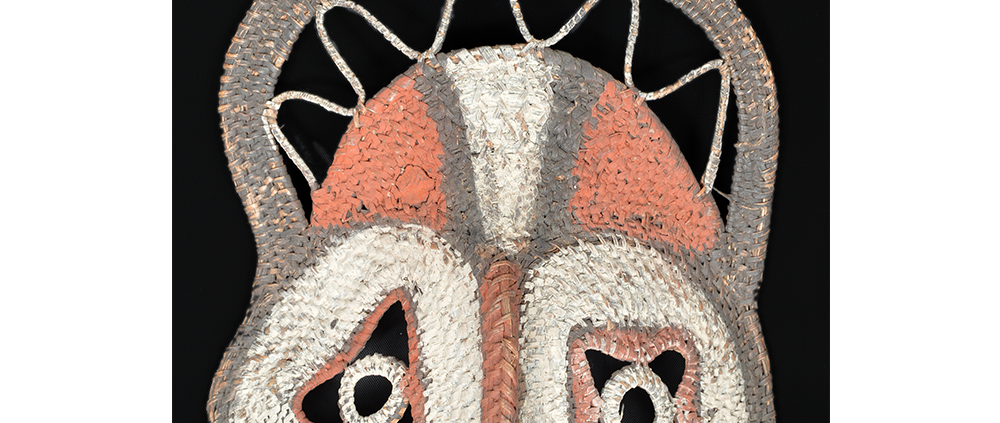
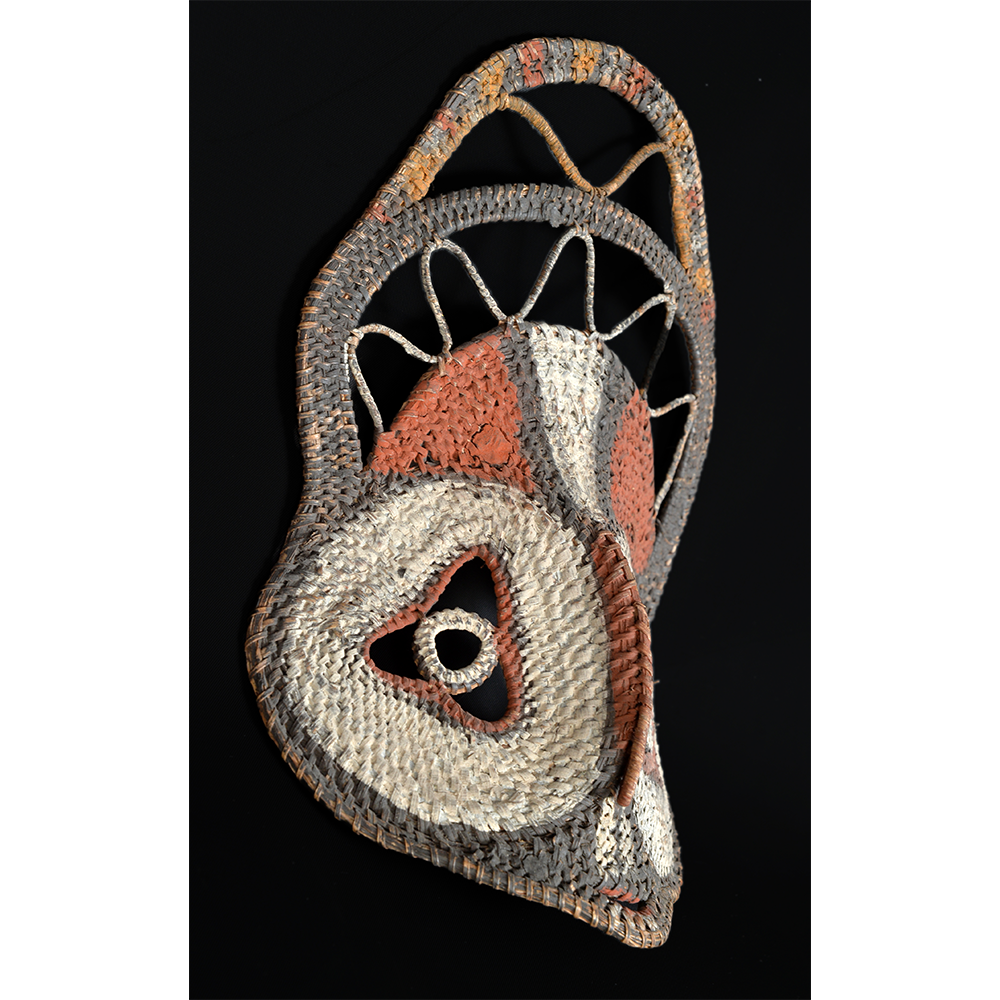
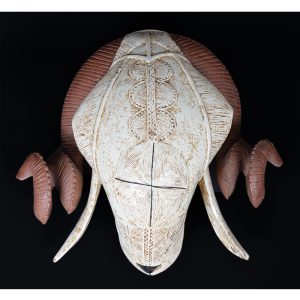
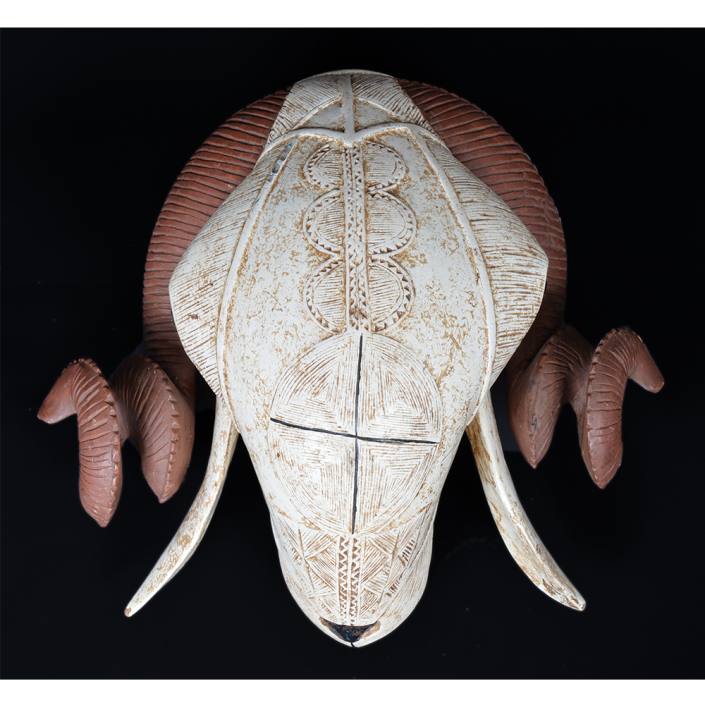
DESCRIPTION: Tigre (Jaguar) Helmet Mask
CATALOG ID: LAMX026
MAKER: Unknown maker in Zitlala
CEREMONY: Batalla de los Tigres (Tecuanis)
