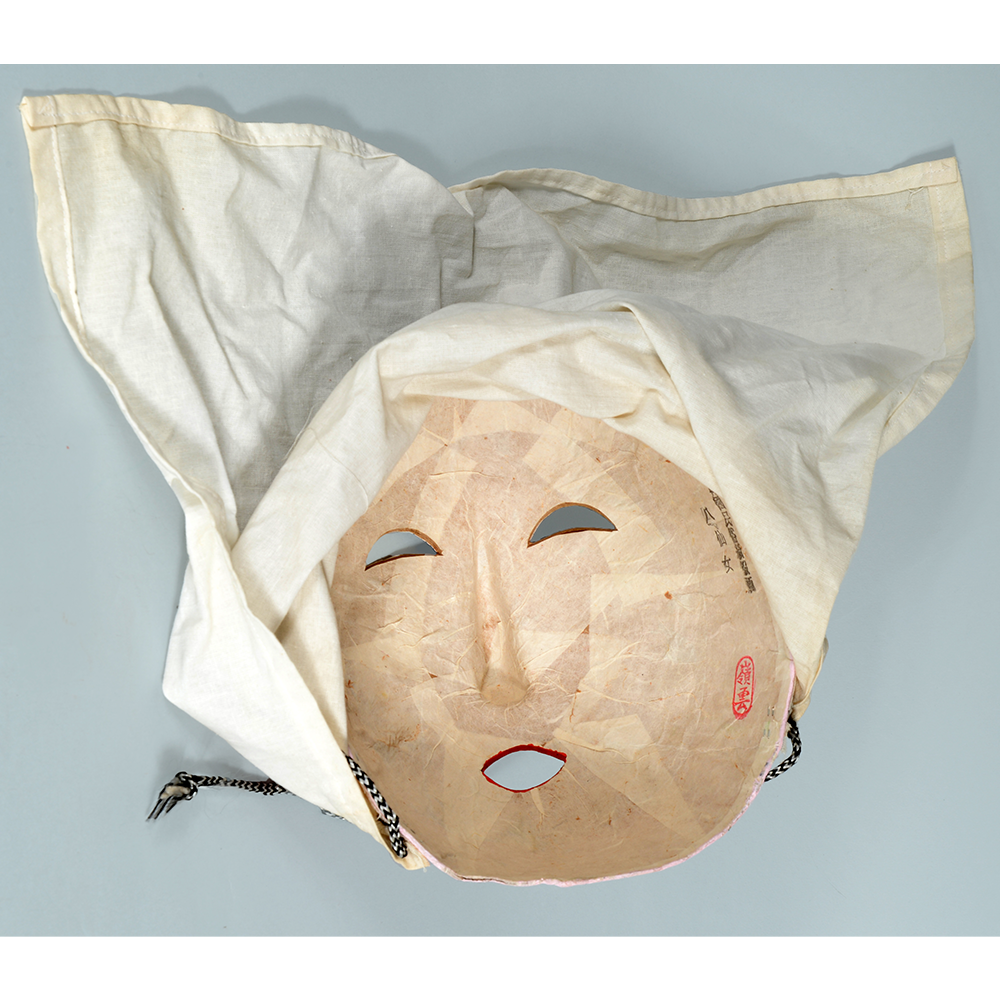
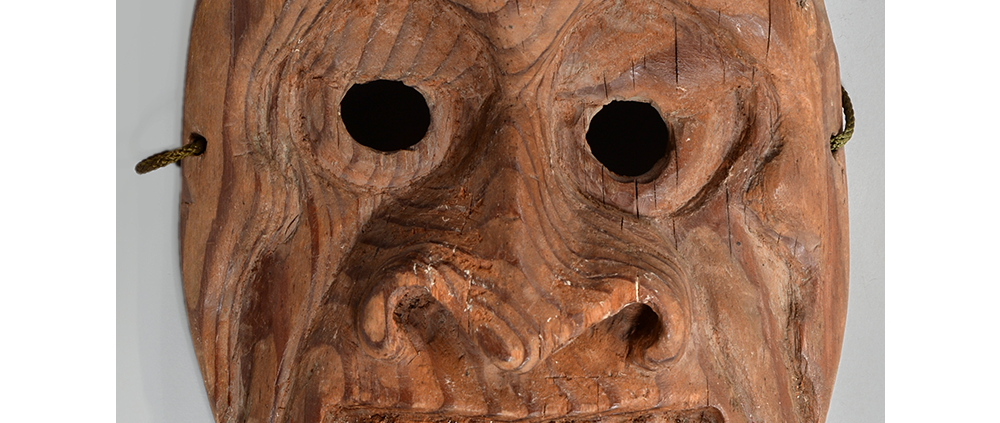
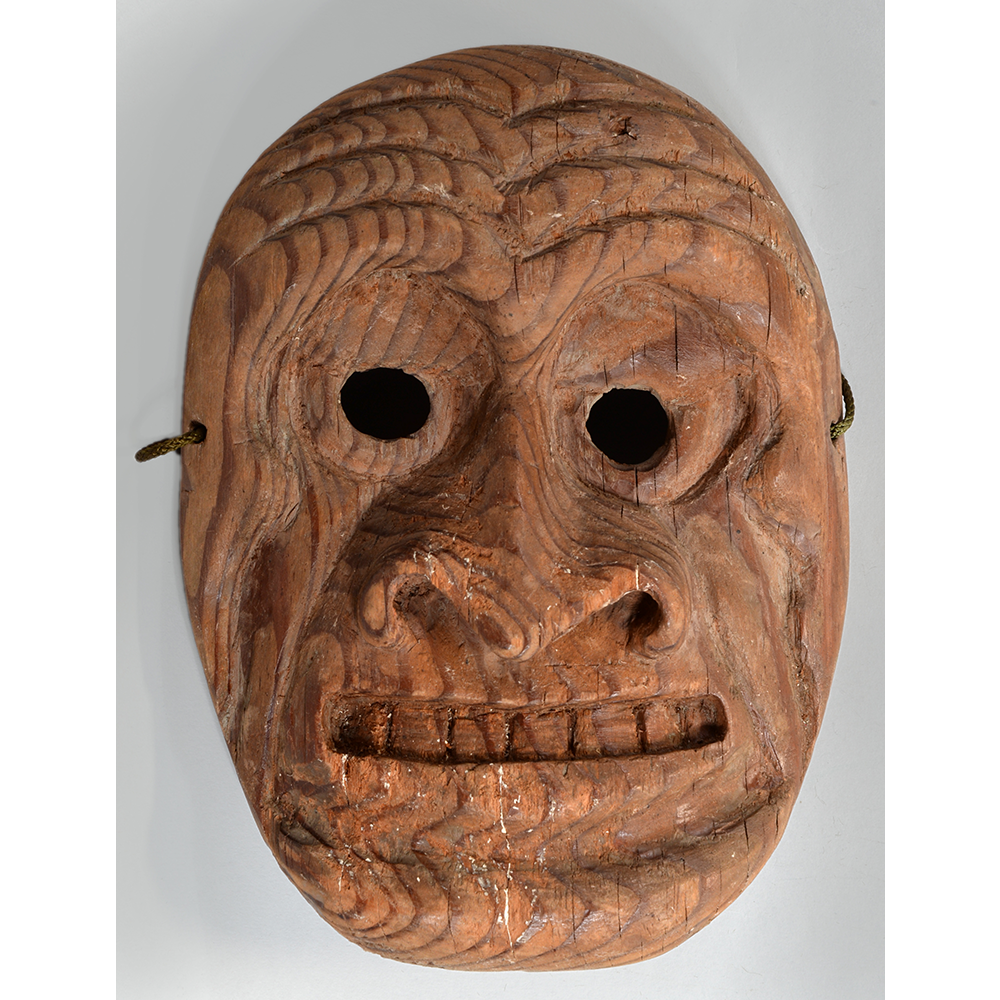
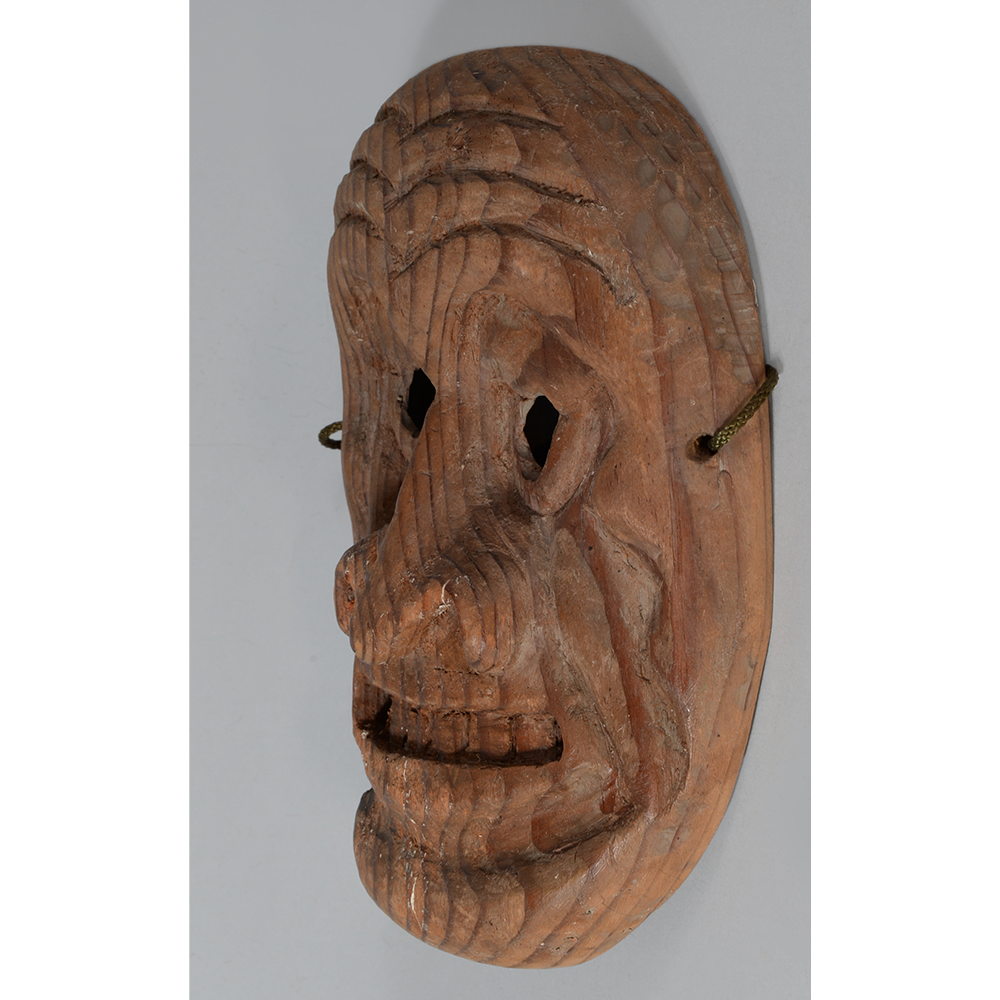
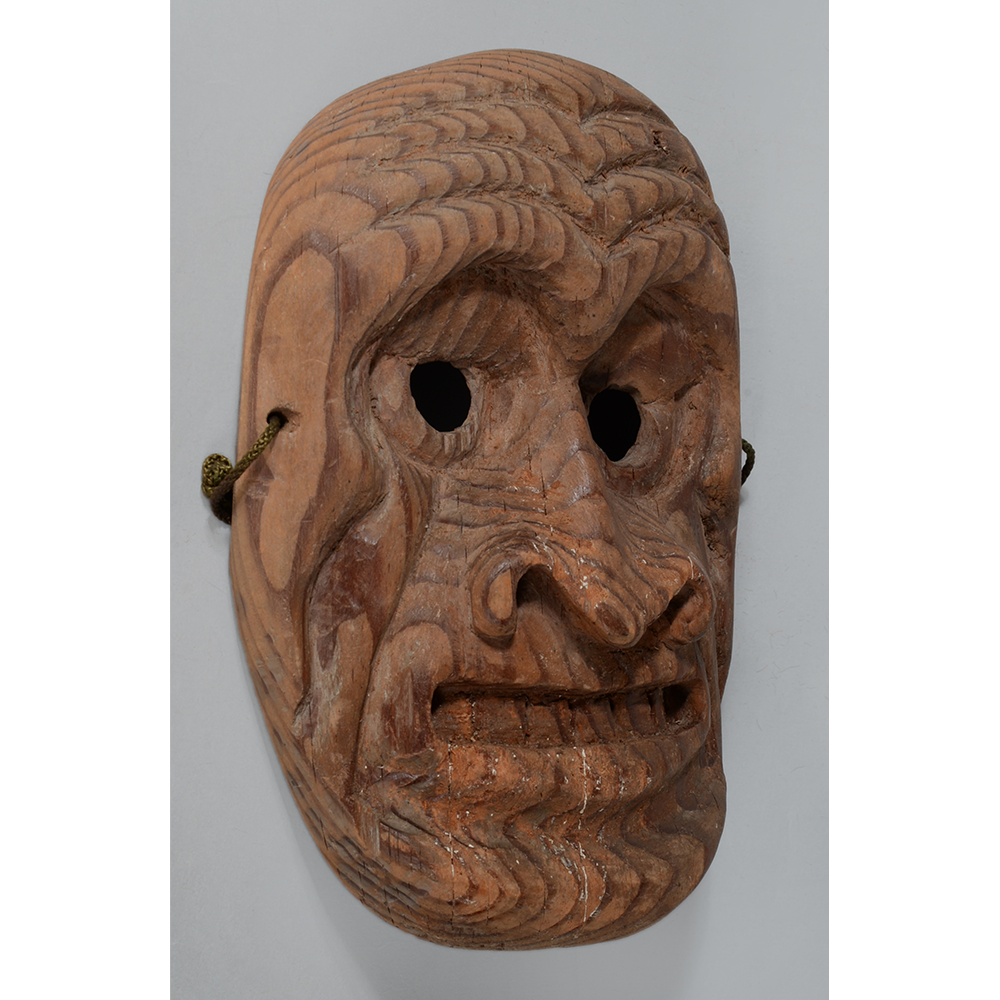
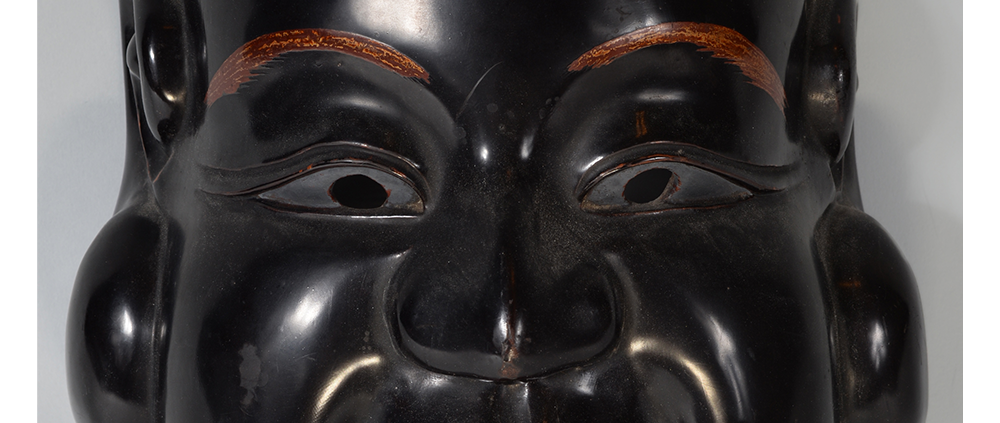
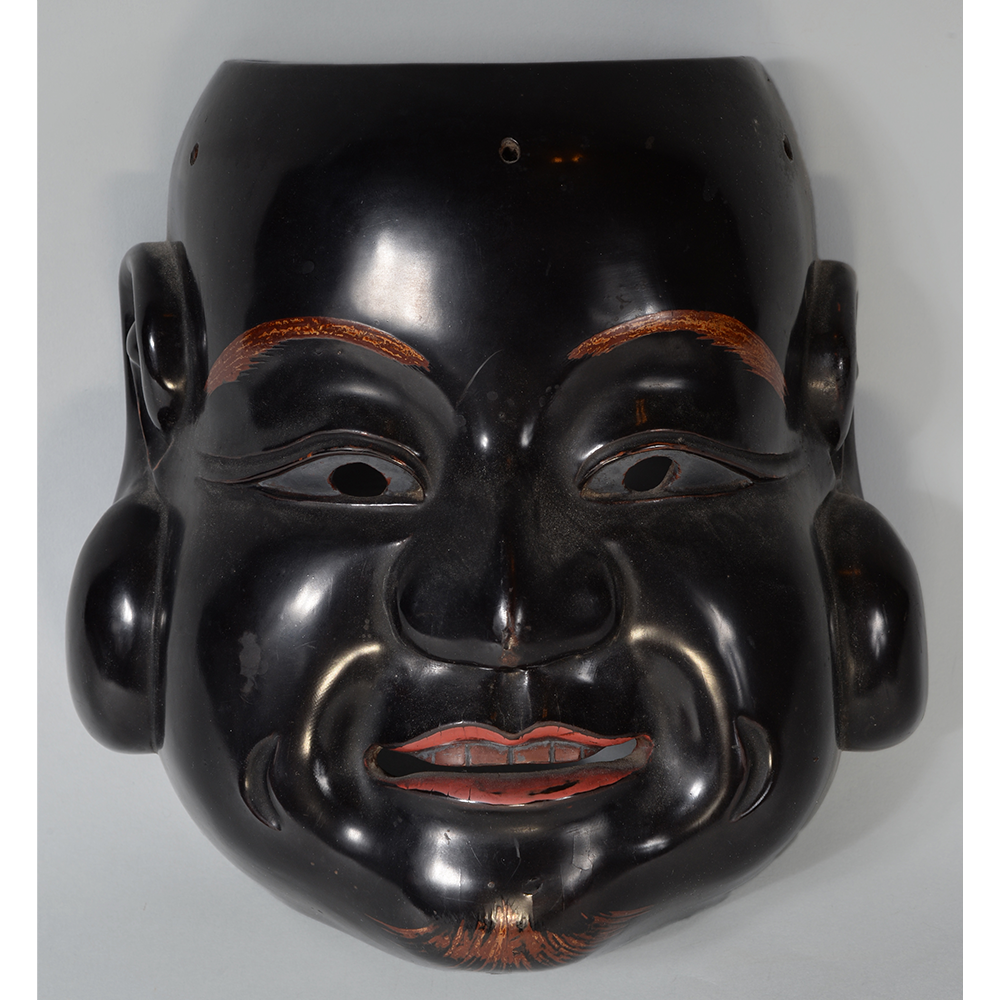
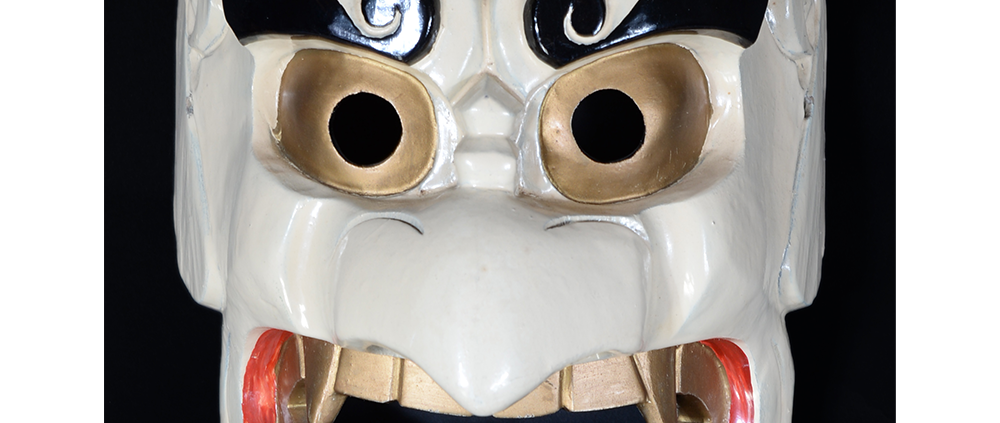
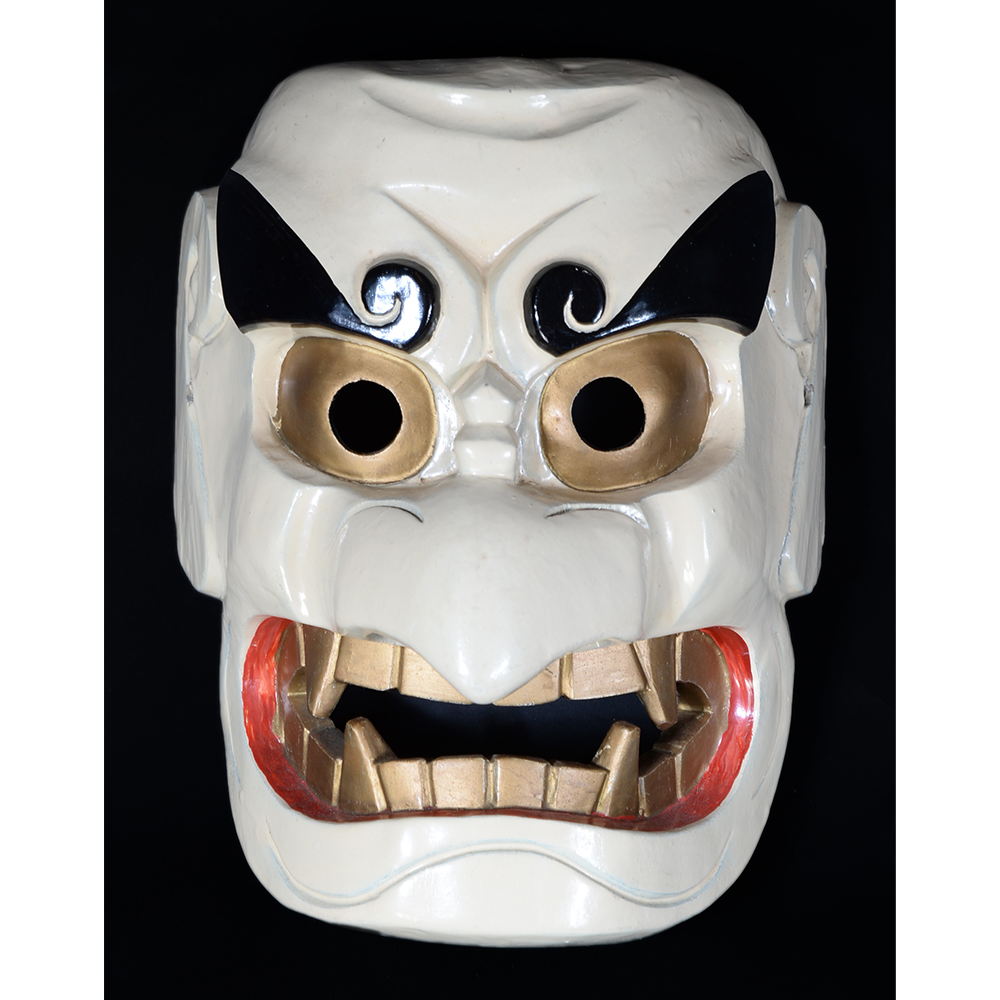