AGE: ca. 1970s
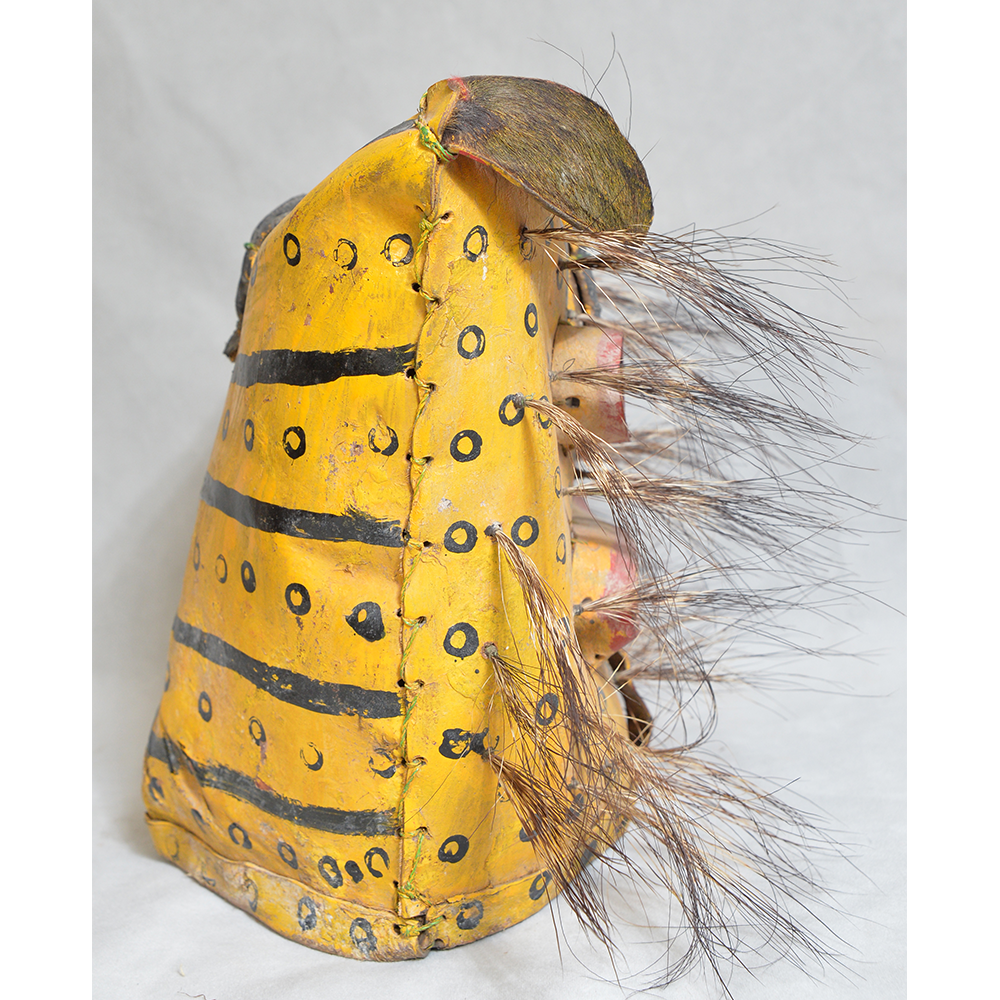
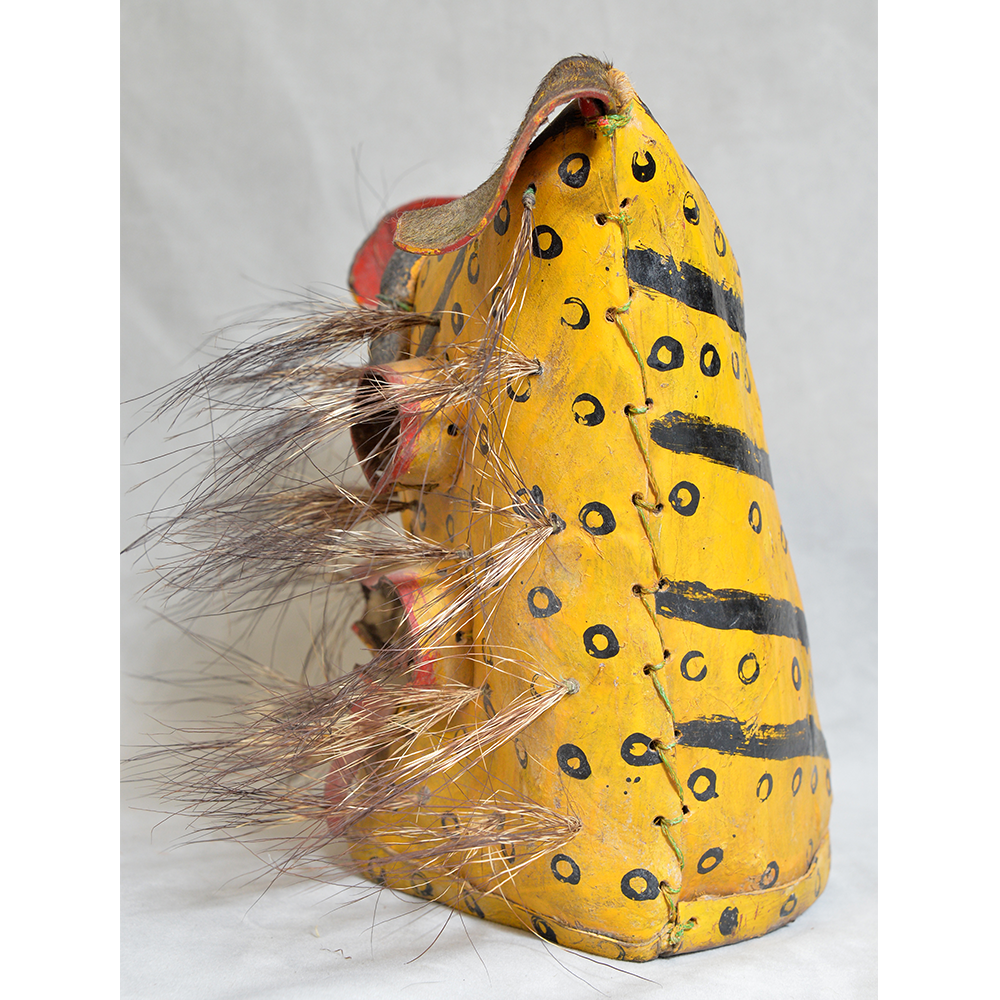
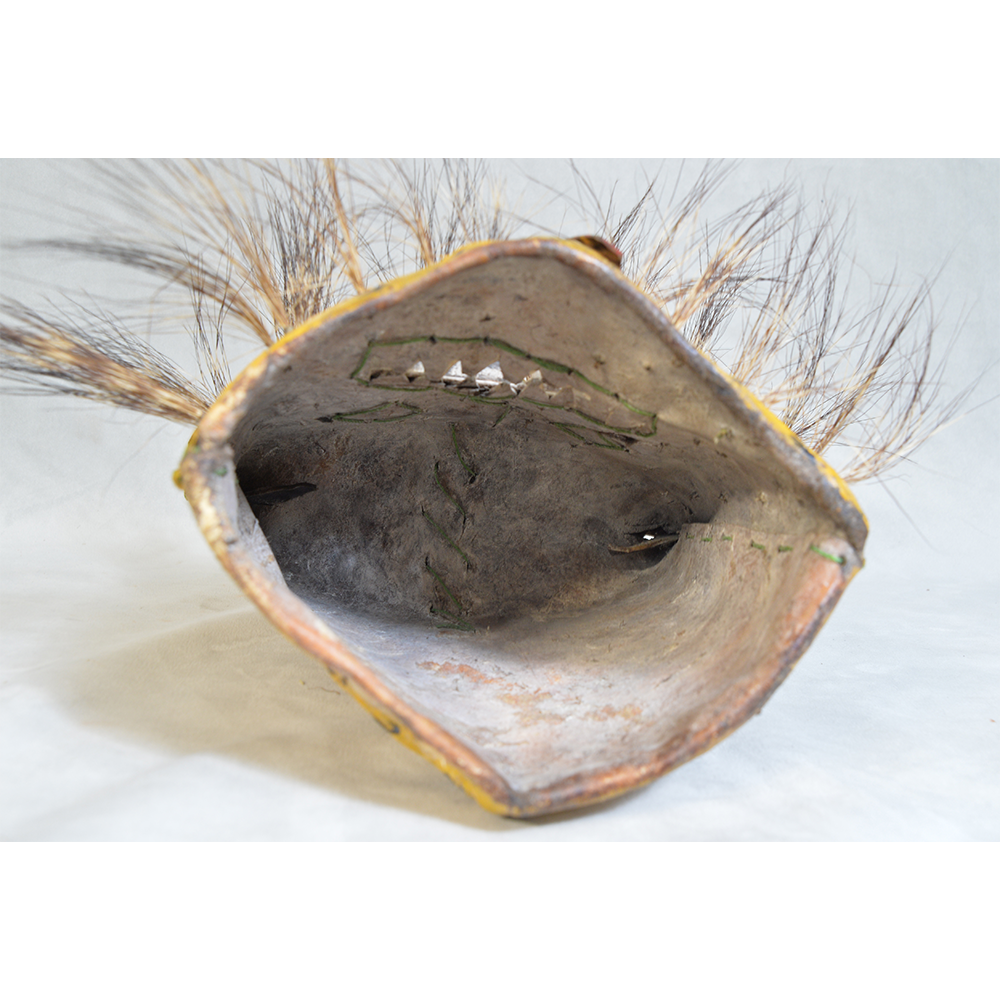
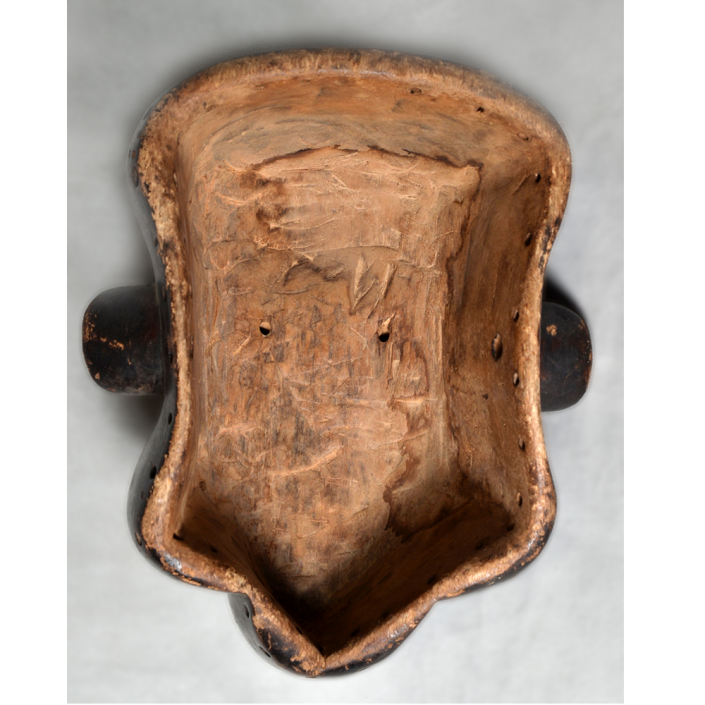
MAIN MATERIAL: leather
OTHER MATERIALS: mirrors; thread; boar hair; paint
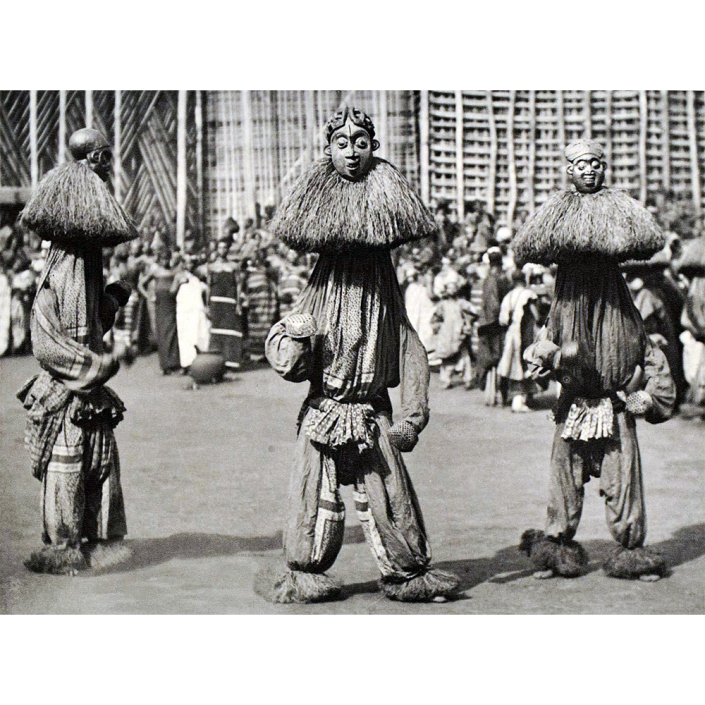