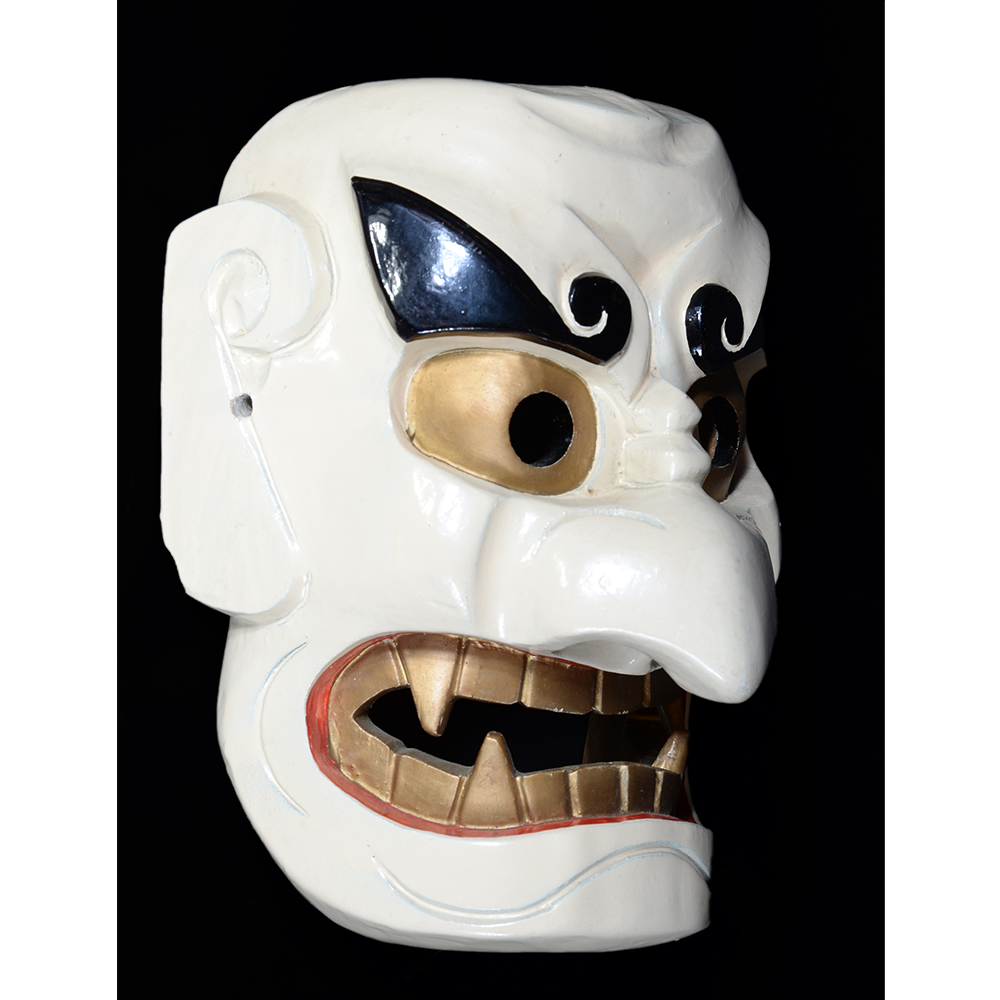
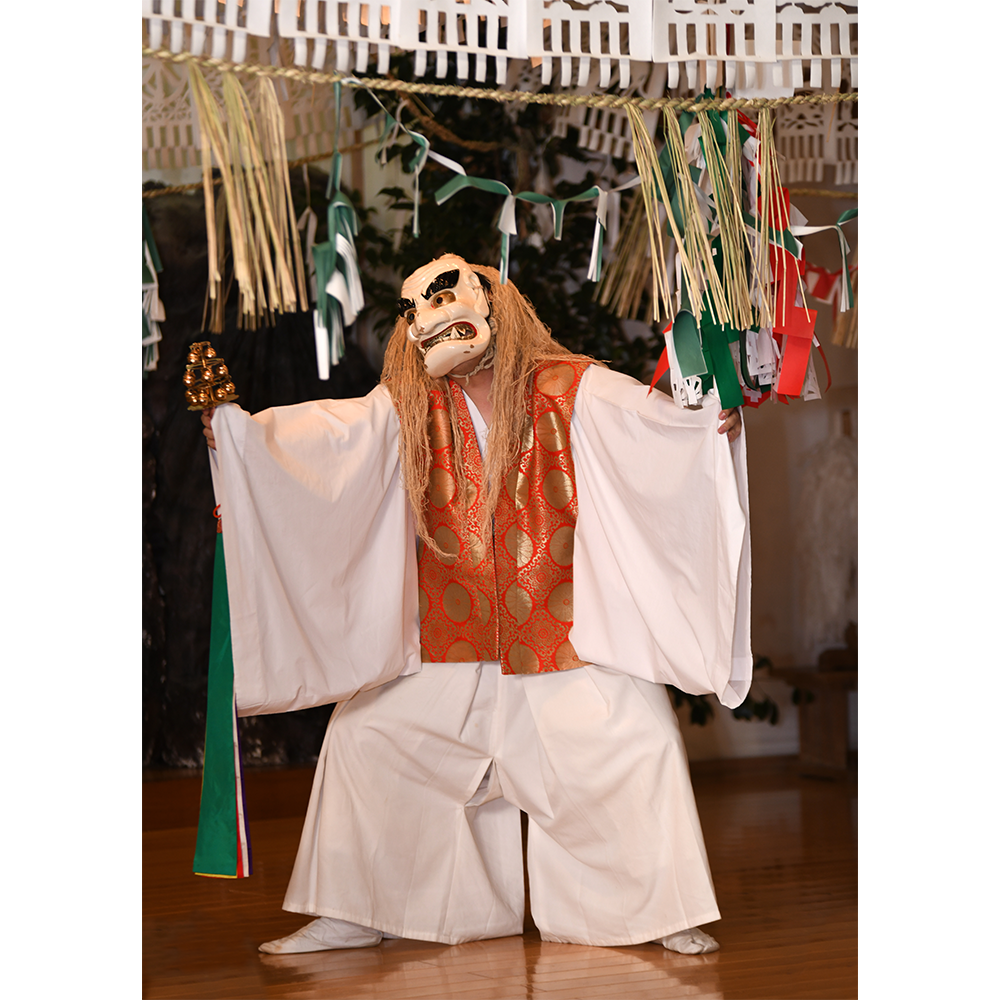
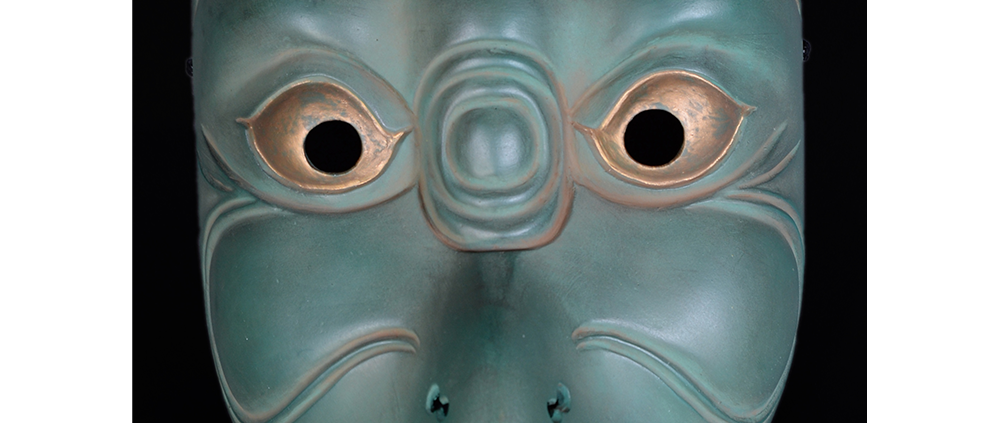
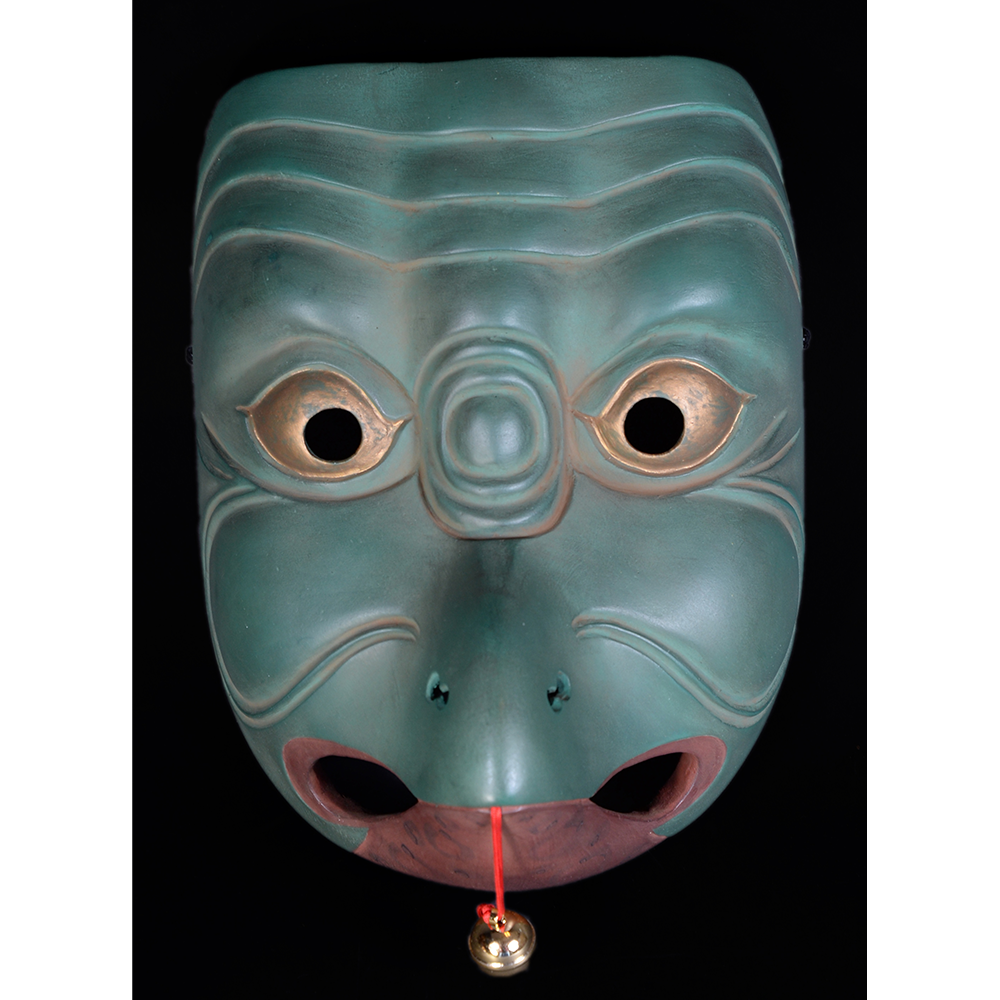
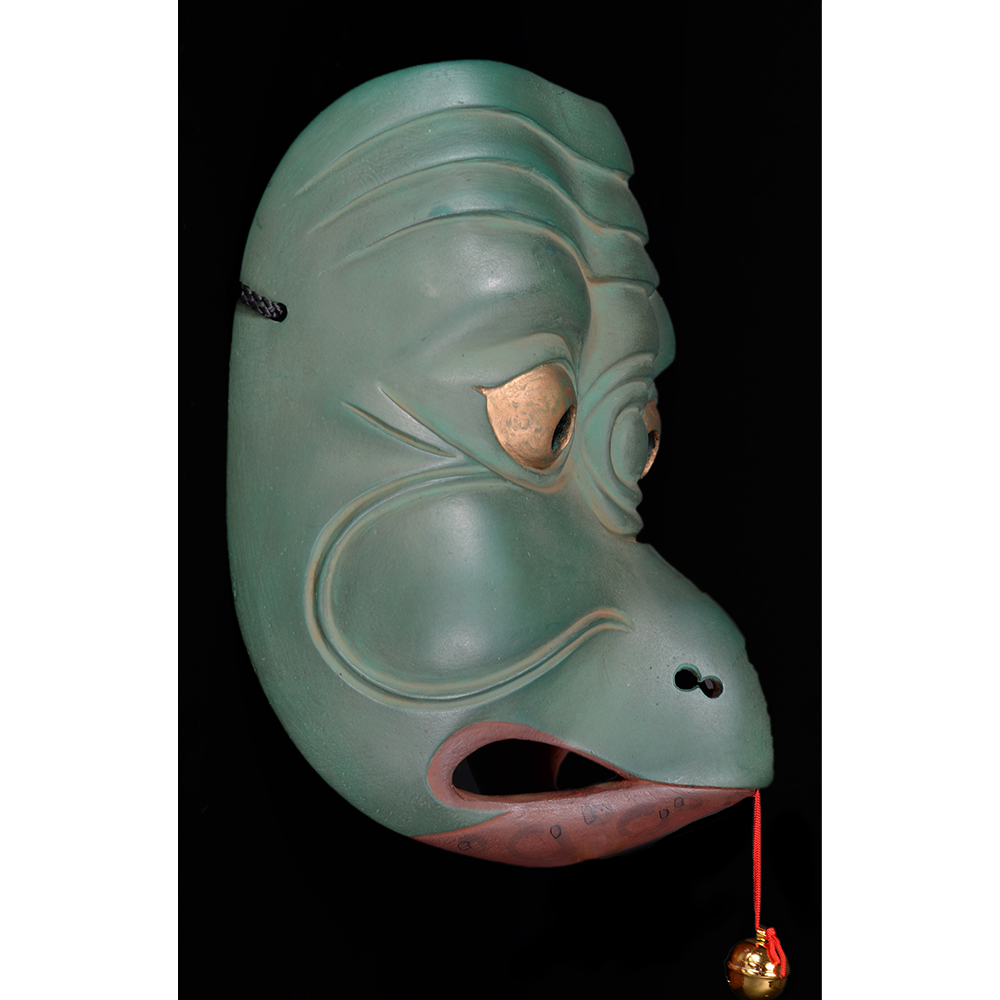
TITLE: Eight Heavenly Maidens Mask
TYPE: face mask
GENERAL REGION: Asia
COUNTRY: Korea
SUBREGION: Korean expatriates in China
ETHNICITY: Korean
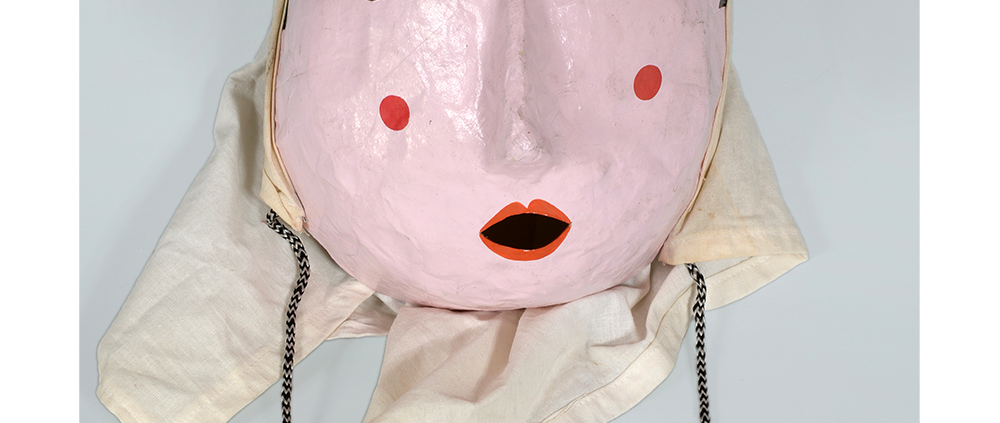
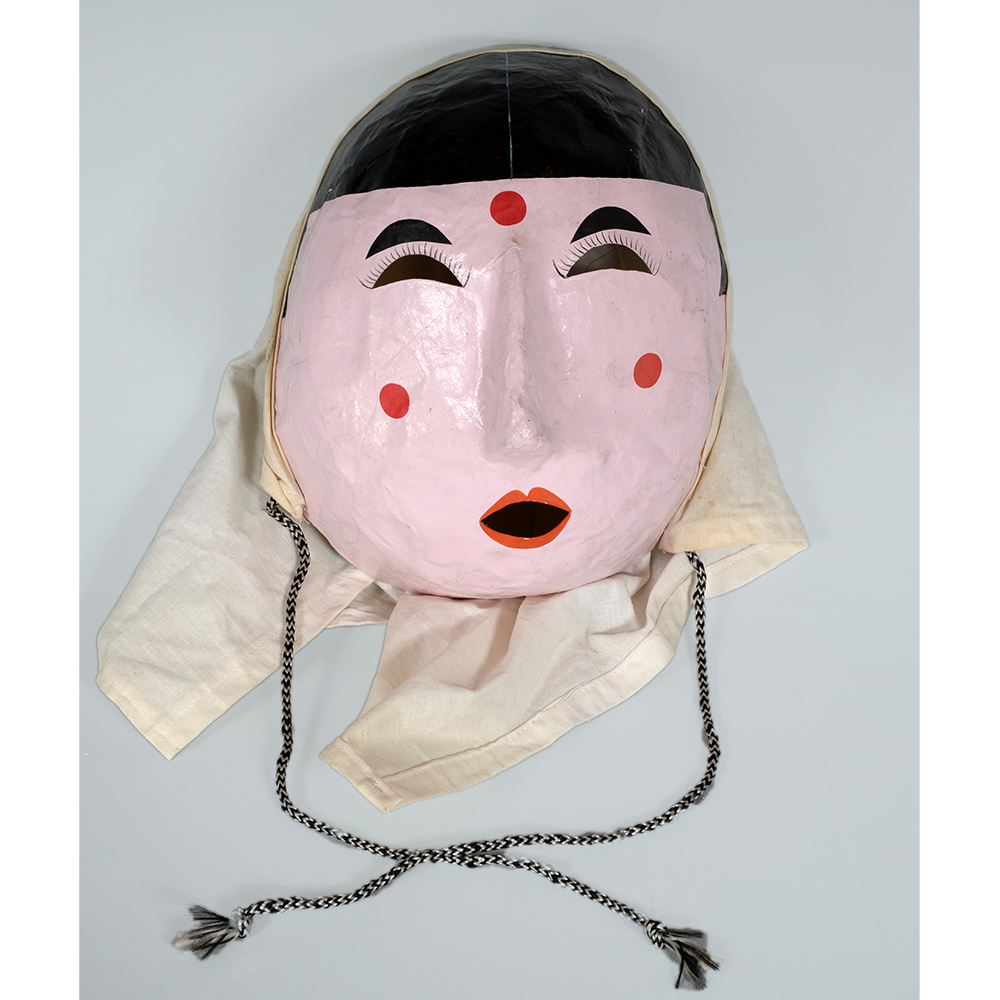
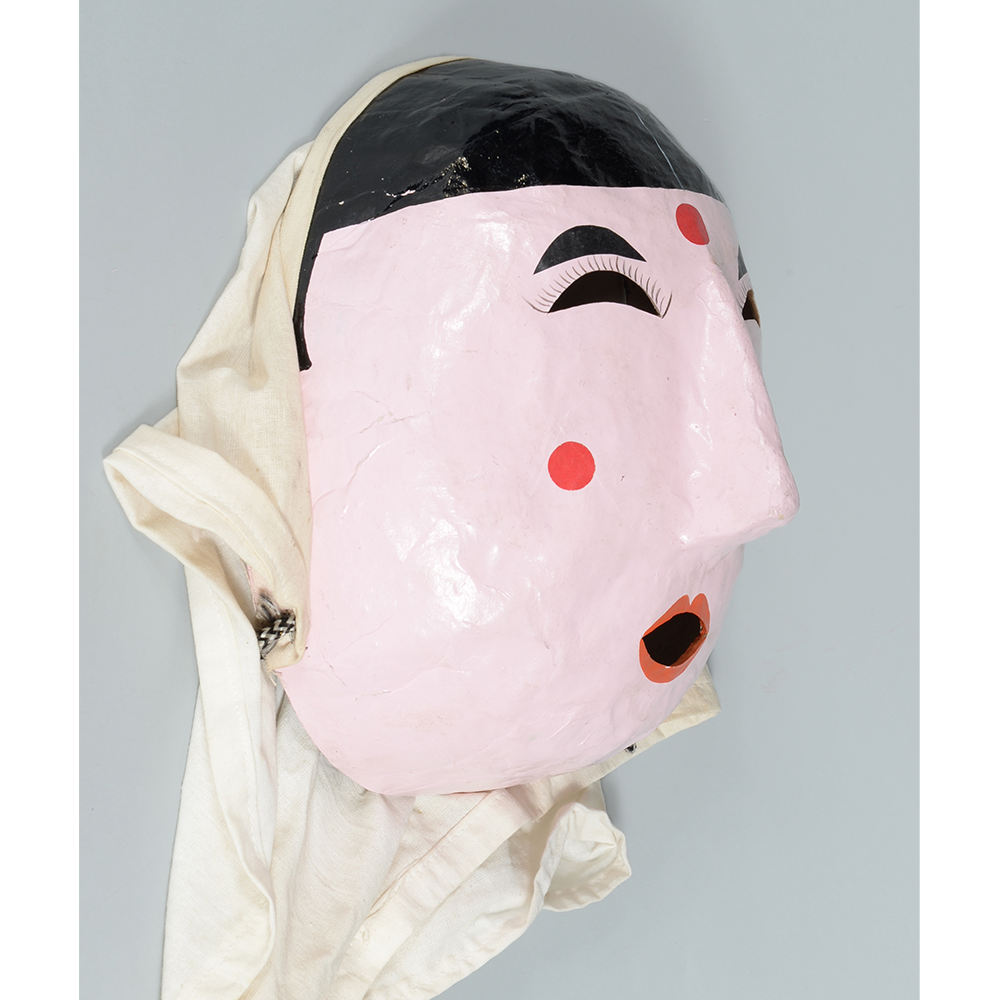
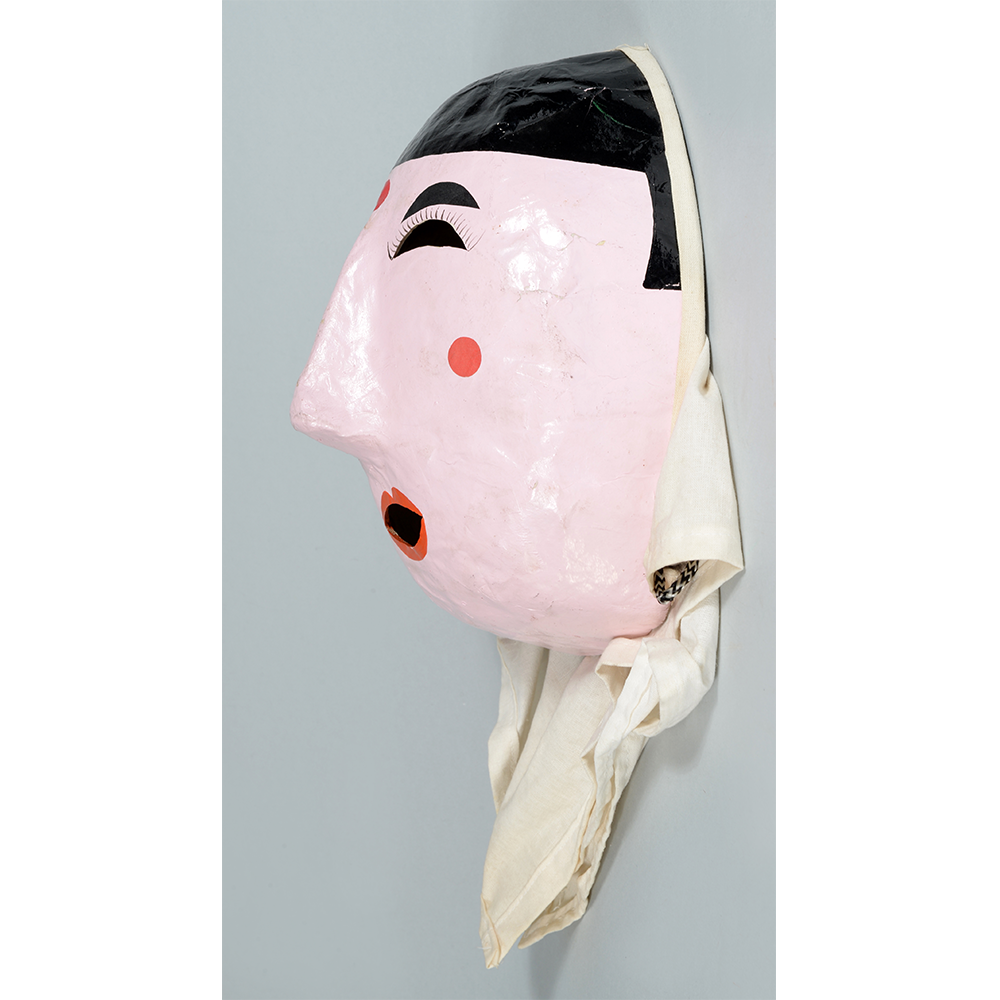
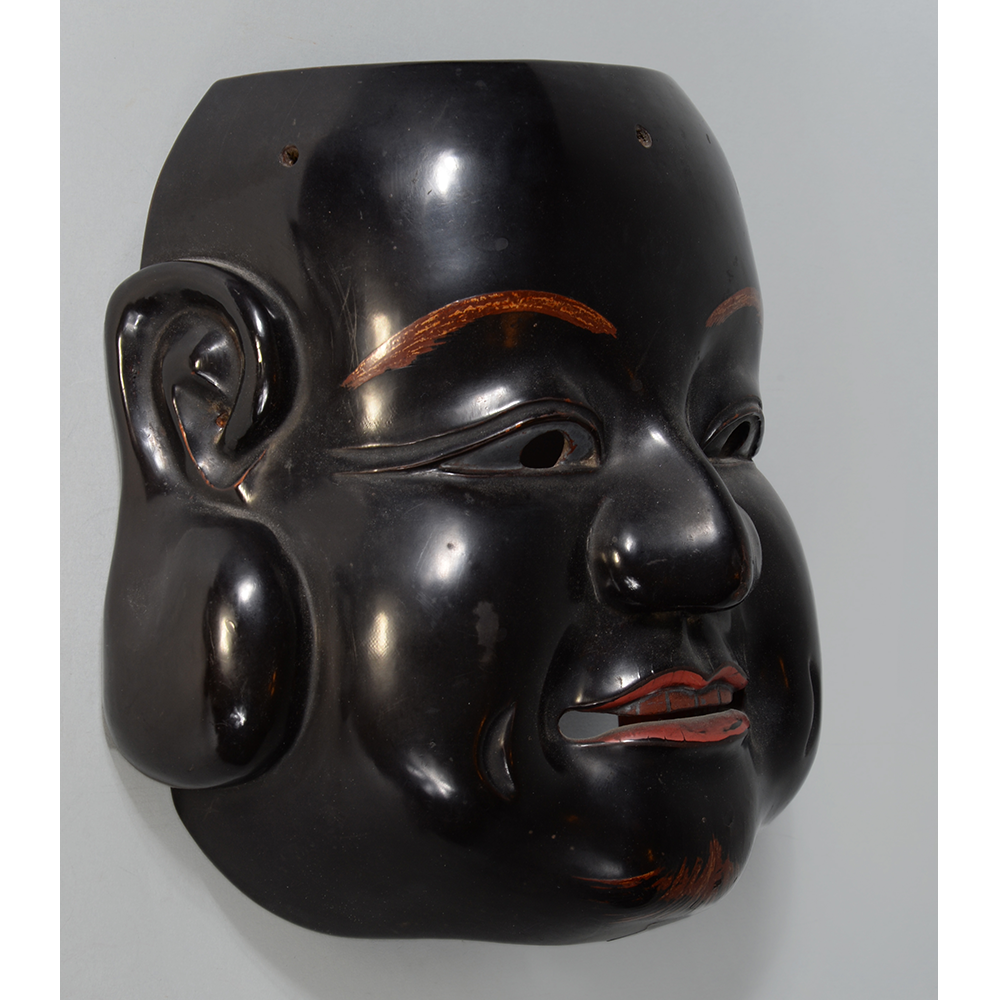
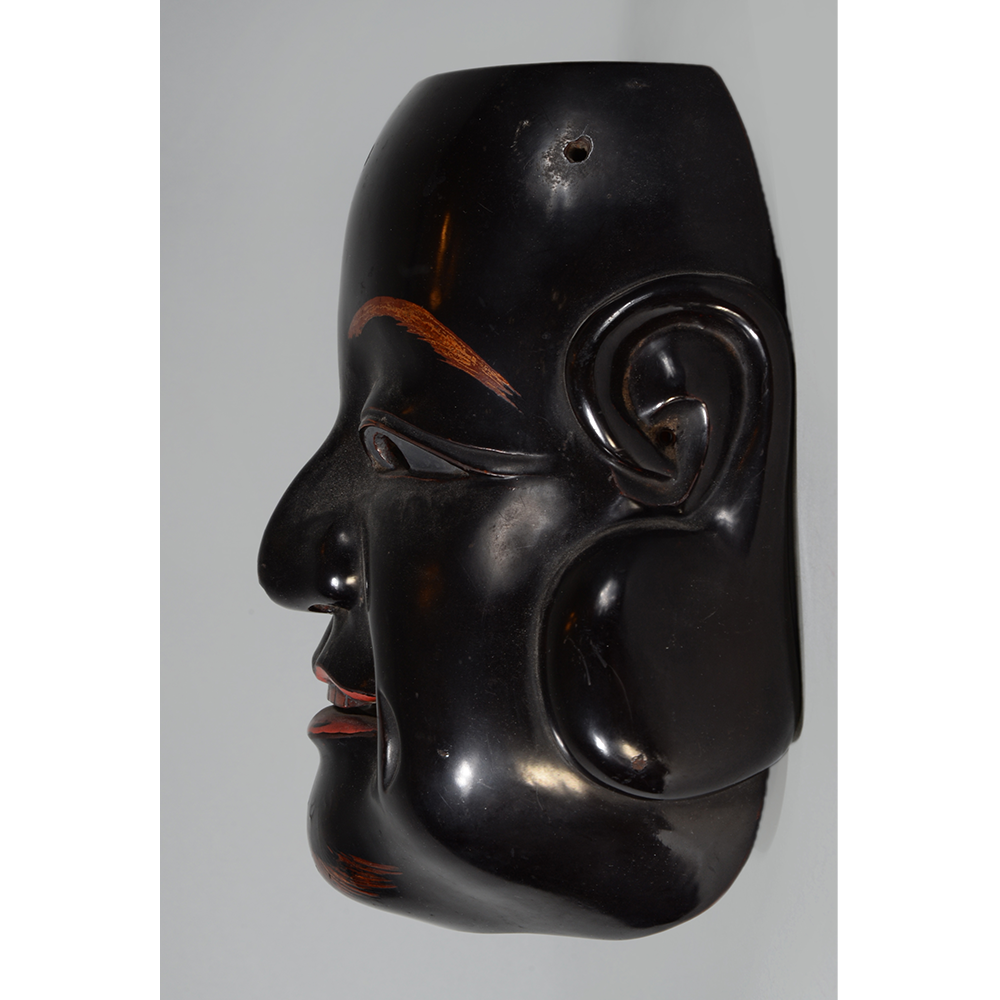
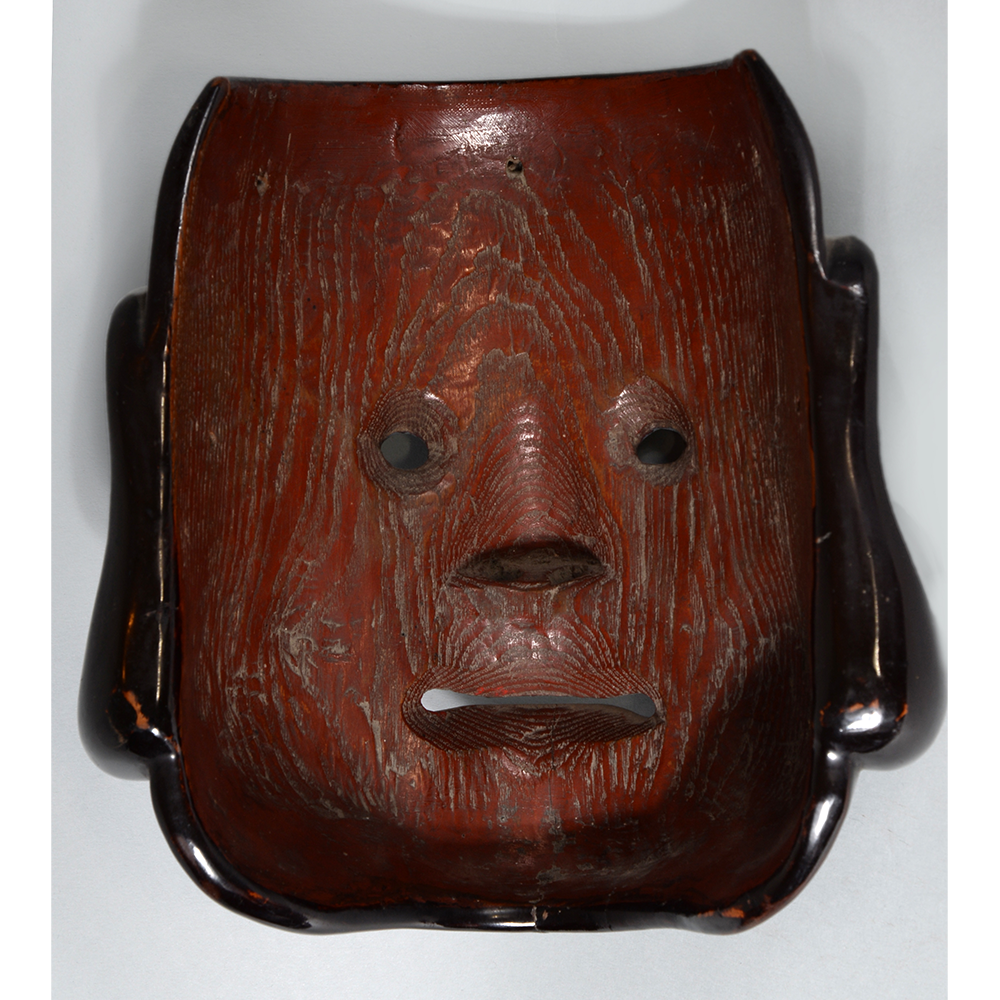
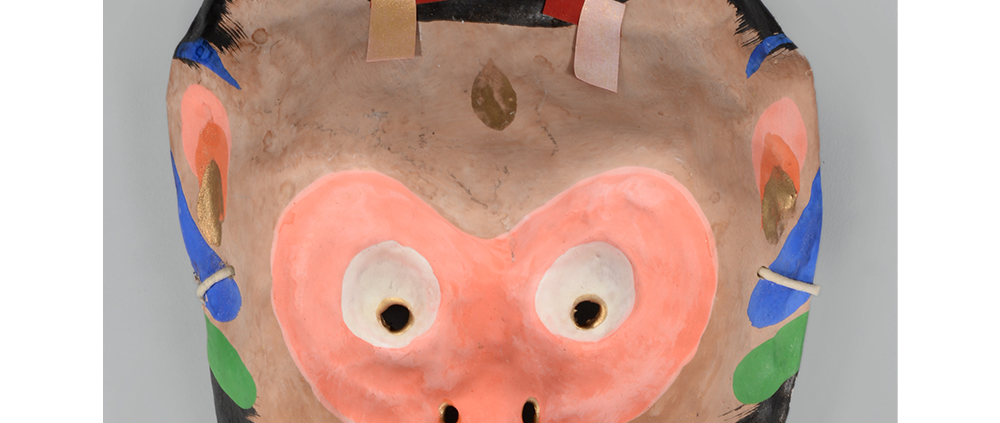
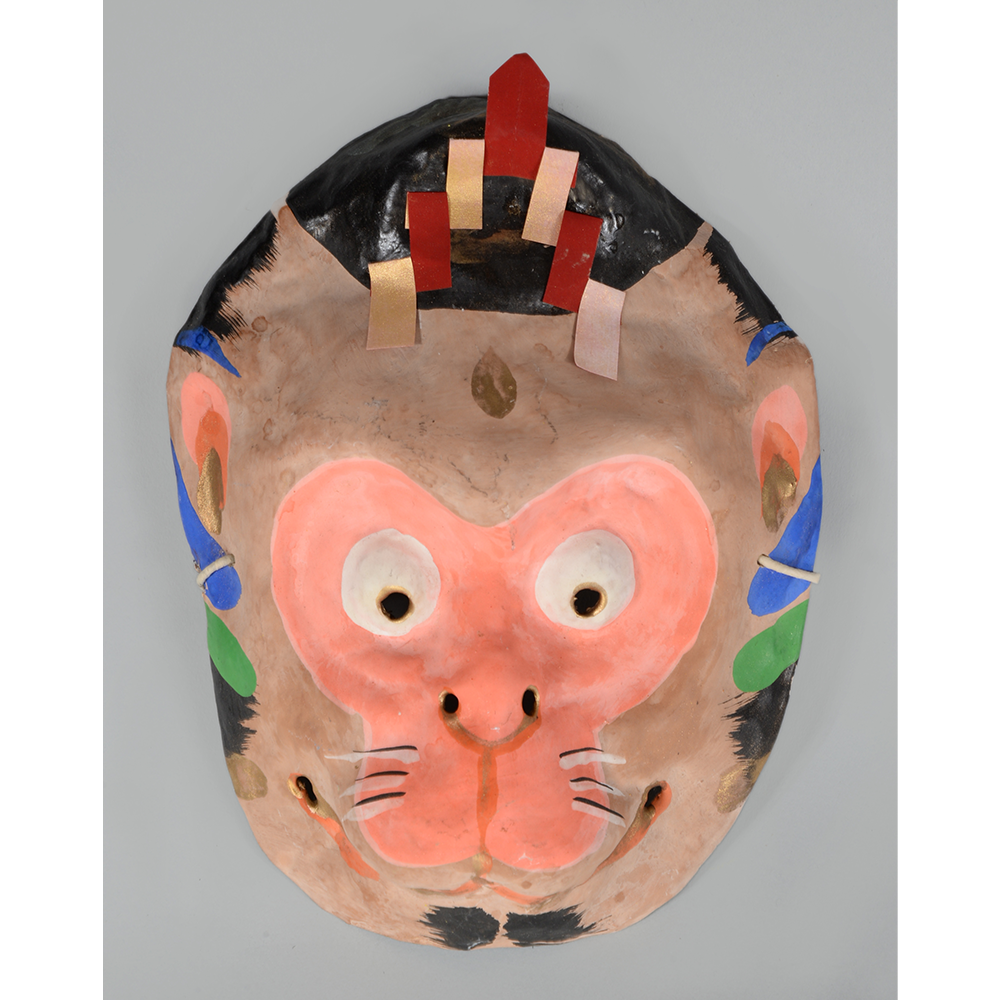
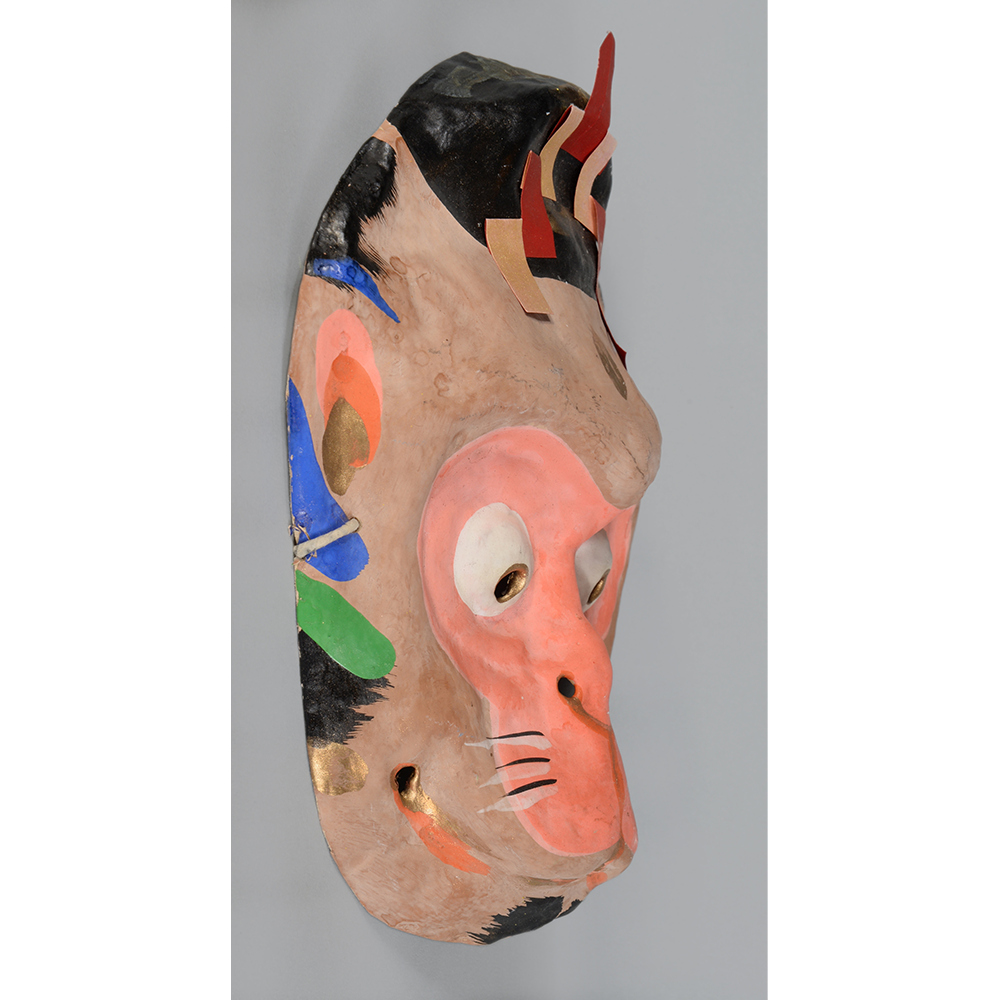