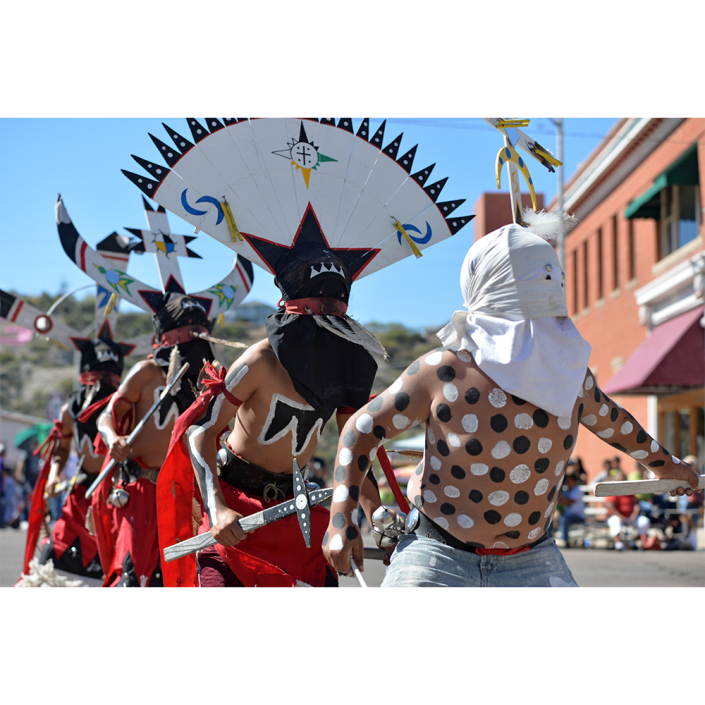
In Guerrero, Mexico, the Batalla de los Tigres (Tiger Battles) are today part of the Catholic feast day of the Holy Cross, but its origins probably reach back into the pre-conquest era worship of a jaguar god (notwithstanding the name and appearance of the mask, there are no tigers in any part of the Americas). Indeed, in many parts of Guerrero, the dancers are referred to as tecuani, the Nahuatl word for jaguar (literally, “man-eater”). The modern dance is used to summon rain for the spring planting season. The jaguars engage in a fierce battle, striking each other with knotted ropes.
This mask is from Zitlala, where hard leather helmet masks are typically used to protect the masquerader’s head from the blows of the ropes. Such masks are either yellow or green depending on the neighborhood (barrio) where it was made.