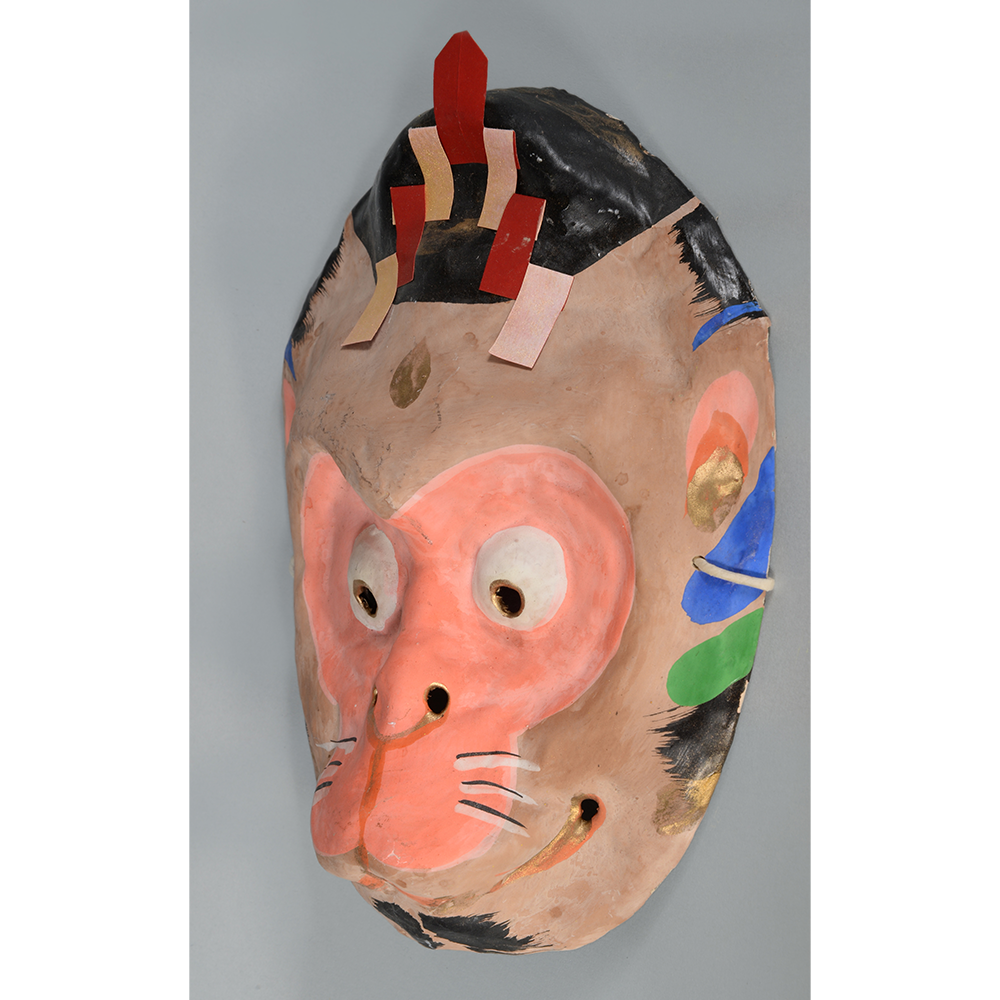
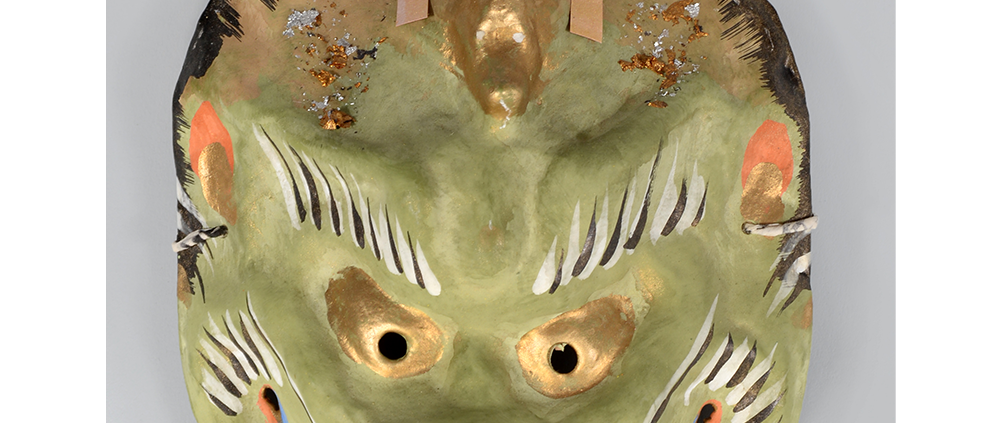
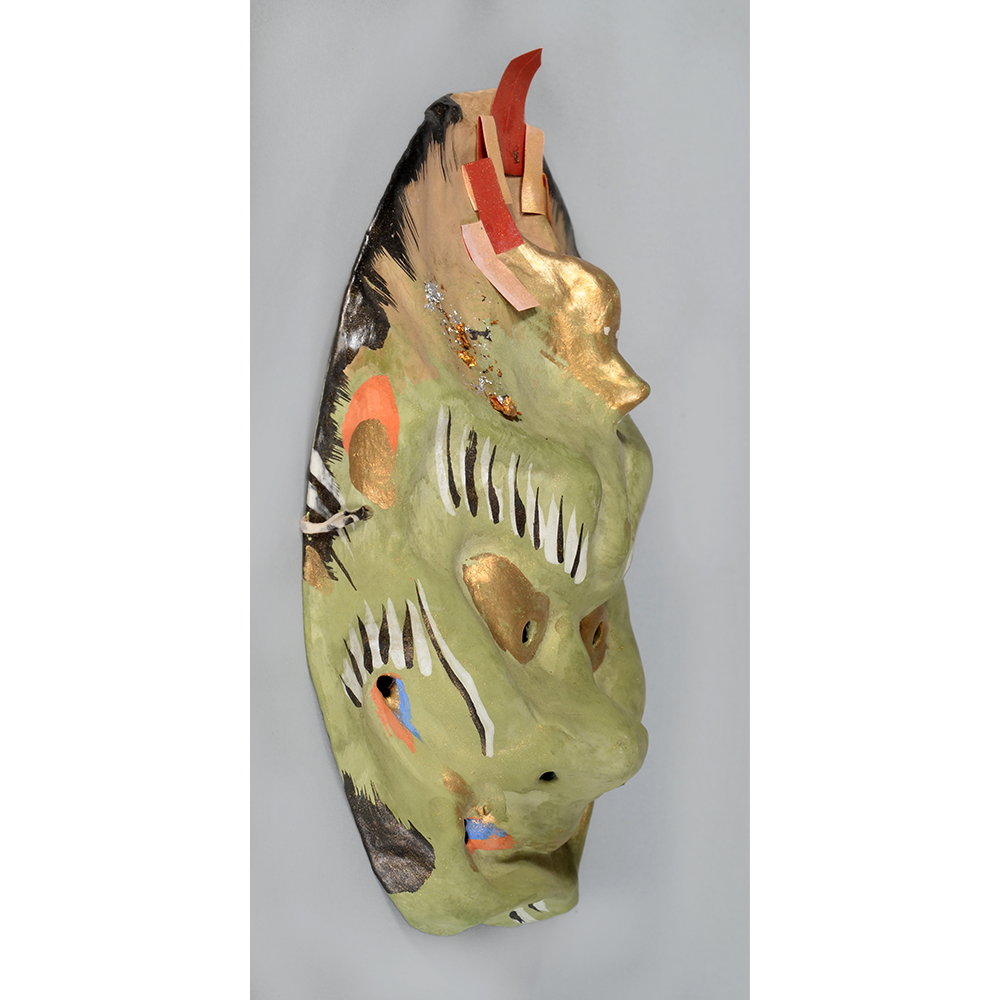
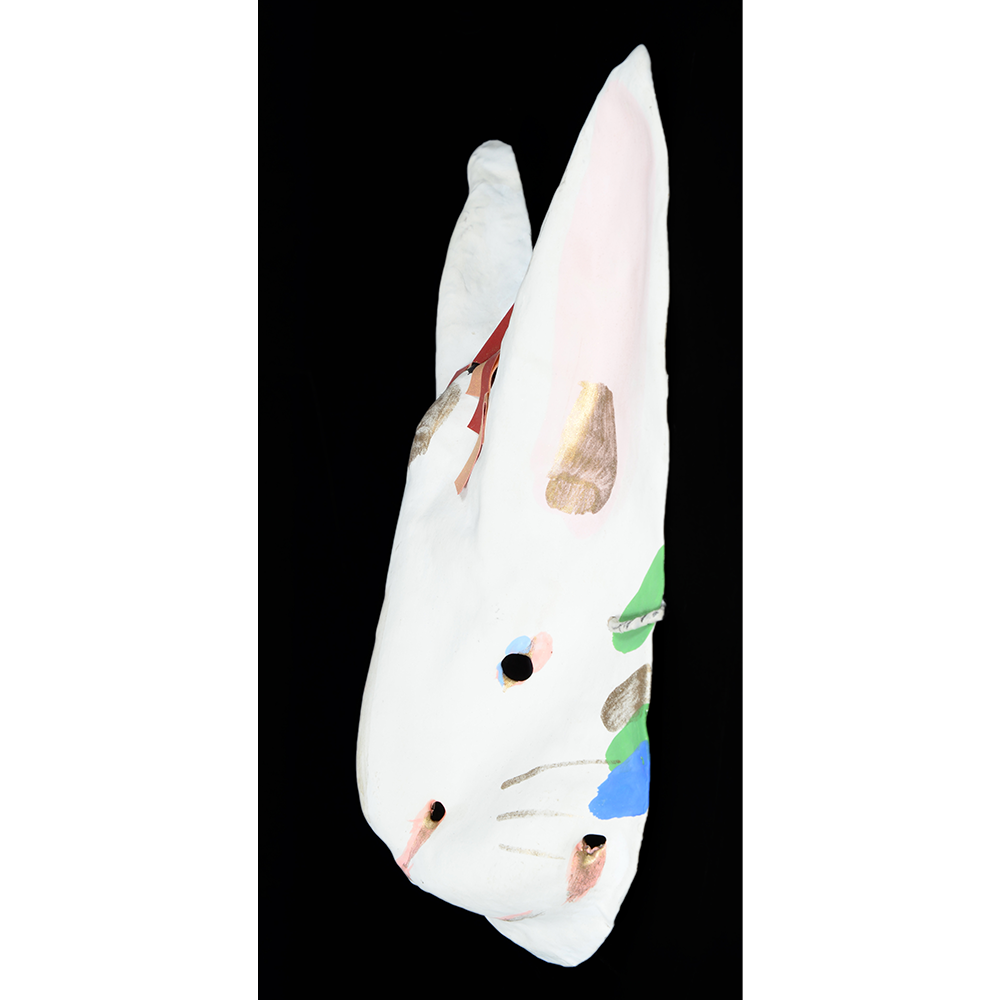
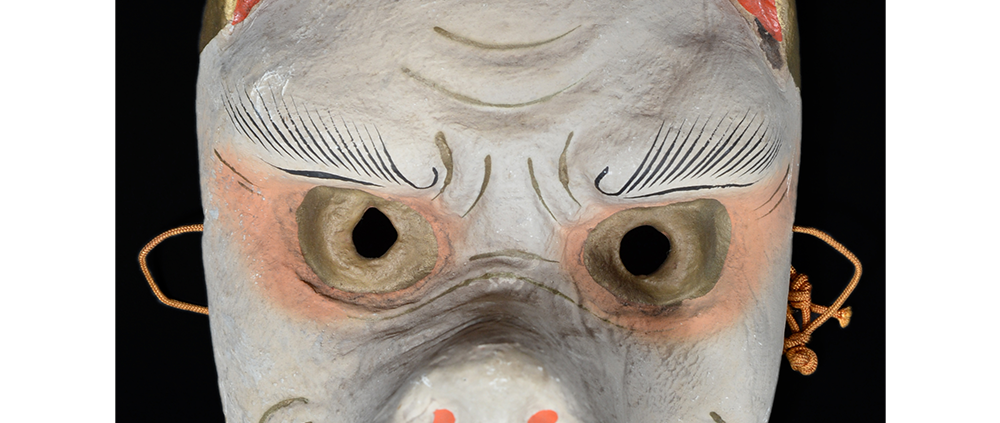
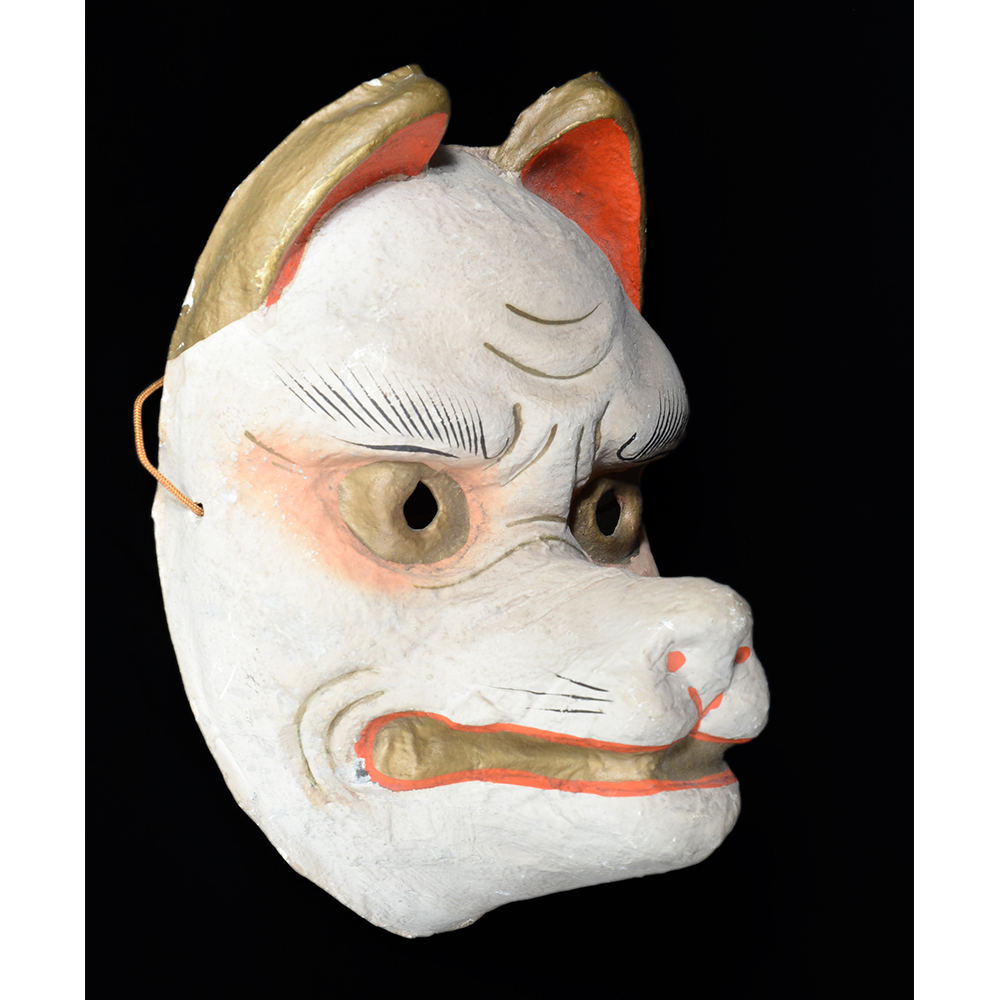
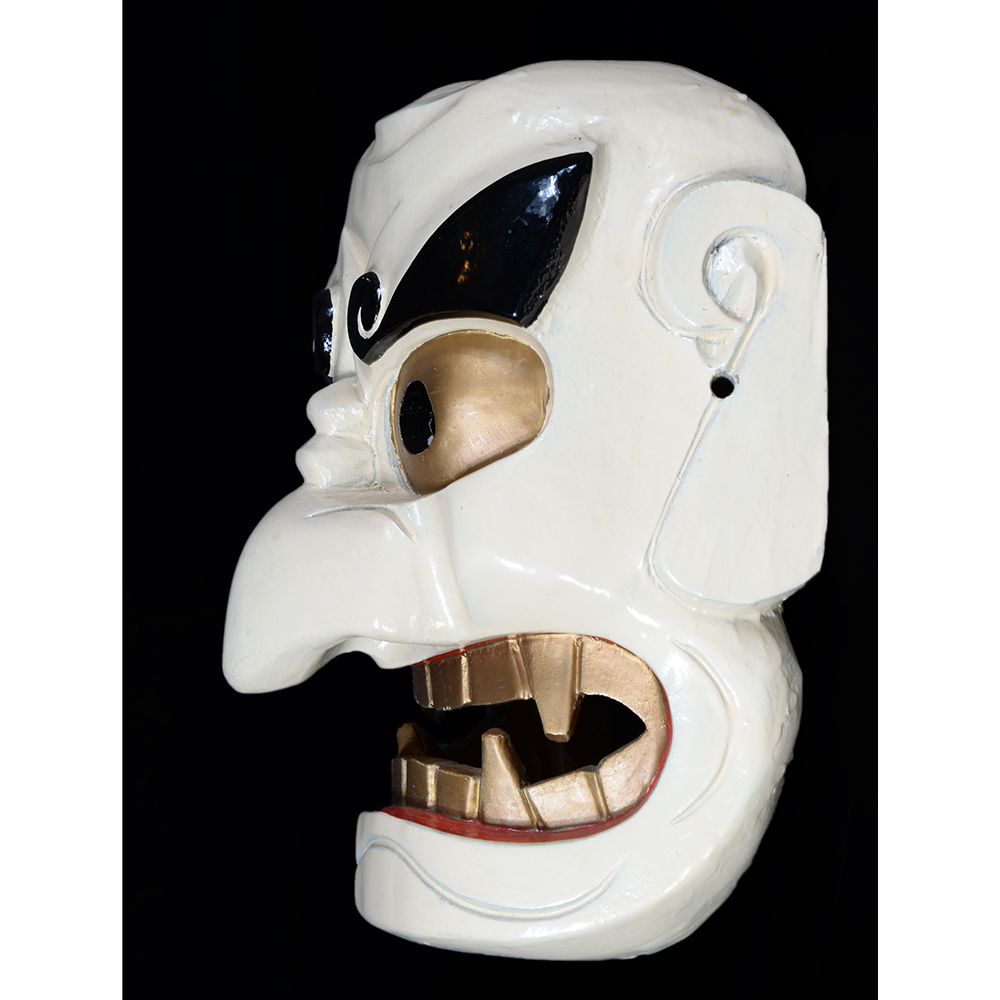
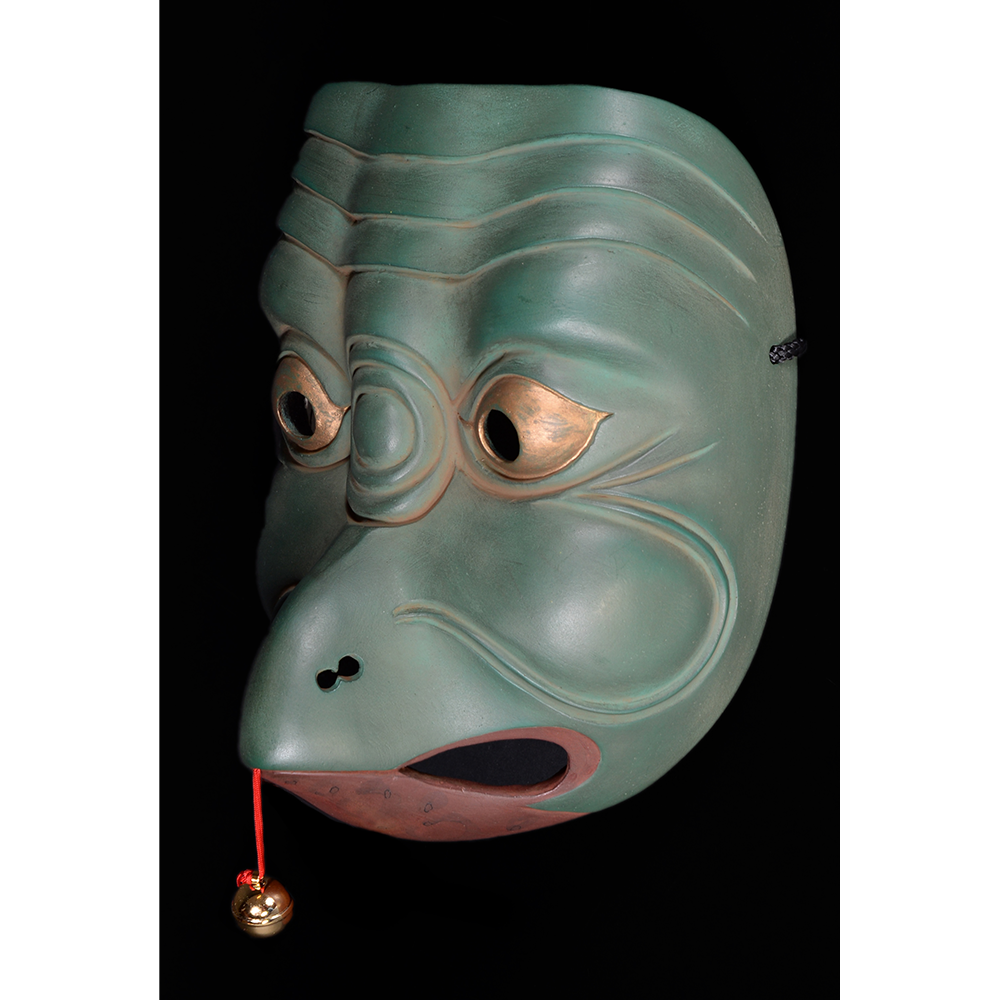
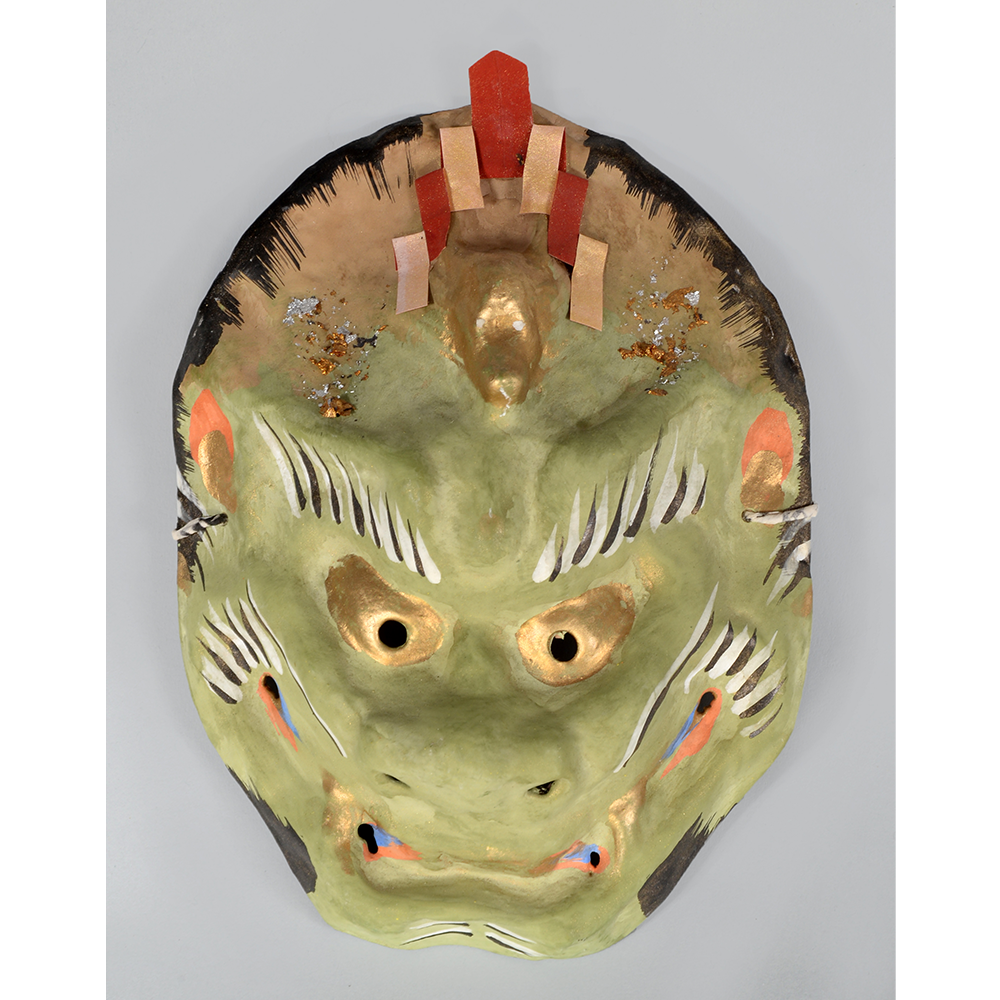
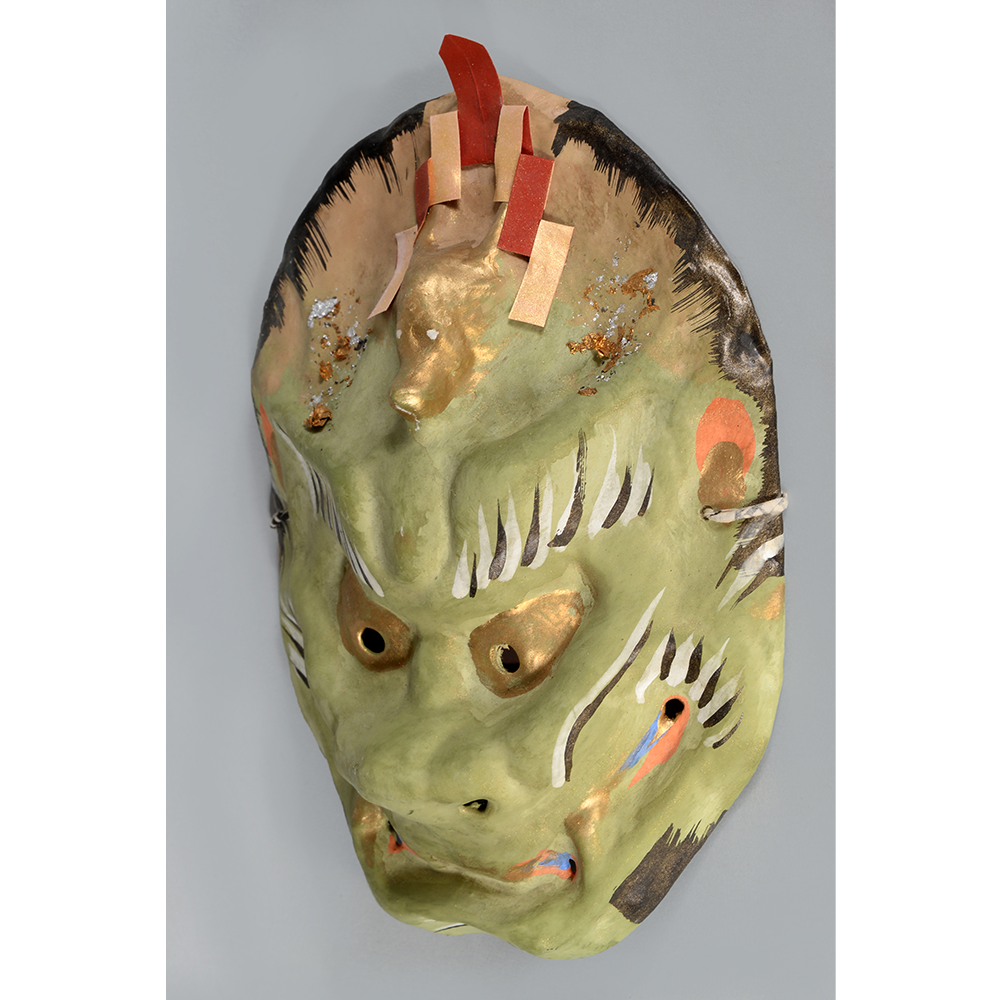
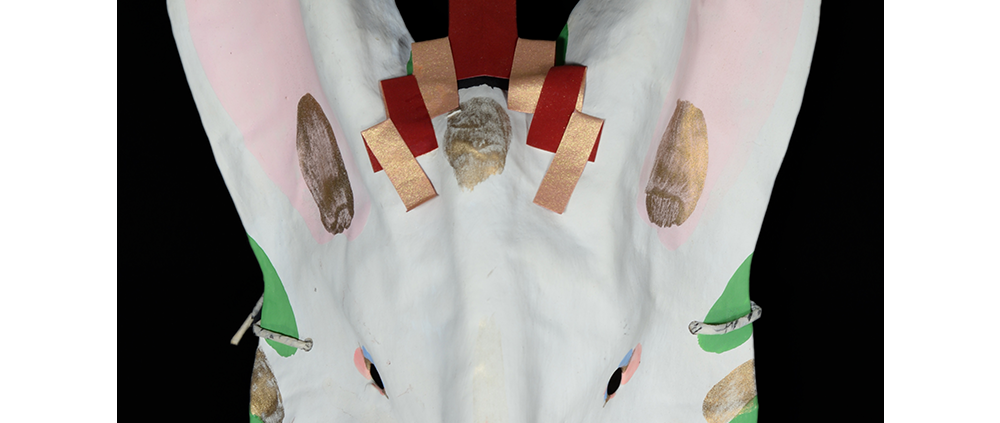
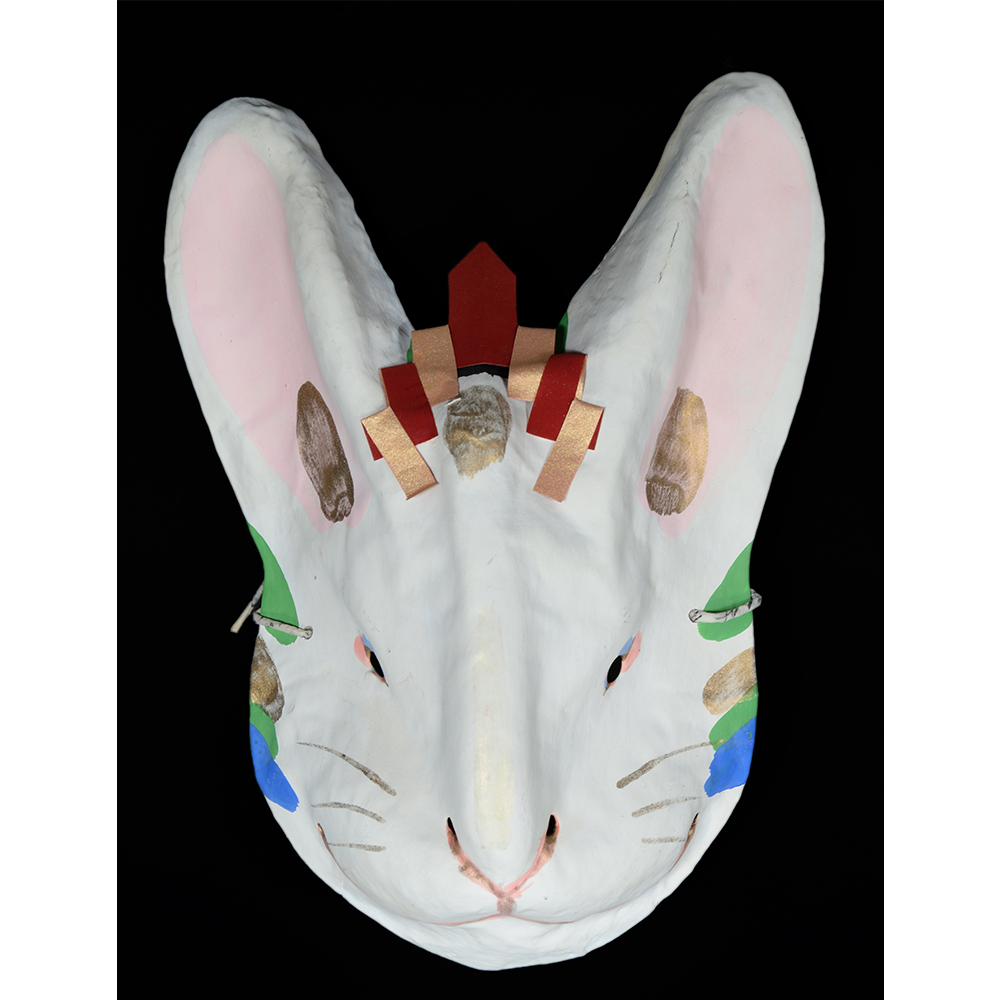
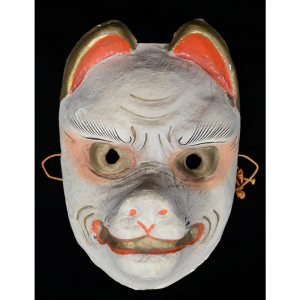
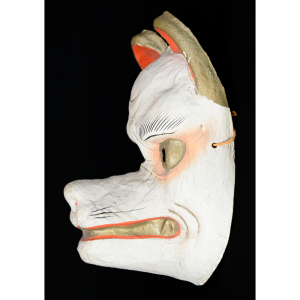
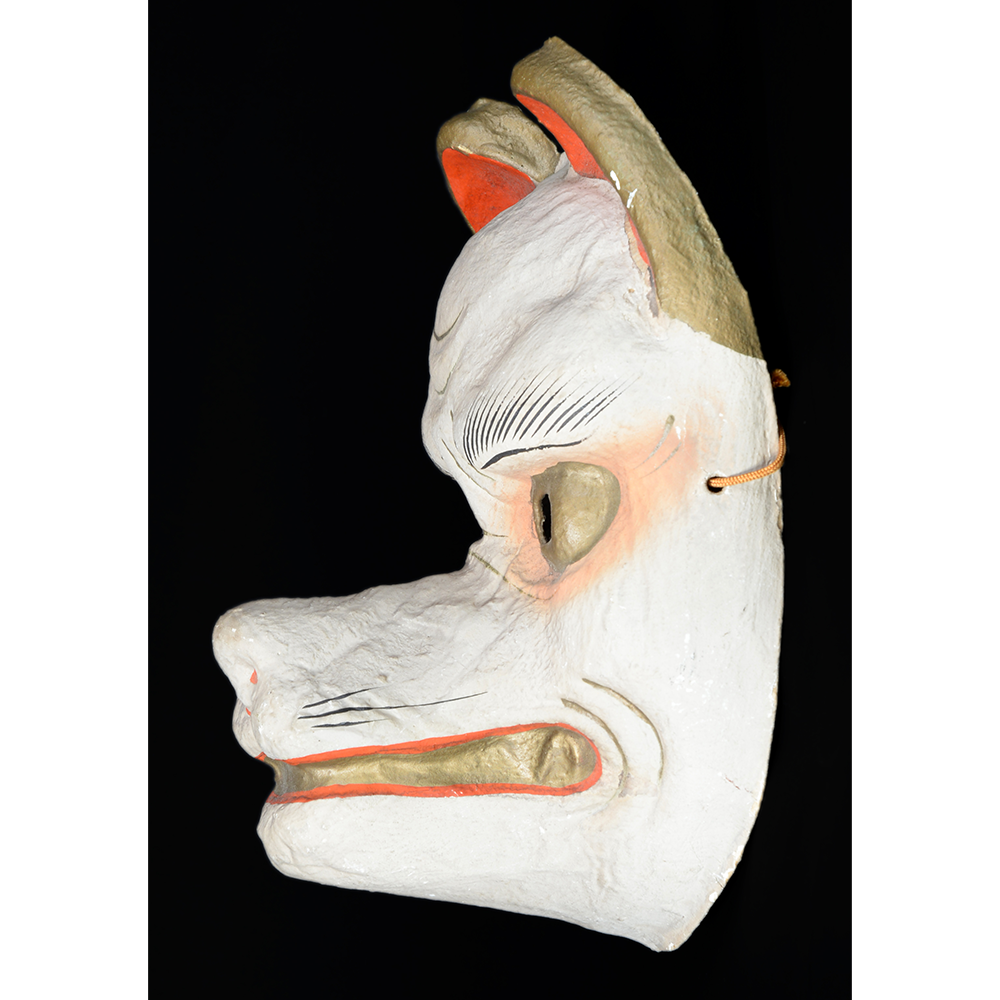
DESCRIPTION: Eight Heavenly Maidens Mask
CATALOG ID: ASKR011
MAKER: Unknown
CEREMONY: Kuunmong Drama
FUNCTION: entertainment
AGE: 1980s
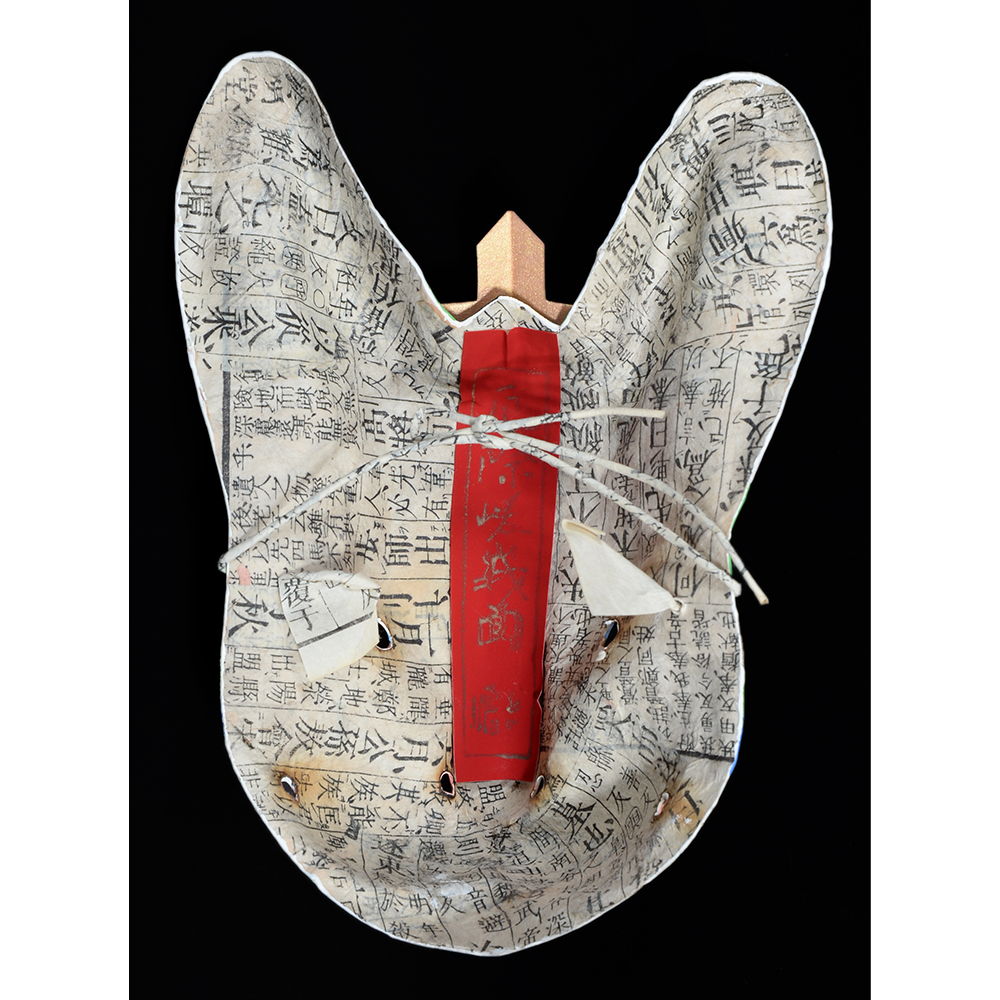
MAIN MATERIAL: paper maché
OTHER MATERIALS: paint; stitching; cotton cloth; dyed cotton cords; elastic band; hardware
This mask was probably made by Korean expatriates living in China for use in a performance of the Kuunmong drama. Kuunmong, or “The Cloud Dream of the Nine,” is a 17th century Korean novel set in China during the Tang Dynasty (618-907 CE). Although probably originally written in Chinese, it was early translated into Korean and is considered one of the main masterpieces of Korean literature. Kuunmong tells the story of two young men who live strict Buddhist and Confucian lives, respectively. The Confucian hero, So-yoo, marries or takes as concubines eight beautiful maidens, of which this mask probably represents one. The mask is thus not made for a traditional cultural ceremony of Korea, but rather as a form of entertainment and cultural education.
For more on Korean masquerade, see Jeon Kyung-wook, Korean Mask Dance Dramas: Their History and Structural Principles (Gyeonggi-do, Rep. of Korea: Youlhwadang Pub. 2005).